Abstract
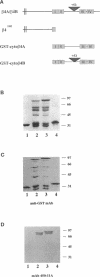
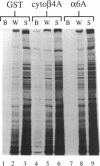
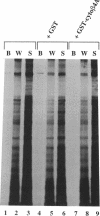
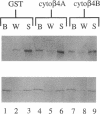
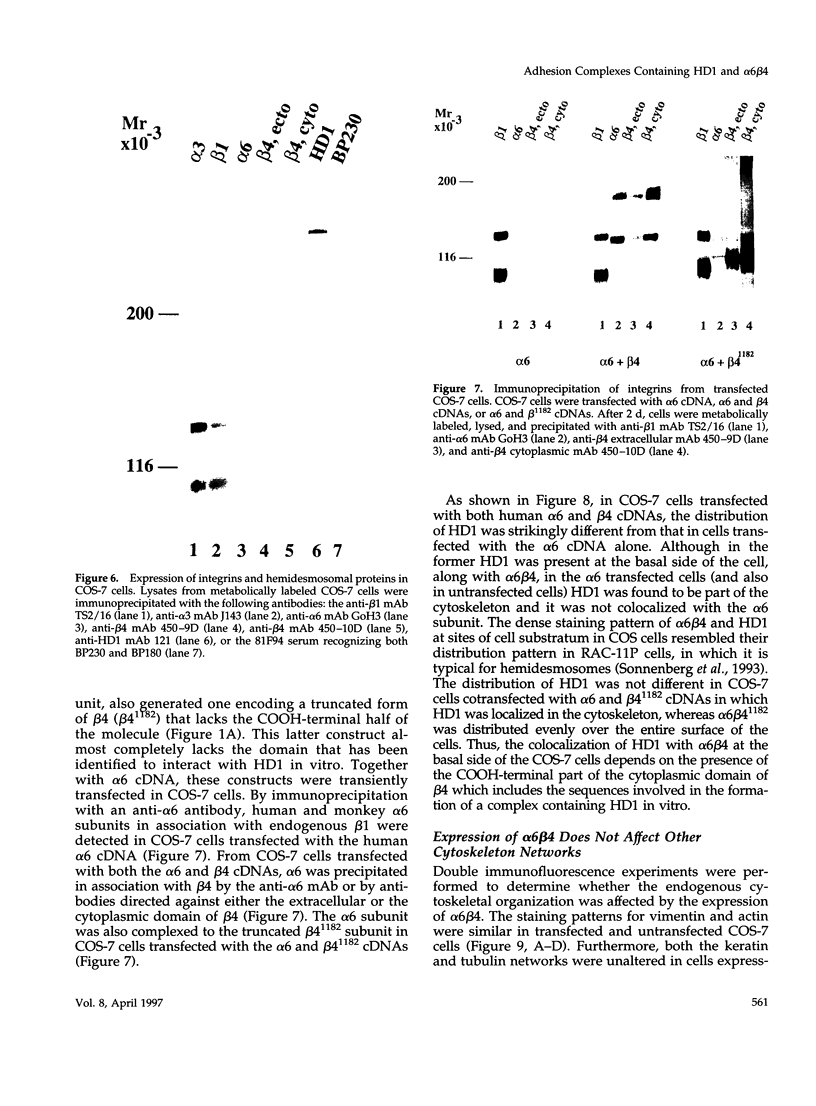
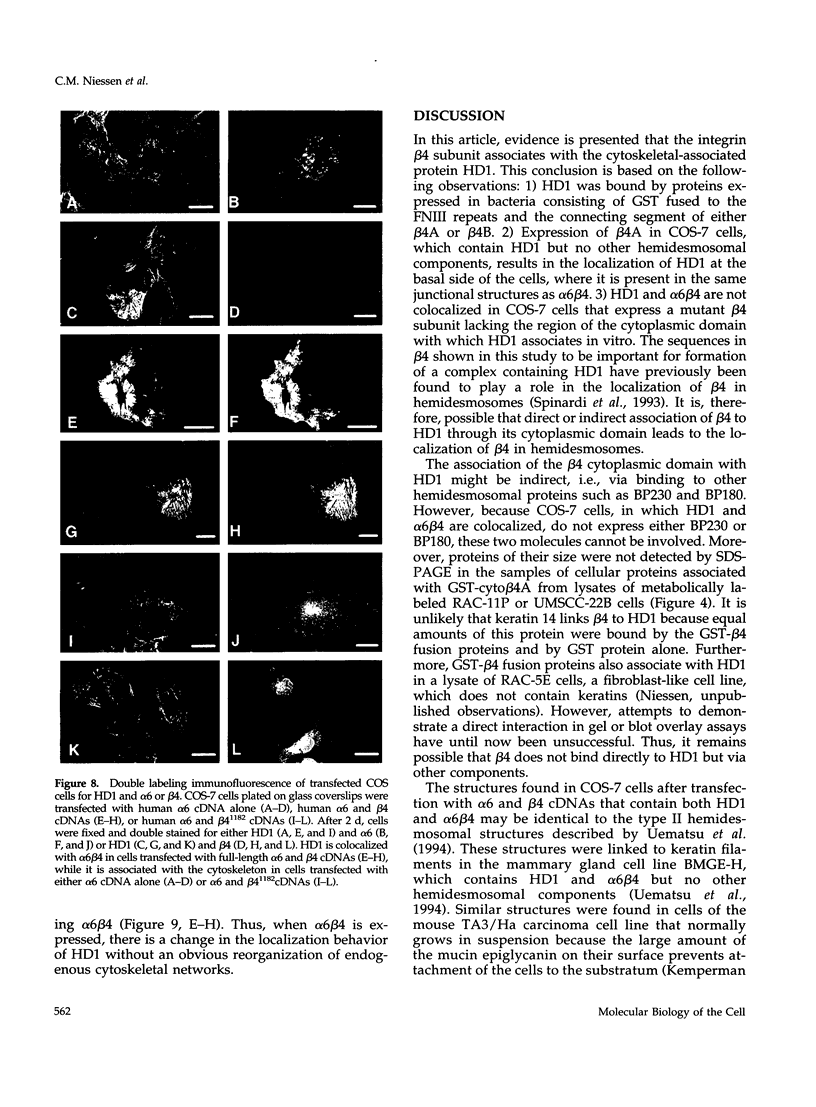
The integrin alpha 6 beta 4 is a major component of hemidesmosomes, in which it is linked to intermediate filaments. Its presence in these structures is dependent on the beta 4 cytoplasmic domain but it is not known whether beta 4 interacts directly with keratin filaments or by interaction with other proteins. In this study, we have investigated the interaction of GST-cyto beta 4A fusion proteins with cellular proteins and demonstrate that a fragment of beta 4A, consisting of the two pairs of fibronectin type III repeats, separated by the connecting segment, forms a specific complex containing a 500-kDa protein that comigrates with HD1, a hemidesmosomal plaque protein. A similar protein was also bound by a glutathione S-transferase fusion protein containing the cytoplasmic domain of a variant beta 4 subunit (beta 4B), in which a stretch of 53 amino acids is inserted in the connecting segment. Subsequent immunoblot analysis revealed that the 500-kDa protein is in fact HD1. In COS-7 cells, which do not express alpha 6 beta 4 or the hemidesmosomal components BP230 and BP180, HD1 is associated with the cytoskeleton, but after transfecting the cells with cDNAs for human alpha 6 and beta 4, it was, instead, colocalized with alpha 6 beta 4 at the basal side of the cells. The organization of the vimentin, keratin, actin, and tubulin cytoskeletal networks was not affected by the expression of alpha 6 beta 4 in COS-7 cells. The localization of HD1 at the basal side of the cells depends on the same region of beta 4 that forms a complex containing HD1 in vitro, since the expression of alpha 6 with a mutant beta 4 subunit that lacks the four fibronectin type III repeats and the connecting segment did not alter the distribution of HD1. The results indicate that for association of alpha 6 beta 4 with HD1, the cytoplasmic domain of beta 4 is essential. We suggest that this association may be crucial for hemidesmosome assembly.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borradori L., Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes: roles in adhesion, signaling and human diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;8(5):647–656. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. S., Lotz M. M., Mercurio A. M. A novel structural variant of the human beta 4 integrin cDNA. Cell Adhes Commun. 1994 Apr;2(1):1–6. doi: 10.3109/15419069409014197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Fuchs E. Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;134(2):559–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Leichtfried F. E., Herrmann H., Small J. V., Lawson D., Wiche G. Cytoskeleton-associated plectin: in situ localization, in vitro reconstitution, and binding to immobilized intermediate filament proteins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):723–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Wiche G. Intermediate filament-associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gache Y., Chavanas S., Lacour J. P., Wiche G., Owaribe K., Meneguzzi G., Ortonne J. P. Defective expression of plectin/HD1 in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1996 May 15;97(10):2289–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI118671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Labouesse E., Messaddeq N., Yehia G., Cadalbert L., Dierich A., Le Meur M. Absence of integrin alpha 6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):370–373. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Stepp M. A., Suzuki S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Proteolytic processing of endogenous and recombinant beta 4 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):951–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Jones J. C. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: structure and function of molecular components. FASEB J. 1996 Jun;10(8):871–881. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.10.8.8666164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Virata M. L., Elgart G. W., Stanley J. R., Parry D. A. Comparative structural analysis of desmoplakin, bullous pemphigoid antigen and plectin: members of a new gene family involved in organization of intermediate filaments. Int J Biol Macromol. 1992 Jun;14(3):145–153. doi: 10.1016/s0141-8130(05)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L., Degenstein L., Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Wollmann R., Perman B., Fuchs E. Gene targeting of BPAG1: abnormalities in mechanical strength and cell migration in stratified epithelia and neurologic degeneration. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E., Engvall E. Basement membrane diversity detected by monoclonal antibodies. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieda Y., Nishizawa Y., Uematsu J., Owaribe K. Identification of a new hemidesmosomal protein, HD1: a major, high molecular mass component of isolated hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1497–1506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Admiraal L. G., Niessen C., Kuikman I., Janssen H., Daams H., Sonnenberg A. Biochemical characterization and tissue distribution of the A and B variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):179–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., von dem Borne A. E., Sonnenberg A. Cloning and sequence analysis of beta-4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kd cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):765–770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson S. B., Baker S. E., Jones J. C. Molecular genetic studies of a human epidermal autoantigen (the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen/BP180): identification of functionally important sequences within the BP180 molecule and evidence for an interaction between BP180 and alpha 6 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(1):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Kurpakus M. A., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):427–438. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman M. F., de Jong M. C., Heeres K., Pas H. H., van der Meer J. B., Owaribe K., Martinez de Velasco A. M., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A. 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BP180) is deficient in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1345–1352. doi: 10.1172/JCI117785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemperman H., Wijnands Y., Wesseling J., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A., Roos E. The mucin epiglycanin on TA3/Ha carcinoma cells prevents alpha 6 beta 4-mediated adhesion to laminin and kalinin and E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell interaction. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):2071–2080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Foote L. J., Falcioni R., Sonnenberg A., Stringer C. D., Crouse C., Hemler M. E. Analysis of the tumor-associated antigen TSP-180. Identity with alpha 6-beta 4 in the integrin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15515–15521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Godfrey V., Ch'ang L. Y., Lankford T. K., Foote L. J., Makkinje A. The beta 4 subunit of the integrin family is displayed on a restricted subset of endothelium in mice. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):145–150. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurpakus M. A., Jones J. C. A novel hemidesmosomal plaque component: tissue distribution and incorporation into assembling hemidesmosomes in an in vitro model. Exp Cell Res. 1991 May;194(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90143-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurpakus M. A., Quaranta V., Jones J. C. Surface relocation of alpha 6 beta 4 integrins and assembly of hemidesmosomes in an in vitro model of wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1737–1750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainiero F., Pepe A., Wary K. K., Spinardi L., Mohammadi M., Schlessinger J., Giancotti F. G. Signal transduction by the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin: distinct beta 4 subunit sites mediate recruitment of Shc/Grb2 and association with the cytoskeleton of hemidesmosomes. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4470–4481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. A., Gatalica B., Christiano A. M., Li K., Owaribe K., McMillan J. R., Eady R. A., Uitto J. Mutations in the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a hemidesmosomal transmembrane collagen (COL17A1), in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet. 1995 Sep;11(1):83–86. doi: 10.1038/ng0995-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean W. H., Pulkkinen L., Smith F. J., Rugg E. L., Lane E. B., Bullrich F., Burgeson R. E., Amano S., Hudson D. L., Owaribe K. Loss of plectin causes epidermolysis bullosa with muscular dystrophy: cDNA cloning and genomic organization. Genes Dev. 1996 Jul 15;10(14):1724–1735. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.14.1724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen C. M., Cremona O., Daams H., Ferraresi S., Sonnenberg A., Marchisio P. C. Expression of the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in peripheral nerves: localization in Schwann and perineural cells and different variants of the beta 4 subunit. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):543–552. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen C. M., Hogervorst F., Jaspars L. H., de Melker A. A., Delwel G. O., Hulsman E. H., Kuikman I., Sonnenberg A. The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin is a receptor for both laminin and kalinin. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Apr;211(2):360–367. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen C. M., van der Raaij-Helmer M. H., Hulsman E. H., van der Neut R., Jonkman M. F., Sonnenberg A. Deficiency of the integrin beta 4 subunit in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia: consequences for hemidesmosome formation and adhesion properties. J Cell Sci. 1996 Jul;109(Pt 7):1695–1706. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.7.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owaribe K., Nishizawa Y., Franke W. W. Isolation and characterization of hemidesmosomes from bovine corneal epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):622–630. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts A. J., Croall D. E., Hemler M. E. Proteolytic cleavage of the integrin beta 4 subunit. Exp Cell Res. 1994 May;212(1):2–9. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Jones J. C., Gagescu R., Goldman R. D. IFAP 300 is common to desmosomes and hemidesmosomes and is a possible linker of intermediate filaments to these junctions. