Abstract
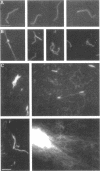
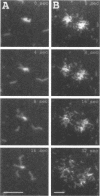
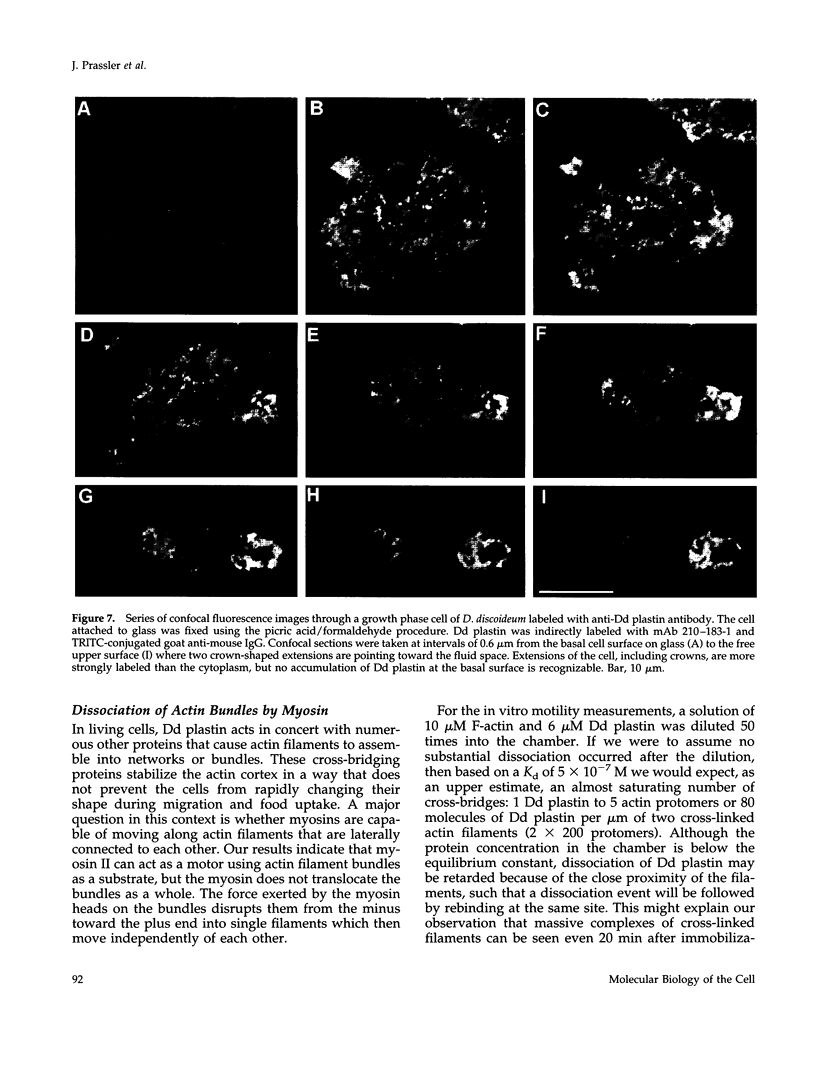
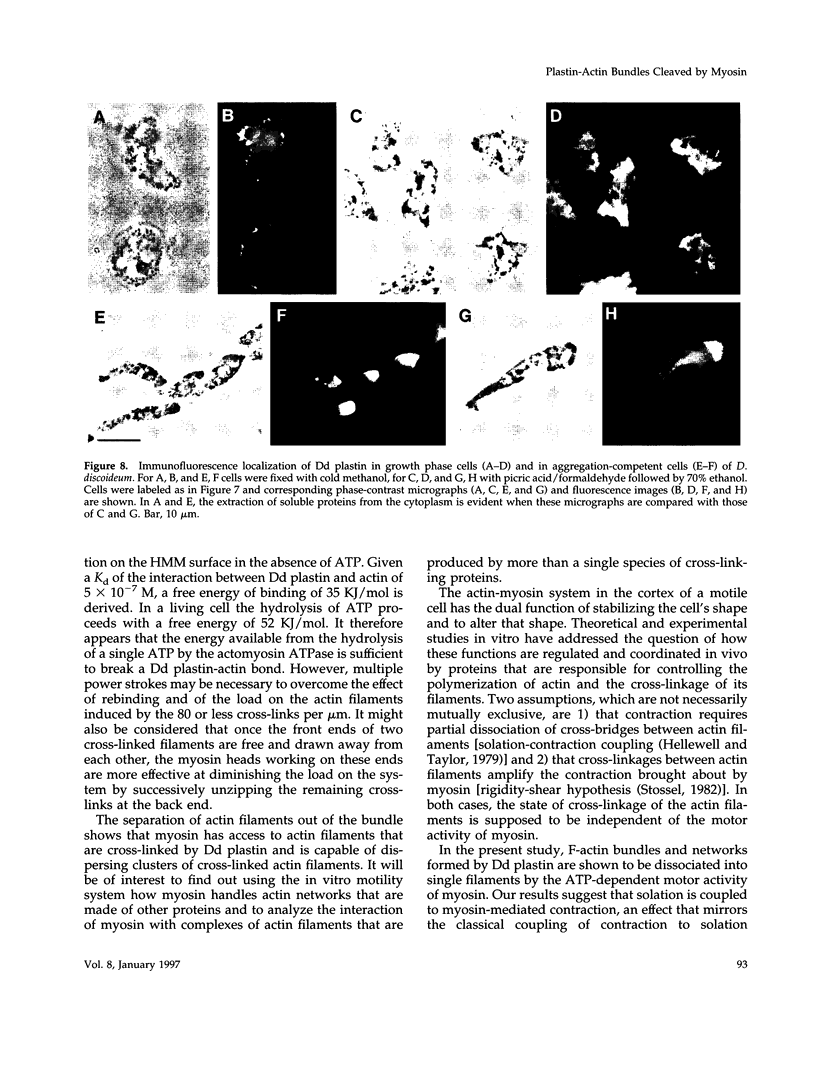
A protein purified from cytoskeletal fractions of Dictyostelium discoideum proved to be a member of the fimbrin/plastin family of actin-bundling proteins. Like other family members, this Ca(2+)-inhibited 67-kDa protein contains two EF hands followed by two actin-binding sites of the alpha-actinin/beta-spectrin type. Dd plastin interacted selectively with actin isoforms: it bound to D. discoideum actin and to beta/gamma-actin from bovine spleen but not to alpha-actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Immunofluorescence labeling of growth phase cells showed accumulation of Dd plastin in cortical structures associated with cell surface extensions. In the elongated, streaming cells of the early aggregation stage, Dd plastin was enriched in the front regions. To examine how the bundled actin filaments behave in myosin II-driven motility, complexes of F-actin and Dd plastin were bound to immobilized heavy meromyosin, and motility was started by photoactivating caged ATP. Actin filaments were immediately propelled out of bundles or even larger aggregates and moved on the myosin as separate filaments. This result shows that myosin can disperse an actin network when it acts as a motor and sheds light on the dynamics of protein-protein interactions in the cortex of a motile cell where myosin II and Dd plastin are simultaneously present.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Botstein D., Drubin D. G. A yeast actin-binding protein is encoded by SAC6, a gene found by suppression of an actin mutation. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):231–233. doi: 10.1126/science.2643162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams A. E., Botstein D., Drubin D. G. Requirement of yeast fimbrin for actin organization and morphogenesis in vivo. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):404–408. doi: 10.1038/354404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André E., Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A., Schleicher M., Segall J. E., Wallraff E. A Dictyostelium mutant deficient in severin, an F-actin fragmenting protein, shows normal motility and chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):985–995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpin M., Friederich E., Algrain M., Vernel F., Louvard D. Functional differences between L- and T-plastin isoforms. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1995–2008. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick A. R., Janmey P. A., Condeelis J. Evidence that a 27-residue sequence is the actin-binding site of ABP-120. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12989–12993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Fimbrin is a cytoskeletal protein that crosslinks F-actin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6849–6853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Fimbrin, a new microfilament-associated protein present in microvilli and other cell surface structures. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier J., Fechheimer M., Swanson J., Taylor D. L. Abundance, relative gelation activity, and distribution of the 95,000-dalton actin-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):178–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A. A., Segall J. E., Wallraff E., Schleicher M. A Dictyostelium mutant lacking an F-actin cross-linking protein, the 120-kD gelation factor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1477–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. S. A Ca2+ insensitive actin-crosslinking protein from Dicytostelium discoideum. Cell Motil. 