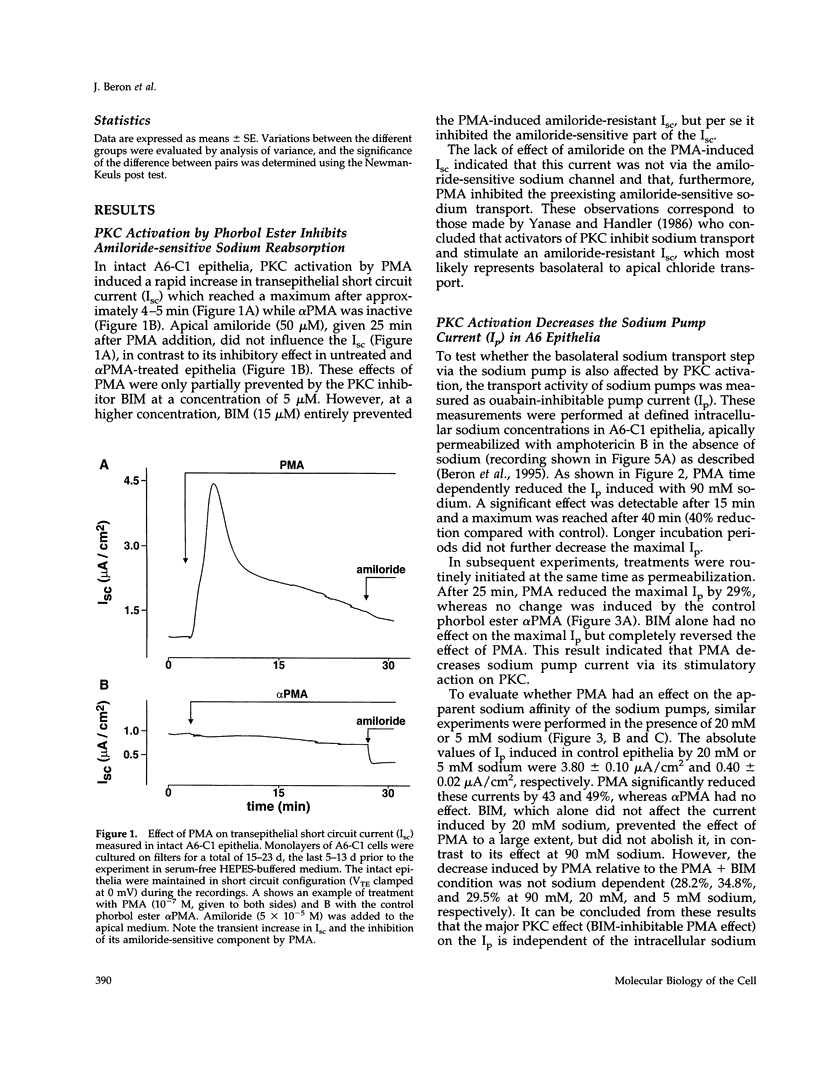
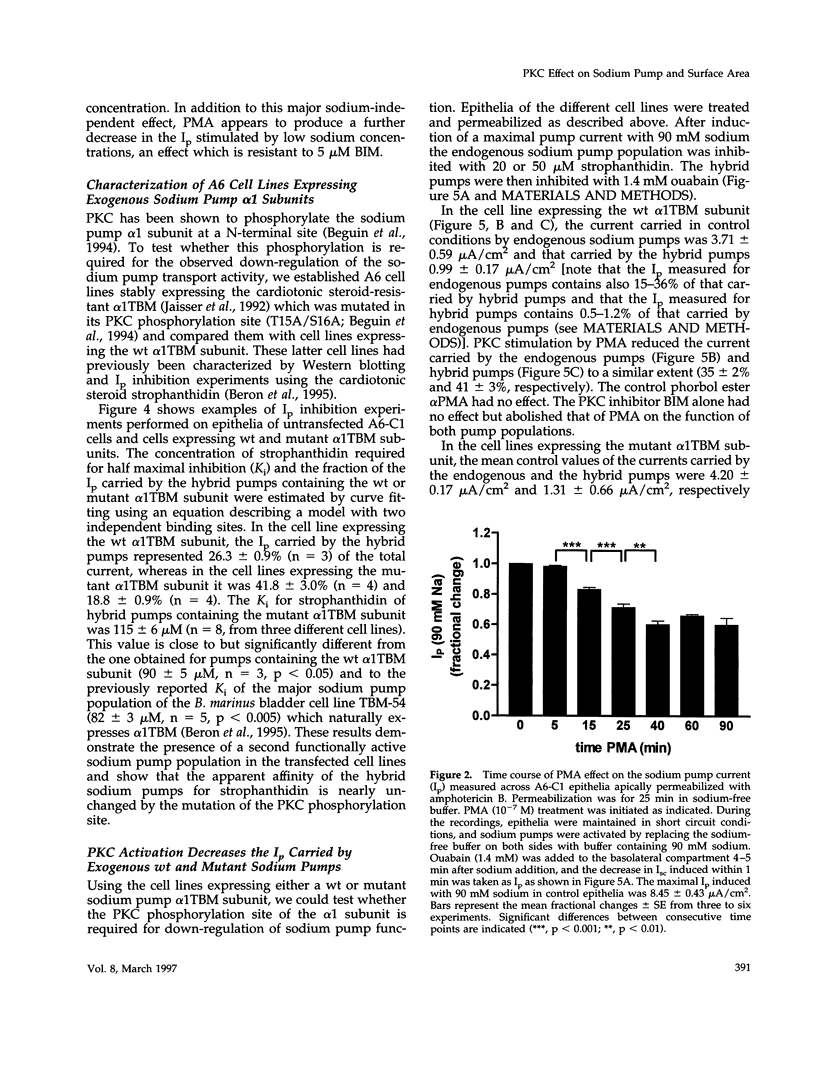
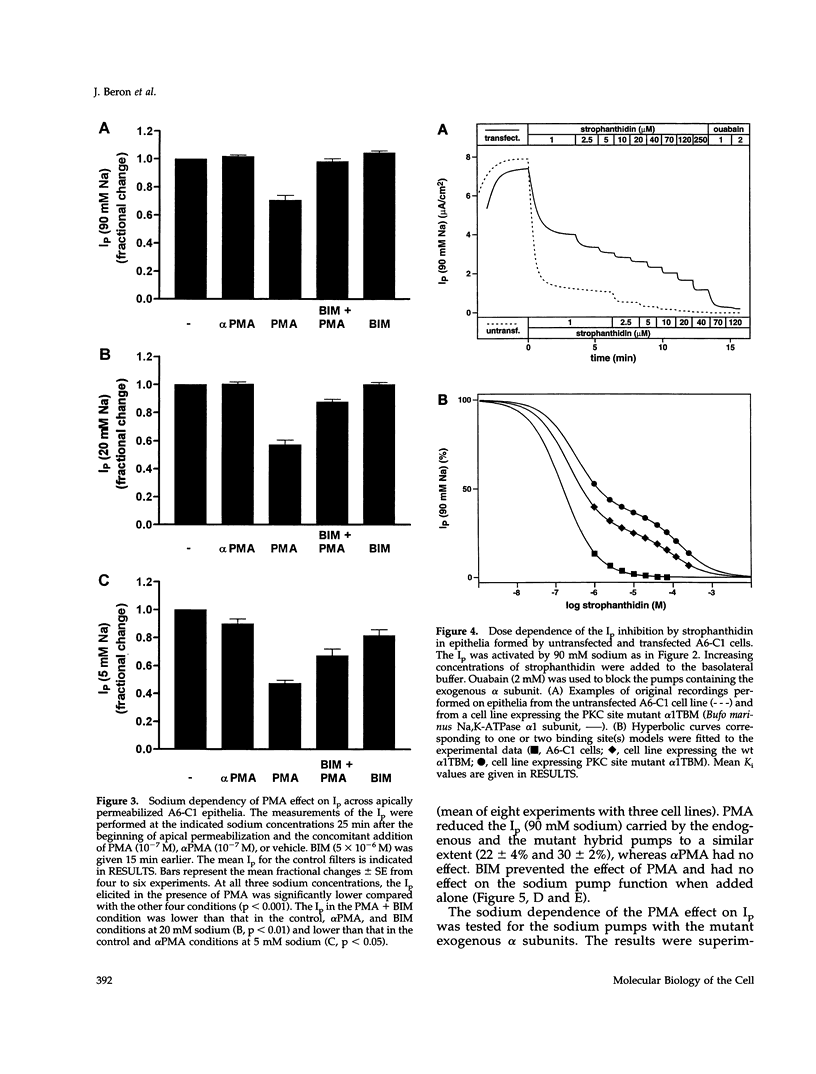
Abstract
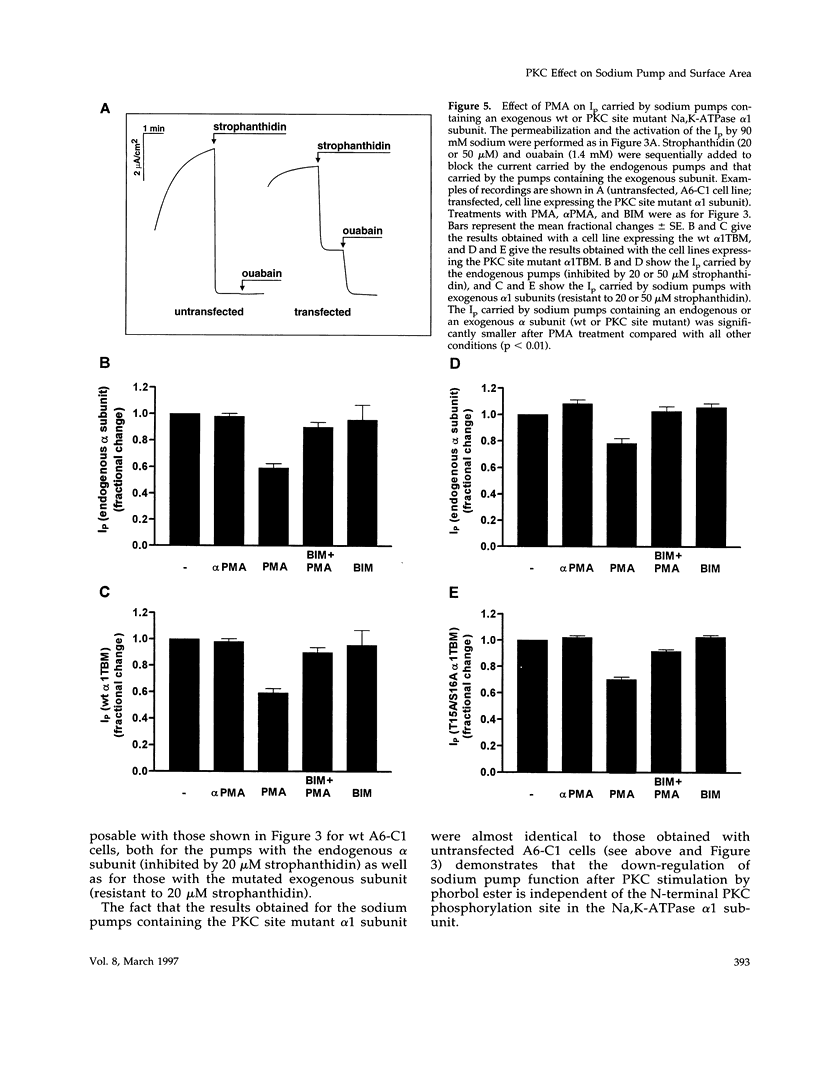
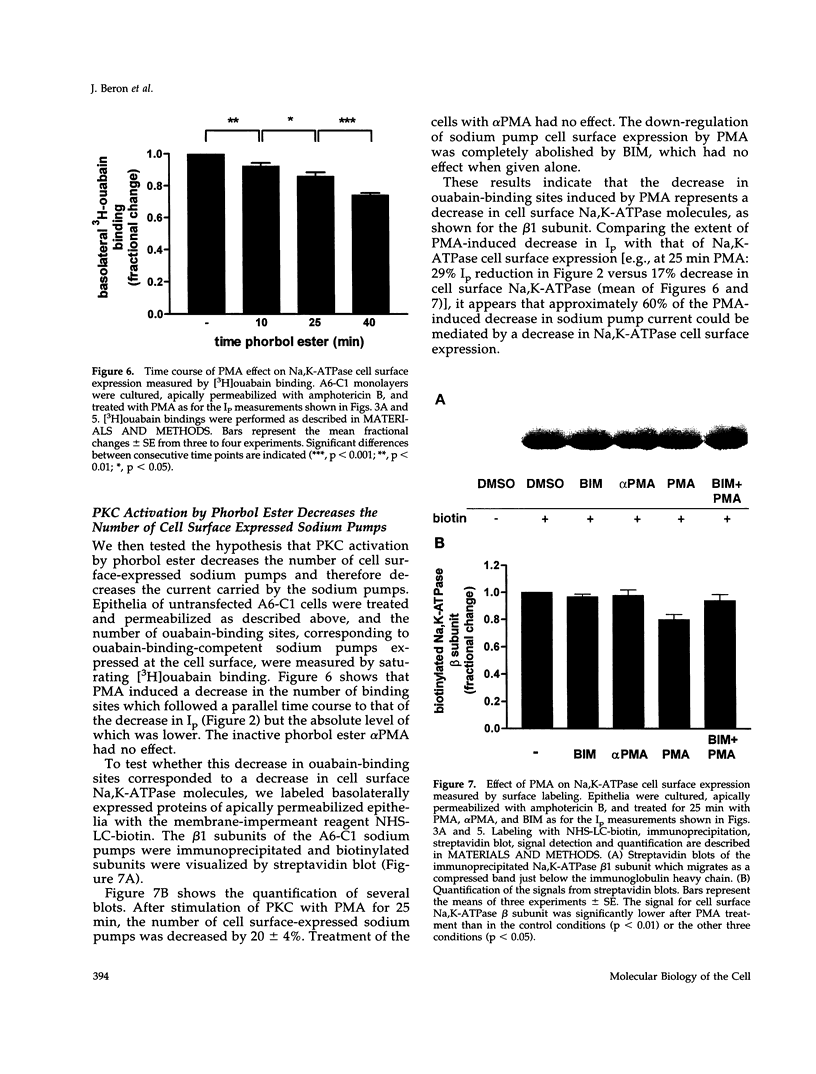
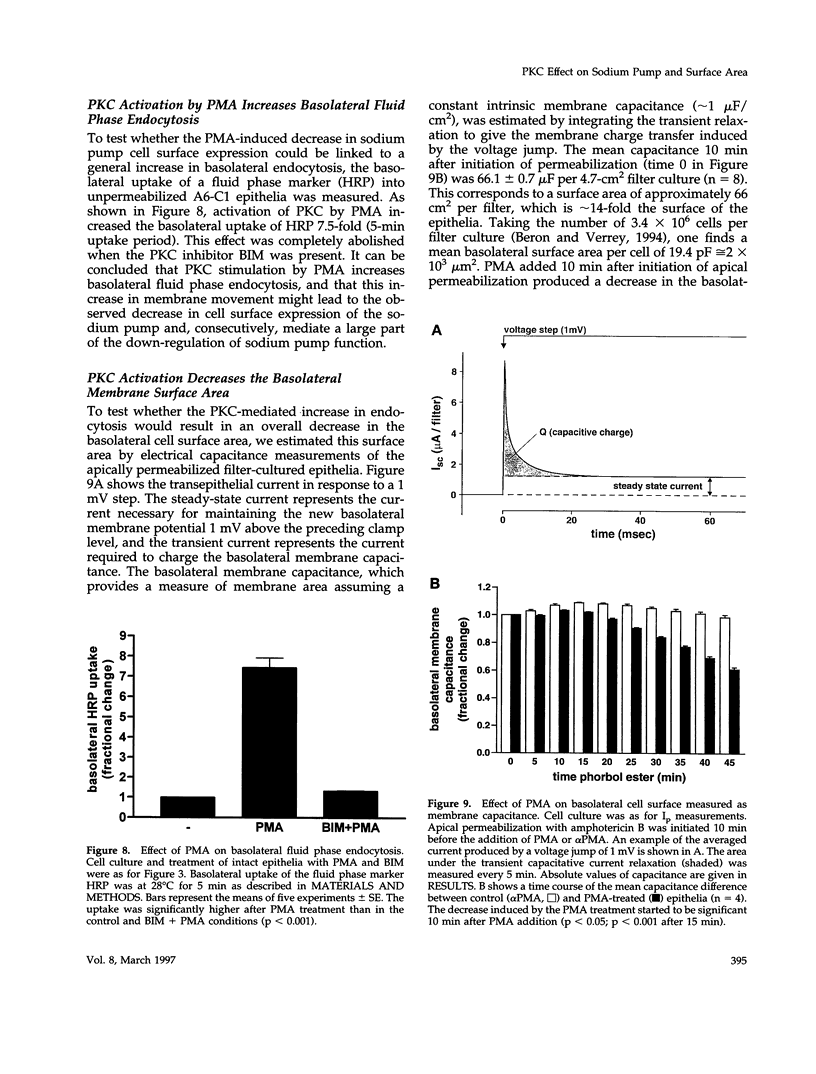
The effect of protein kinase C (PKC) stimulation on the pump current (Ip) generated by the Na,K-ATPase was measured in A6 epithelia apically permeabilized with amphotericin B. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) produced a decrease in Ip carried by sodium pumps containing the endogenous Xenopus laevis or transfected Bufo marinus alpha 1 subunits (approximately 30% reduction within 25 min, maximum after 40 min) independent of the PKC phosphorylation site (T15A/S16A). In addition to this major effect of PMA, which was independent of the intracellular sodium concentration and was prevented by the PKC inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X (BIM), another BIM-resistant, PKC site-independent decrease was observed when the Ip was measured at low sodium concentrations (total reduction approximately 50% at 5 mM sodium). Using ouabain binding and cell surface biotinylation, stimulation of PKC was shown to reduce surface Na,K-ATPase by 14 to 20% within 25 min. The same treatment stimulated fluid phase endocytosis sevenfold and decreased by 16.5% the basolateral cell surface area measured by transepithelial capacitance measurements. In conclusion, PKC stimulation produces a decrease in sodium pump function which can be attributed, to a large extent, to a withdrawal of sodium pumps from the basolateral cell surface independent of their PKC site. This reduction of the number of sodium pumps is parallel to a decrease in basolateral membrane area.