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):159–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. J., Eady R. A., Leigh I. M., McMillan J. R., Rugg E. L., Kelsell D. P., Bryant S. P., Spurr N. K., Geddes J. F., Kirtschig G. Plectin deficiency results in muscular dystrophy with epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):450–457. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Daams J. H., Kennel S. J. The alpha 6 beta 1 (VLA-6) and alpha 6 beta 4 protein complexes: tissue distribution and biochemical properties. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):207–217. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., de Melker A. A., Martinez de Velasco A. M., Janssen H., Calafat J., Niessen C. M. Formation of hemidesmosomes in cells of a transformed murine mammary tumor cell line and mechanisms involved in adherence of these cells to laminin and kalinin. J Cell Sci. 1993 Dec;106(Pt 4):1083–1102. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.4.1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinardi L., Ren Y. L., Sanders R., Giancotti F. G. The beta 4 subunit cytoplasmic domain mediates the interaction of alpha 6 beta 4 integrin with the cytoskeleton of hemidesmosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):871–884. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S. H., Shevach E. M., Katz S. I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp M. A., Spurr-Michaud S., Tisdale A., Elwell J., Gipson I. K. Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8970–8974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Naitoh Y. Amino acid sequence of a novel integrin beta 4 subunit and primary expression of the mRNA in epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):757–763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Parry D. A., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinert P. M., Stanley J. R. Comparison of molecularly cloned bullous pemphigoid antigen to desmoplakin I confirms that they define a new family of cell adhesion junction plaque proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12555–12559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu J., Nishizawa Y., Sonnenberg A., Owaribe K. Demonstration of type II hemidesmosomes in a mammary gland epithelial cell line, BMGE-H. J Biochem. 1994 Mar;115(3):469–476. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Halvorson M. J., Coligan J. E. Developmentally regulated expression of the beta 4 integrin on immature mouse thymocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):421–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Becker B., Luber K., Weitzer G., Castañon M. J., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Stewart M. Cloning and sequencing of rat plectin indicates a 466-kD polypeptide chain with a three-domain structure based on a central alpha-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):83–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Gromov D., Donovan A., Castañn M. J., Fuchs E. Expression of plectin mutant cDNA in cultured cells indicates a role of COOH-terminal domain in intermediate filament association. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):607–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Krepler R., Artlieb U., Pytela R., Aberer W. Identification of plectin in different human cell types and immunolocalization at epithelial basal cell surface membranes. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Nov;155(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90766-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Neut R., Krimpenfort P., Calafat J., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A. Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta 4 null mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):366–369. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]