1985;5(6):529–543. doi: 10.1002/cm.970050608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J. S., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of amoeboid movement. V. The control of gelation, solation, and contraction in extracts from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):901–927. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Condeelis J., Wessels D., Soll D., Kern H., Knecht D. A. Targeted disruption of the ABP-120 gene leads to cells with altered motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):943–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Ridsdale J. A., Condeelis J., Hartwig J. Genetic deletion of ABP-120 alters the three-dimensional organization of actin filaments in Dictyostelium pseudopods. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):819–835. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demma M., Warren V., Hock R., Dharmawardhane S., Condeelis J. Isolation of an abundant 50,000-dalton actin filament bundling protein from Dictyostelium amoebae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2286–2291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Miller K. G., Botstein D. Yeast actin-binding proteins: evidence for a role in morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2551–2561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faix J., Steinmetz M., Boves H., Kammerer R. A., Lottspeich F., Mintert U., Murphy J., Stock A., Aebi U., Gerisch G. Cortexillins, major determinants of cell shape and size, are actin-bundling proteins with a parallel coiled-coil tail. Cell. 1996 Aug 23;86(4):631–642. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Taylor D. L. Isolation and characterization of a 30,000-dalton calcium-sensitive actin cross-linking protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M. The Dictyostelium discoideum 30,000-dalton protein is an actin filament-bundling protein that is selectively present in filopodia. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1539–1551. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Albrecht R., De Hostos E., Wallraff E., Heizer C., Kreitmeier M., Müller-Taubenberger A. Actin-associated proteins in motility and chemotaxis of Dictyostelium cells. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1993;47:297–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Kaulfus P., Matsudaira P., Weber K. F-actin binding and bundling properties of fimbrin, a major cytoskeletal protein of microvillus core filaments. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9283–9288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D., Djeu J., Latter G., Burbeck S., Leavitt J. Abundant synthesis of the transformation-induced protein of neoplastic human fibroblasts, plastin, in normal lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5643–5647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C., Schekman R. Actin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1270–1278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugwitz M., Noegel A. A., Rieger D., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. Dictyostelium discoideum contains two profilin isoforms that differ in structure and function. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):481–489. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker M., Yan-Marriott Y., Marriott G. Proximity relationships and structural dynamics of the phalloidin binding site of actin filaments in solution and on single actin filaments on heavy meromyosin. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 5;34(35):11017–11025. doi: 10.1021/bi00035a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of ameboid movement. VI. The solation-contraction coupling hypothesis. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):633–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey E. S., Drummond D. R., Sparrow J. C. Molecular genetics of actin function. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):657–671. doi: 10.1042/bj2910657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman D. A., Wertman K. F., Drubin D. G. Mapping actin surfaces required for functional interactions in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):423–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honts J. E., Sandrock T. S., Brower S. M., O'Dell J. L., Adams A. E. Actin mutations that show suppression with fimbrin mutations identify a likely fimbrin-binding site on actin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):413–422. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug C., Jay P. Y., Reddy I., McNally J. G., Bridgman P. C., Elson E. L., Cooper J. A. Capping protein levels influence actin assembly and cell motility in dictyostelium. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson L. W., Sellers J. R., Taylor D. L. Actin-binding proteins regulate the work performed by myosin II motors on single actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(4):274–280. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Itoh H., Ishiwata S., Hirano K., Nishizaka T., Hayakawa T. Dual-view microscopy with a single camera: real-time imaging of molecular orientations and calcium. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):67–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):119–174. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. Assays for actin sliding movement over myosin-coated surfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:399–416. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Aebersold R. H., Kent S. B., Varma M., Leavitt J. Molecular cloning and characterization of plastin, a human leukocyte protein expressed in transformed human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4659–4668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Shen W., Chen Z. P., Tu Y. H., Matsudaira P. Identification of I-plastin, a human fimbrin isoform expressed in intestine and kidney. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2457–2467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S. D., Pollard T. D. Viscometric analysis of the gelation of Acanthamoeba extracts and purification of two gelation factors. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):414–428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott G., Heidecker M. Light-directed generation of the actin-activated ATPase activity of caged heavy meromyosin. Biochemistry. 1996 Mar 12;35(10):3170–3174. doi: 10.1021/bi952207o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Shiroo M., Kung H. F., Copeland T. D. Purification and characterization of a cytosolic 65-kilodalton phosphoprotein in human leukocytes whose phosphorylation is augmented by stimulation with interleukin 1. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3765–3770. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Ito M., Zu Y., Shigesada K., Maruyama K. Human T cell L-plastin bundles actin filaments in a calcium-dependent manner. J Biochem. 