Abstract
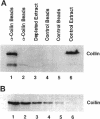
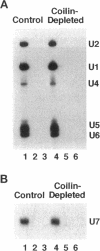
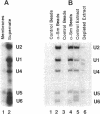
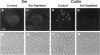
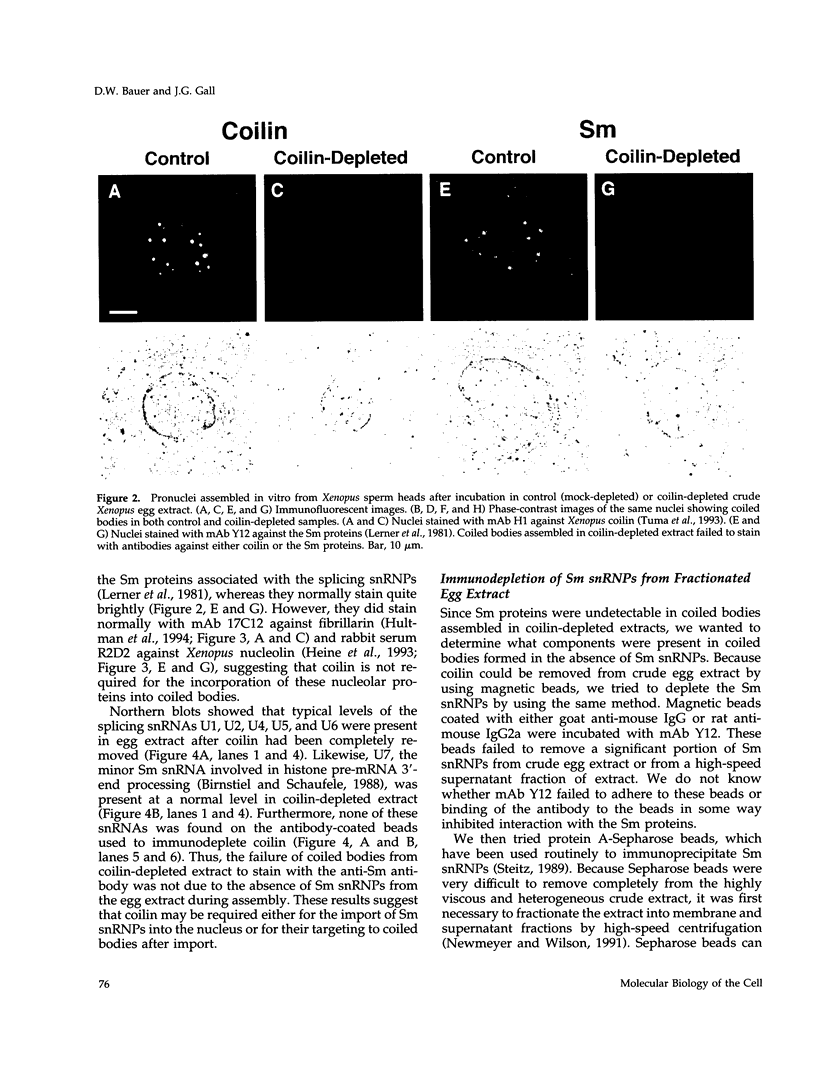
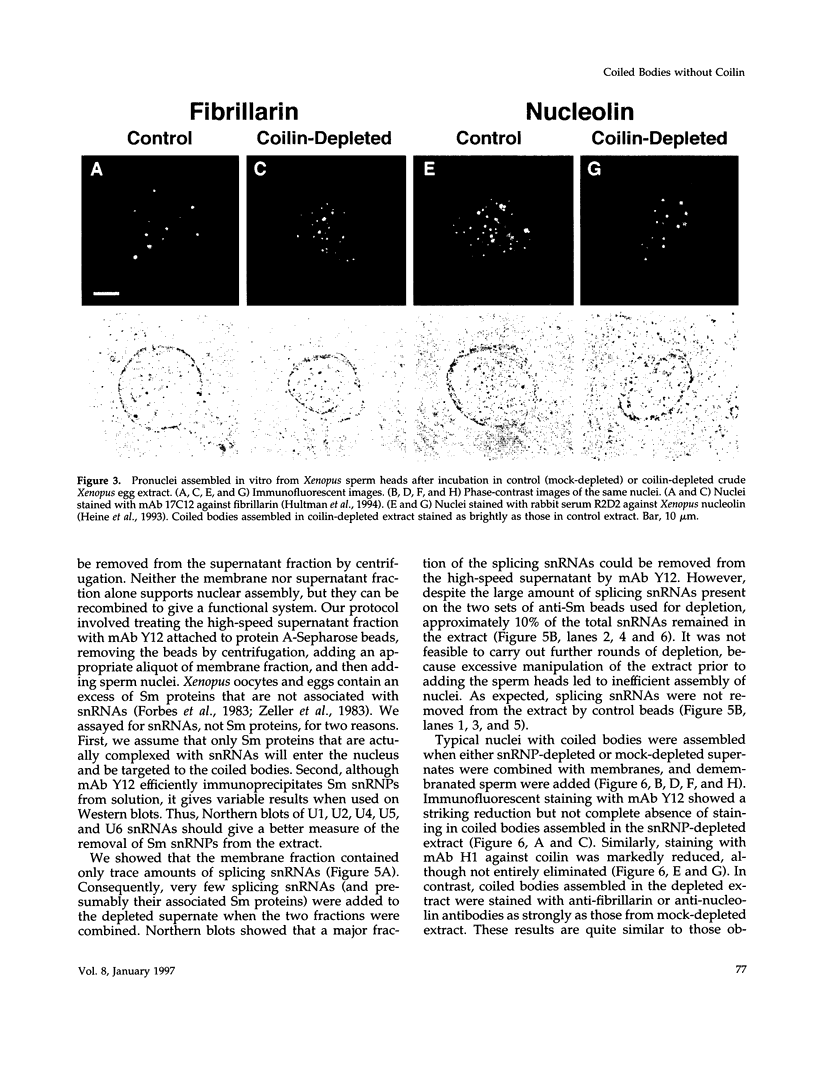
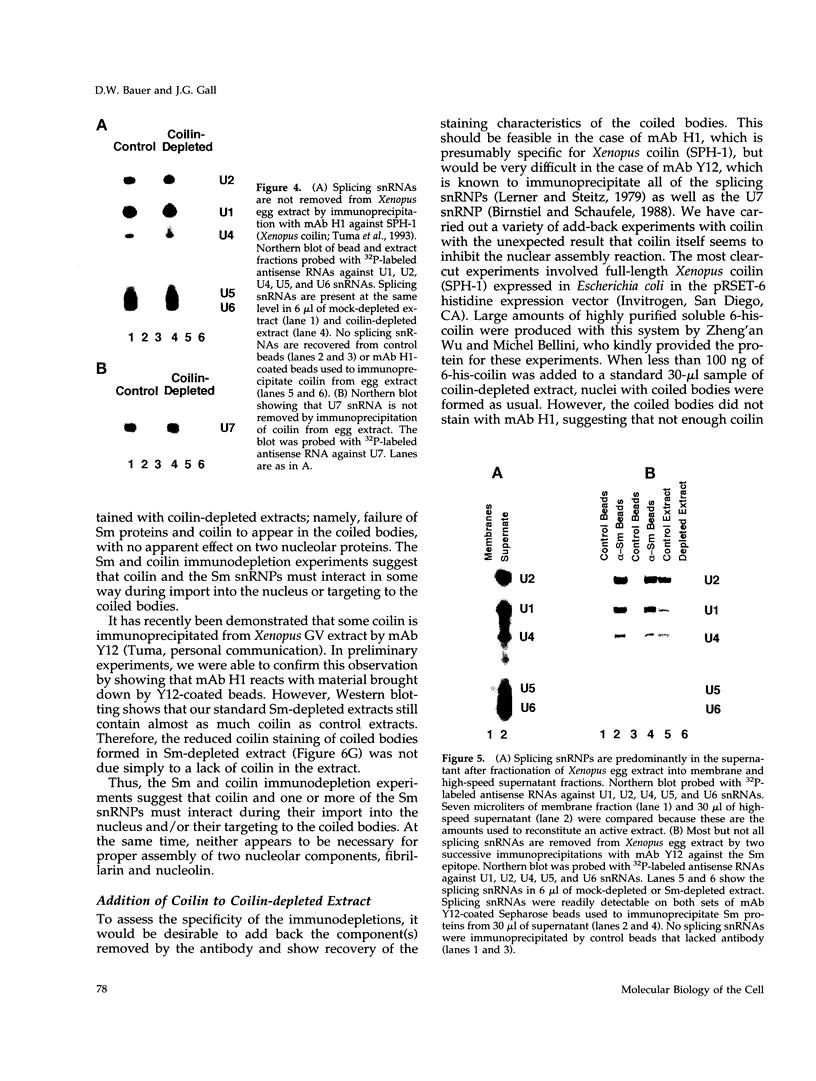
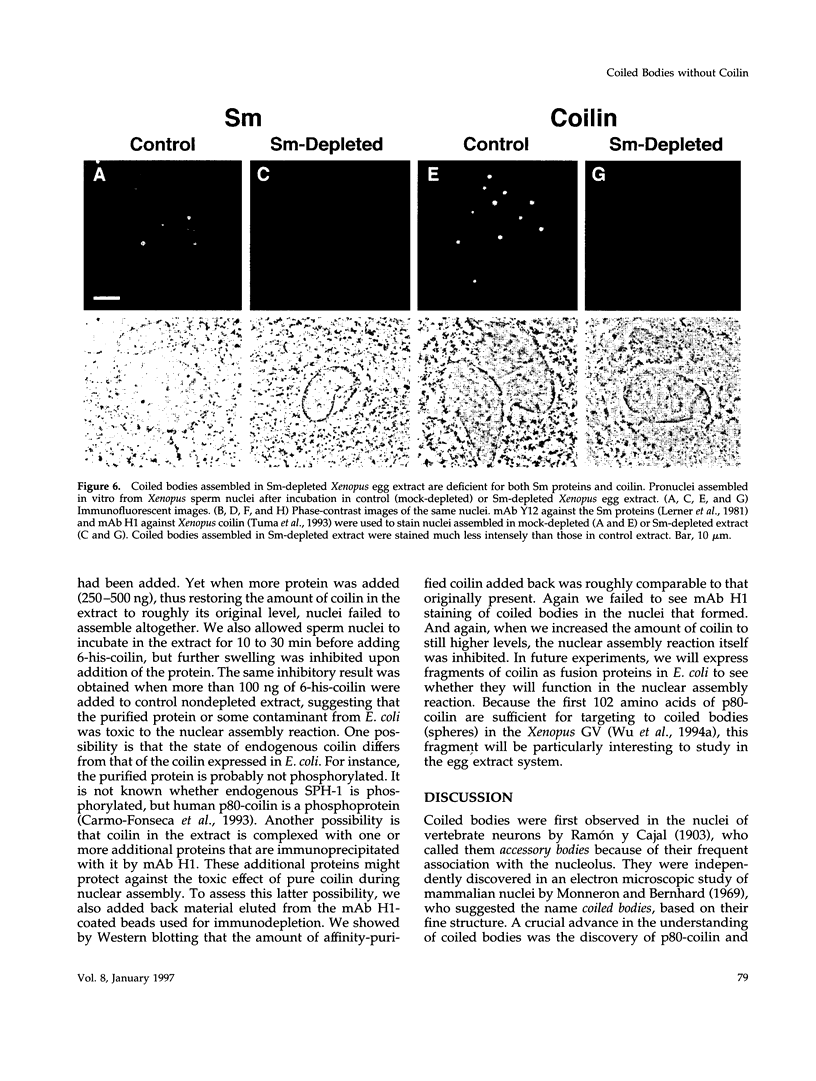
Nuclei assembled in vitro in Xenopus egg extract contain coiled bodies that have components from three different RNA processing pathways: pre-mRNA splicing, pre-rRNA processing, and histone pre-mRNA 3'-end formation. In addition, they contain SPH-1, the Xenopus homologue of p80-coilin, a protein characteristic of coiled bodies. To determine whether coilin is an essential structural component of the coiled body, we removed it from the egg extract by immunoprecipitation. We showed that nuclei with bodies morphologically identical to coiled bodies (at the light microscope level) formed in such coilin-depleted extract. As expected, these bodies did not stain with antibodies against coilin. Moreover, they failed to stain with an antibody against the Sm proteins, although Sm proteins associated with snRNAs were still present in the extract. Staining of the coilin- and Sm-depleted coiled bodies was normal with antibodies against two nucleolar proteins, fibrillarin and nucleolin. Similar results were observed when Sm proteins were depleted from egg extract: staining of the coiled bodies with antibodies against the Sm proteins and coilin was markedly reduced but bright nucleolin and fibrillarin staining remained. These immunodepletion experiments demonstrate an interdependence between coilin and Sm snRNPs and suggest that neither is essential for assembly of nucleolar components in coiled bodies. We propose that coiled bodies are structurally heterogeneous organelles in which the components of the three RNA processing pathways may occur in separate compartments.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Laemmli U. K. Study of the cell cycle-dependent assembly of the DNA pre-replication centres in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4153–4164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almouzni G., Wolffe A. P. Nuclear assembly, structure, and function: the use of Xenopus in vitro systems. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Mar;205(1):1–15. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade L. E., Chan E. K., Raska I., Peebles C. L., Roos G., Tan E. M. Human autoantibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1407–1419. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade L. E., Tan E. M., Chan E. K. Immunocytochemical analysis of the coiled body in the cell cycle and during cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1947–1951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azum-Gélade M. C., Noaillac-Depeyre J., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Gas N. Cell cycle redistribution of U3 snRNA and fibrillarin. Presence in the cytoplasmic nucleolus remnant and in the prenucleolar bodies at telophase. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):463–475. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer D. W., Murphy C., Wu Z., Wu C. H., Gall J. G. In vitro assembly of coiled bodies in Xenopus egg extract. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jun;5(6):633–644. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.6.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P., Dabauvalle M. C., Scheer U. In vitro assembly of prenucleolar bodies in Xenopus egg extract. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1297–1304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Pinto A. L. U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein: RNA structure analysis and ATP-dependent interaction with U4/U6. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3350–3359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann K., Ferreira J., Santama N., Weis K., Lamond A. I. Molecular analysis of the coiled body. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1995;19:107–113. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1995.supplement_19.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Ferreira J., Lamond A. I. Assembly of snRNP-containing coiled bodies is regulated in interphase and mitosis--evidence that the coiled body is a kinetic nuclear structure. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):841–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Tollervey D., Pepperkok R., Barabino S. M., Merdes A., Brunner C., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurt E., Lamond A. I. Mammalian nuclei contain foci which are highly enriched in components of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):195–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kornberg T. B., Kirschner M. W. Small nuclear RNA transcription and ribonucleoprotein assembly in early Xenopus development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):62–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey M. R., Matera A. G. Coiled bodies contain U7 small nuclear RNA and associate with specific DNA sequences in interphase human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):5915–5919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.5915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Antony C., Wright M., Maro B. Centrosome assembly in vitro: role of gamma-tubulin recruitment in Xenopus sperm aster formation. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):19–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Tsvetkov A., Wu Z., Murphy C. Is the sphere organelle/coiled body a universal nuclear component? Dev Genet. 1995;16(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine M. A., Rankin M. L., DiMario P. J. The Gly/Arg-rich (GAR) domain of Xenopus nucleolin facilitates in vitro nucleic acid binding and in vivo nucleolar localization. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Nov;4(11):1189–1204. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.11.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. U1 and U2 small nuclear RNAs are present in nuclear speckles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):305–308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman P., Eneström S., Turley S. J., Pollard K. M. Selective induction of anti-fibrillarin autoantibodies by silver nitrate in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 May;96(2):285–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Rothblum L. I., Busch H., Ochs R. L. Nucleologenesis: use of non-isotopic in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry to compare the localization of rDNA and nucleolar proteins during mitosis. Biol Cell. 1989;65(3):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1989.tb00795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Segura-Valdez M. L., Ochs R. L., Rothblum L. I., Hannan R., Spector D. L. Nucleologenesis: U3 snRNA-containing prenucleolar bodies move to sites of active pre-rRNA transcription after mitosis. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Sep;5(9):955–966. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.9.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. The coiled body. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90214-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Formation in vitro of sperm pronuclei and mitotic chromosomes induced by amphibian ooplasmic components. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):719–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6601299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Roles of cytosol and cytoplasmic particles in nuclear envelope assembly and sperm pronuclear formation in cell-free preparations from amphibian eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1222–1230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Bernhard W. Fine structural organization of the interphase nucleus in some mammalian cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Wilson K. L. Egg extracts for nuclear import and nuclear assembly reactions. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:607–634. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Wilson K. L., Dunphy W. G. A lamin-independent pathway for nuclear envelope assembly. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2247–2259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Shen E., Carroll R. E., Busch H. Nucleologenesis: composition and fate of prenucleolar bodies. Chromosoma. 1985;92(5):330–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00327463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Andrade L. E., Ochs R. L., Chan E. K., Chang C. M., Roos G., Tan E. M. Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90496-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B. Spheres, coiled bodies and nuclear bodies. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh H., Cooke C. A., Burgess W. H., Earnshaw W. C., Dasso M. Direct and indirect association of the small GTPase ran with nuclear pore proteins and soluble transport factors: studies in Xenopus laevis egg extracts. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Sep;7(9):1319–1334. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.9.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Systems for the study of nuclear assembly, DNA replication, and nuclear breakdown in Xenopus laevis egg extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;35:449–468. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60583-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Immunoprecipitation of ribonucleoproteins using autoantibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:468–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. Identification and characterization of a sphere organelle protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):767–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Gall J. G. U7 small nuclear RNA in C snurposomes of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6257–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Murphy C., Gall J. G. Human p80-coilin is targeted to sphere organelles in the amphibian germinal vesicle. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Oct;5(10):1119–1127. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.10.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Murphy C., Wu C. H., Tsvetkov A., Gall J. G. Snurposomes and coiled bodies. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:747–754. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]