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beguin P., Beggah A. T., Chibalin A. V., Burgener-Kairuz P., Jaisser F., Mathews P. M., Rossier B. C., Cotecchia S., Geering K. Phosphorylation of the Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit by protein kinase A and C in vitro and in intact cells. Identification of a novel motif for PKC-mediated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24437–24445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beron J., Mastroberardino L., Spillmann A., Verrey F. Aldosterone modulates sodium kinetics of Na,K-ATPase containing an alpha 1 subunit in A6 kidney cell epithelia. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Mar;6(3):261–271. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beron J., Verrey F. Aldosterone induces early activation and late accumulation of Na-K-ATPase at surface of A6 cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 1):C1278–C1290. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.5.C1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Aperia A., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11359–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A., Aperia A. Na+-K+-ATPase is an effector protein for protein kinase C in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F370–F373. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibalin A. V., Vasilets L. A., Hennekes H., Pralong D., Geering K. Phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunits in microsomes and in homogenates of Xenopus oocytes resulting from the stimulation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22378–22384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Becchetti A., Ma H., Ling B. N. Renal sodium channels: regulation and single channel properties. Kidney Int. 1995 Oct;48(4):941–949. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewart H. S., Klip A. Hormonal regulation of the Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase: mechanisms underlying rapid and sustained changes in pump activity. Am J Physiol. 1995 Aug;269(2 Pt 1):C295–C311. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.2.C295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feschenko M. S., Sweadner K. J. Structural basis for species-specific differences in the phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14072–14077. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Palmer L. G., Windhager E. E. Feedback regulation of Na channels in rat CCT. IV. Mediation by activation of protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1996 Feb;270(2 Pt 2):F371–F376. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.270.2.F371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Carranza M. L., Buffin-Meyer B., Rousselot M., Doucet A., Favre H. Protein kinase C-dependent stimulation of Na(+)-K(+)-ATP epsilon in rat proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 1):C1277–C1283. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.5.C1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottardi C. J., Dunbar L. A., Caplan M. J. Biotinylation and assessment of membrane polarity: caveats and methodological concerns. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 2):F285–F295. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.2.F285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Baum M., Kokko J. P. Effects of protein kinase C activation on sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2 transport in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1561–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI113242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Primary sequence and functional expression of a novel ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase. The beta subunit modulates potassium activation of the Na,K-pump. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16895–16903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Eaton D. C. Effects of luminal Na+ on single Na+ channels in A6 cells, a regulatory role for protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1094–F1103. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Kokko K. E., Eaton D. C. Inhibition of apical Na+ channels in rabbit cortical collecting tubules by basolateral prostaglandin E2 is modulated by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1328–1334. doi: 10.1172/JCI115998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes J. M., Hokin-Neaverson M., Bertics P. J. Kinetics of phosphorylation of Na+/K(+)-ATPase by protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90069-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny-Baron G., Kazanietz M. G., Mischak H., Blumberg P. M., Kochs G., Hug H., Marmé D., Schächtele C. Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Gö 6976. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9194–9197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton J. P., Khan W. A., Collinsworth G., Hannun Y. A., Medford R. M. Heterogeneity of protein kinase C-mediated rapid regulation of Na/K-ATPase in kidney epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15958–15964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Cohen H. T., Katz A. I. Different mechanisms of renal Na-K-ATPase regulation by protein kinases in proximal and distal nephron. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):F399–F405. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.3.F399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahedi M., Laborde K., Bussières L., Dechaux M., Sachs C. Protein kinase C activation causes inhibition of Na/K-ATPase activity in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial (MDCK) cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Mar;420(3-4):269–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00374458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Yoshitomi K., Taniguchi J., Imai M. Inhibition of amiloride-sensitive apical Na+ conductance by acetylcholine in rabbit cortical collecting duct perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2649–2657. doi: 10.1172/JCI117278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toullec D., Pianetti P., Coste H., Bellevergue P., Grand-Perret T., Ajakane M., Baudet V., Boissin P., Boursier E., Loriolle F. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15771–15781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Schmalzing G., Mädefessel K., Haase W., Schwarz W. Activation of protein kinase C by phorbol ester induces downregulation of the Na+/K(+)-ATPase in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Membr Biol. 1990 Nov;118(2):131–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01868470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrey F. Antidiuretic hormone action in A6 cells: effect on apical Cl and Na conductances and synergism with aldosterone for NaCl reabsorption. J Membr Biol. 1994 Feb;138(1):65–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00211070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrey F., Beron J., Spindler B. Corticosteroid regulation of renal Na,K-ATPase. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996;22(5-6):279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrey F., Digicaylioglu M., Bolliger U. Polarized membrane movements in A6 kidney cells are regulated by aldosterone and vasopressin/vasotocin. J Membr Biol. 1993 May;133(3):213–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00232021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilborn T. W., Schafer J. A. Differential expression of PKC isoforms in fresh and cultured rabbit CCD. Am J Physiol. 1996 May;270(5 Pt 2):F766–F775. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.270.5.F766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. E., Hallam T. J. Protein kinase C: is its pivotal role in cellular activation over-stated? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Feb;15(2):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase M., Handler J. S. Activators of protein kinase C inhibit sodium transport in A6 epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C517–C522. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]