1992 Oct;112(4):503–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Rapp S., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Stewart M. The Dictyostelium gelation factor shares a putative actin binding site with alpha-actinins and dystrophin and also has a rod domain containing six 100-residue motifs that appear to have a cross-beta conformation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):607–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richey B., Cayley D. S., Mossing M. C., Kolka C., Anderson C. F., Farrar T. C., Record M. T., Jr Variability of the intracellular ionic environment of Escherichia coli. Differences between in vitro and in vivo effects of ion concentrations on protein-DNA interactions and gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7157–7164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozycki M., Schutt C. E., Lindberg U. Affinity chromatography-based purification of profilin:actin. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:100–118. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96012-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saran S., Nakao H., Tasaka M., Iida H., Tsuji F. I., Nanjundiah V., Takeuchi I. Intracellular free calcium level and its response to cAMP stimulation in developing Dictyostelium cells transformed with jellyfish apoaequorin cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 3;337(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80626-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindl M., Wallraff E., Deubzer B., Witke W., Gerisch G., Sackmann E. Cell-substrate interactions and locomotion of Dictyostelium wild-type and mutants defective in three cytoskeletal proteins: a study using quantitative reflection interference contrast microscopy. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):1177–1190. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80294-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. II. Purification, properties, and membrane association of actin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6013–6020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. The structure of cortical cytoplasm. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 4;299(1095):275–289. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Vegetative Dictyostelium cells containing 17 actin genes express a single major actin. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):475–477. doi: 10.1038/284475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I., Wallraff E., Albrecht R., Gerisch G. Motility and substratum adhesion of Dictyostelium wild-type and cytoskeletal mutant cells: a study by RICM/bright-field double-view image analysis. J Cell Sci. 1995 Apr;108(Pt 4):1519–1530. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.4.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner A., Isenberg G. 12-fold difference between the critical monomer concentrations of the two ends of actin filaments in physiological salt conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4922–4925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Arruda M. V., Watson S., Lin C. S., Leavitt J., Matsudaira P. Fimbrin is a homologue of the cytoplasmic phosphoprotein plastin and has domains homologous with calmodulin and actin gelation proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1069–1079. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Bradtke B., Lottspeich F., Guggenheim R., Gerisch G. Coronin, an actin binding protein of Dictyostelium discoideum localized to cell surface projections, has sequence similarities to G protein beta subunits. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4097–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]