Abstract
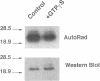
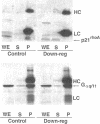
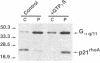
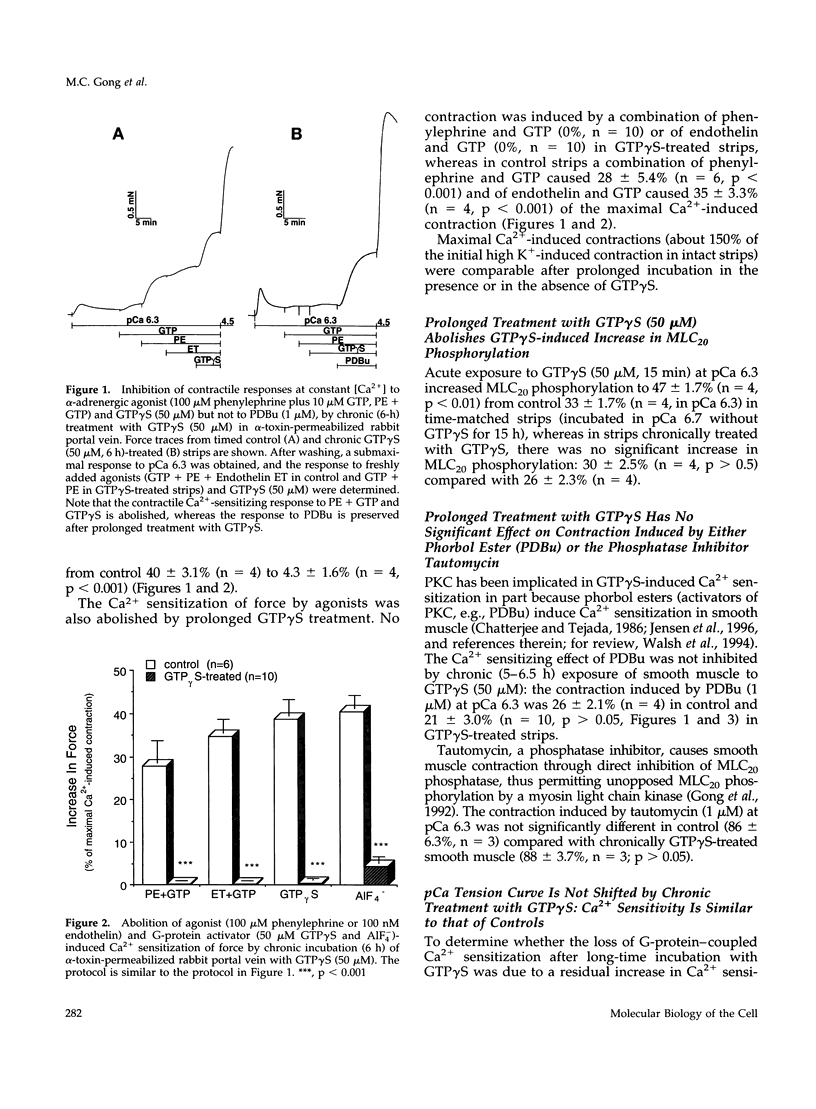
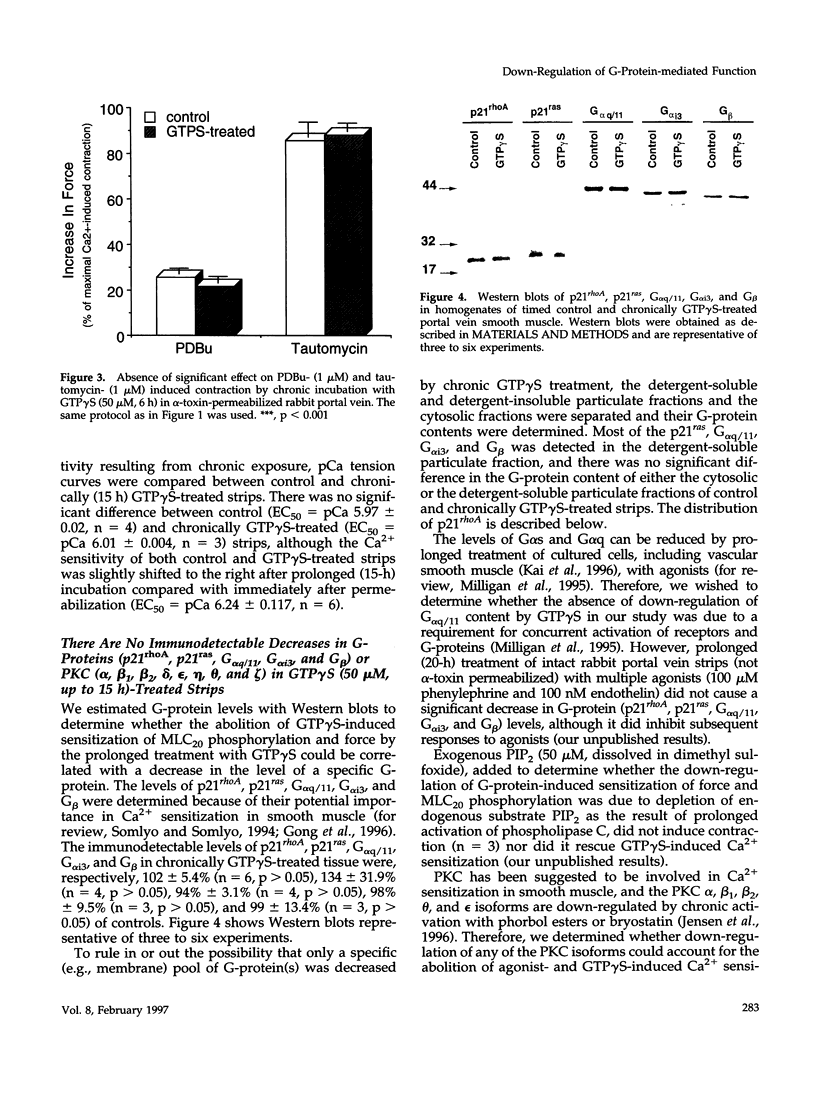
Prolonged treatment with guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP gamma S; 5-16 h, 50 microM) of smooth muscle permeabilized with Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin down-regulated (abolished) the acute Ca2+ sensitization of force by GTP gamma S, AIF-4, phenylephrine, and endothelin, but not the response to phorbol dibutyrate or a phosphatase inhibitor, tautomycin. Down-regulation also abolished the GTP gamma S-induced increase in myosin light chain phosphorylation at constant [Ca2+] and was associated with extensive translocation of p21rhoA to the particulate fraction, prevented its immunoprecipitation, and inhibited its ADP ribosylation without affecting the immunodetectable content of G-proteins (p21rhoA, p21ras, G alpha q/11, G alpha i3, and G beta) or protein kinase C (types alpha, beta 1, beta 2, delta, epsilon, eta, theta, and zeta). We conclude that the loss of GTP gamma S- and agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization through prolonged treatment with GTP gamma S is not due to a decrease in the total content of either trimeric (G alpha q/11, G alpha i3, and G beta) or monomeric (p21rhoA and p21ras) G-protein or protein kinase C but may be related to a structural change of p21rhoA and/or to down-regulation of its (yet to be identified) effector.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D., MacDougall L. K., Sola M. M., Ikebe M., Cohen P. The control of protein phosphatase-1 by targetting subunits. The major myosin phosphatase in avian smooth muscle is a novel form of protein phosphatase-1. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):1023–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M., Tejada M. Phorbol ester-induced contraction in chemically skinned vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita A., Takeuchi T., Nakajima H., Nishio H., Hata F. Involvement of heterotrimeric GTP-binding protein and rho protein, but not protein kinase C, in agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization of skinned muscle of guinea pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong M. C., Cohen P., Kitazawa T., Ikebe M., Masuo M., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Myosin light chain phosphatase activities and the effects of phosphatase inhibitors in tonic and phasic smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14662–14668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong M. C., Iizuka K., Nixon G., Browne J. P., Hall A., Eccleston J. F., Sugai M., Kobayashi S., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Role of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins--ras-family or trimeric proteins or both--in Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead C. M., Gailly P., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Haystead T. A. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a recombinant 72.5 kDa fragment of the 110 kDa regulatory subunit of smooth muscle protein phosphatase 1M. FEBS Lett. 1995 Dec 18;377(2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M., Sato K., Miyamoto S., Ozaki H., Karaki H. Different pathways of calcium sensitization activated by receptor agonists and phorbol esters in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1527–1531. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa K., Ito M., Hartshorne D. J. Phosphorylation of the large subunit of myosin phosphatase and inhibition of phosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4733–4740. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki M., Komori S., Unno T., Syuto B., Ohashi H. Possible involvement of a small G-protein sensitive to exoenzyme C3 of Clostridium botulinum in the regulation of myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in beta-escin skinned smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;67(1):1–7. doi: 10.1254/jjp.67.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E., Gong M. C., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Separate upstream and convergent downstream pathways of G-protein- and phorbol ester-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of myosin light chain phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1996 Sep 1;318(Pt 2):469–475. doi: 10.1042/bj3180469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Fukui T., Lassègue B., Shah A., Minieri C. A., Griendling K. K. Prolonged exposure to agonist results in a reduction in the levels of the Gq/G11 alpha subunits in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;49(1):96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawase T., Van Breemen C. Aluminum fluoride induces a reversible Ca2+ sensitization in alpha-toxin-permeabilized vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 7;214(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90093-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Ito M., Amano M., Chihara K., Fukata Y., Nakafuku M., Yamamori B., Feng J., Nakano T., Okawa K. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) Science. 1996 Jul 12;273(5272):245–248. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5272.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Masuo M., Somlyo A. P. G protein-mediated inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9307–9310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Gong M. C., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Ca2+ channel blockers distinguish between G protein-coupled pharmacomechanical Ca2+ release and Ca2+ sensitization. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):C364–C370. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.2.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Cytosolic heparin inhibits muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. Physiological role of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in pharmacomechanical coupling. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17997–18004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung T., Manser E., Tan L., Lim L. A novel serine/threonine kinase binding the Ras-related RhoA GTPase which translocates the kinase to peripheral membranes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29051–29054. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Amano M., Yamamoto T., Chihara K., Nakafuku M., Ito M., Nakano T., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A., Kaibuchi K. Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J. 1996 May 1;15(9):2208–2216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Wise A., MacEwan D. J., Grassie M. A., Kennedy F. R., Lee T. W., Adie E. J., Kim G. D., McCallum J. F., Burt A. Mechanisms of agonist-induced G-protein elimination. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Feb;23(1):166–170. doi: 10.1042/bst0230166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai H., Kitagawa M., Shibata H., Takanaga H., Mori K., Shimakawa M., Miyahara M., Hirao K., Ono Y. Activation of PKN, a novel 120-kDa protein kinase with leucine zipper-like sequences, by unsaturated fatty acids and by limited proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 14;204(1):348–356. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Rensland H., Pfitzer G. Ras proteins increase Ca(2+)-responsiveness of smooth muscle contraction. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81395-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Ito M., Miyahara M., Ichikawa K., Okubo S., Konishi T., Naka M., Tanaka T., Hirano K., Hartshorne D. J. Characterization of the myosin-binding subunit of smooth muscle myosin phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30407–30411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi A., Iizuka K., Fadden P., Mosse C., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Haystead T. A. Purification and characterization of the mammalian myosin light chain phosphatase holoenzyme. The differential effects of the holoenzyme and its subunits on smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31598–31606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):231–236. doi: 10.1038/372231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkle-Mulcahy L., Ichikawa K., Hartshorne D. J., Siegman M. J., Butler T. M. Thiophosphorylation of the 130-kDa subunit is associated with a decreased activity of myosin light chain phosphatase in alpha-toxin-permeabilized smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 4;270(31):18191–18194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Andrea J. E., Allen B. G., Clément-Chomienne O., Collins E. M., Morgan K. G. Smooth muscle protein kinase C. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;72(11):1392–1399. doi: 10.1139/y94-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]