Abstract
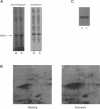
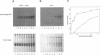
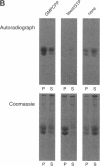
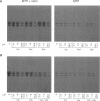
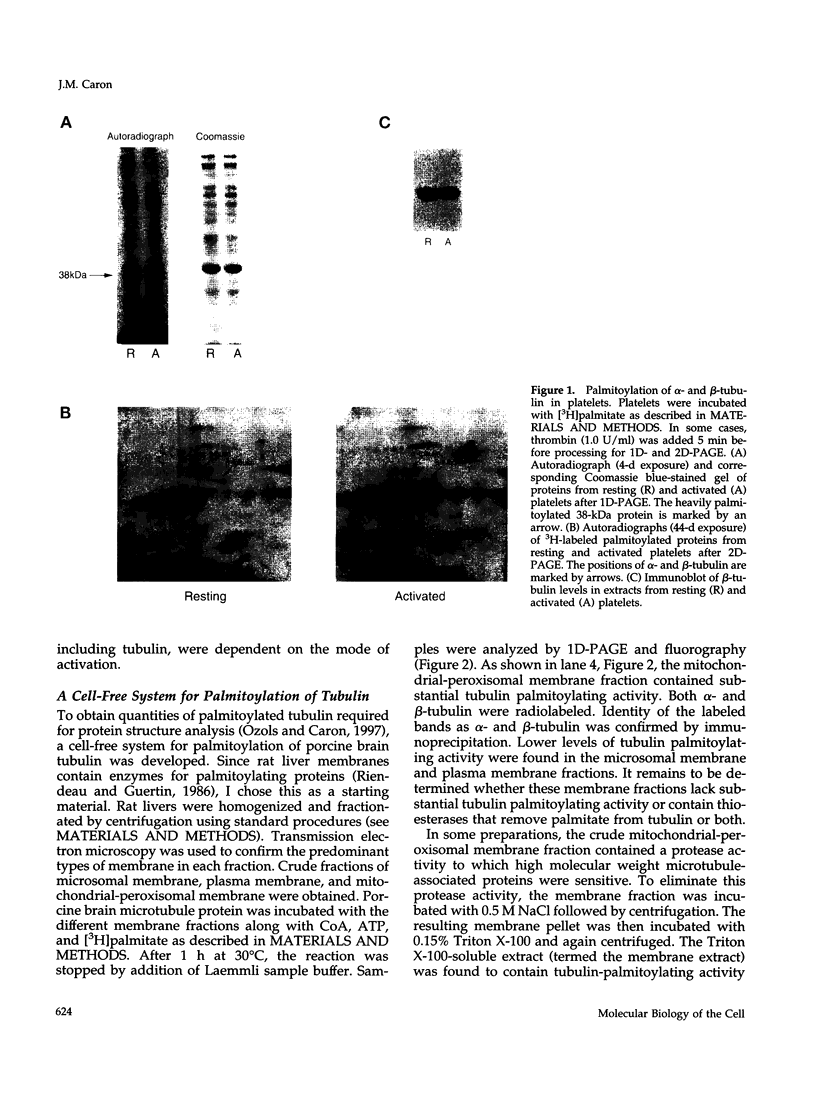
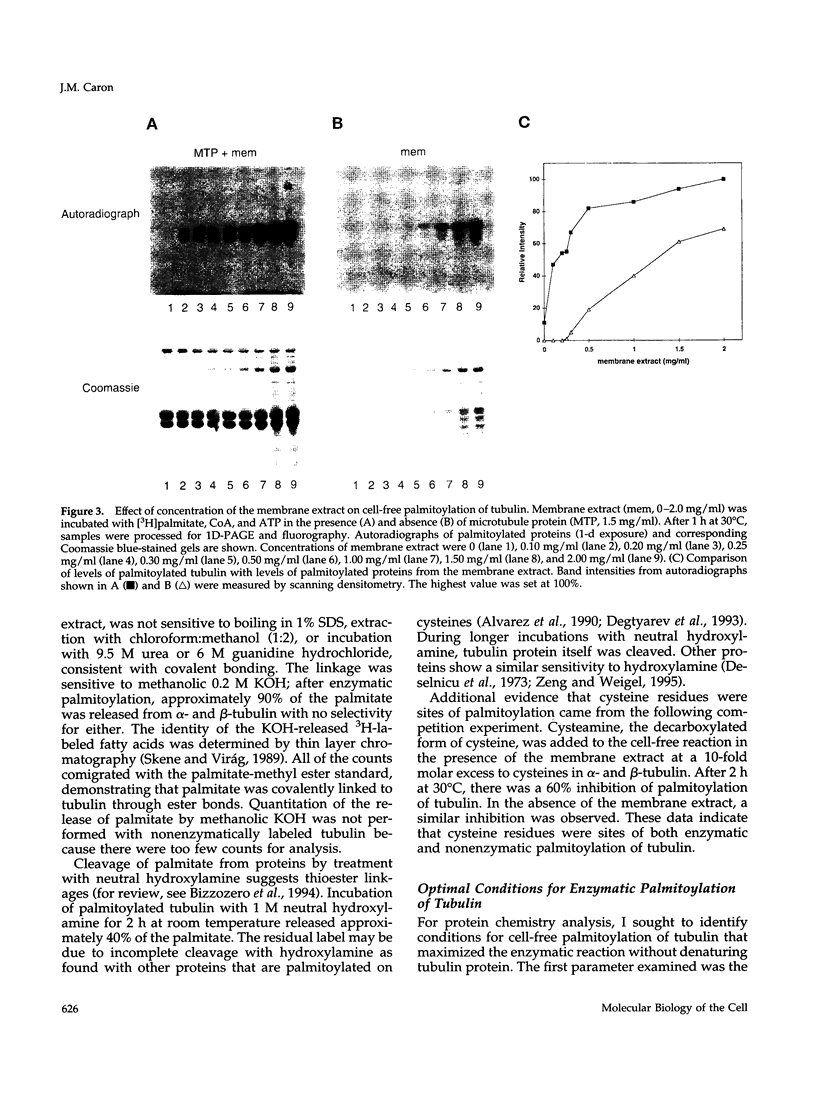
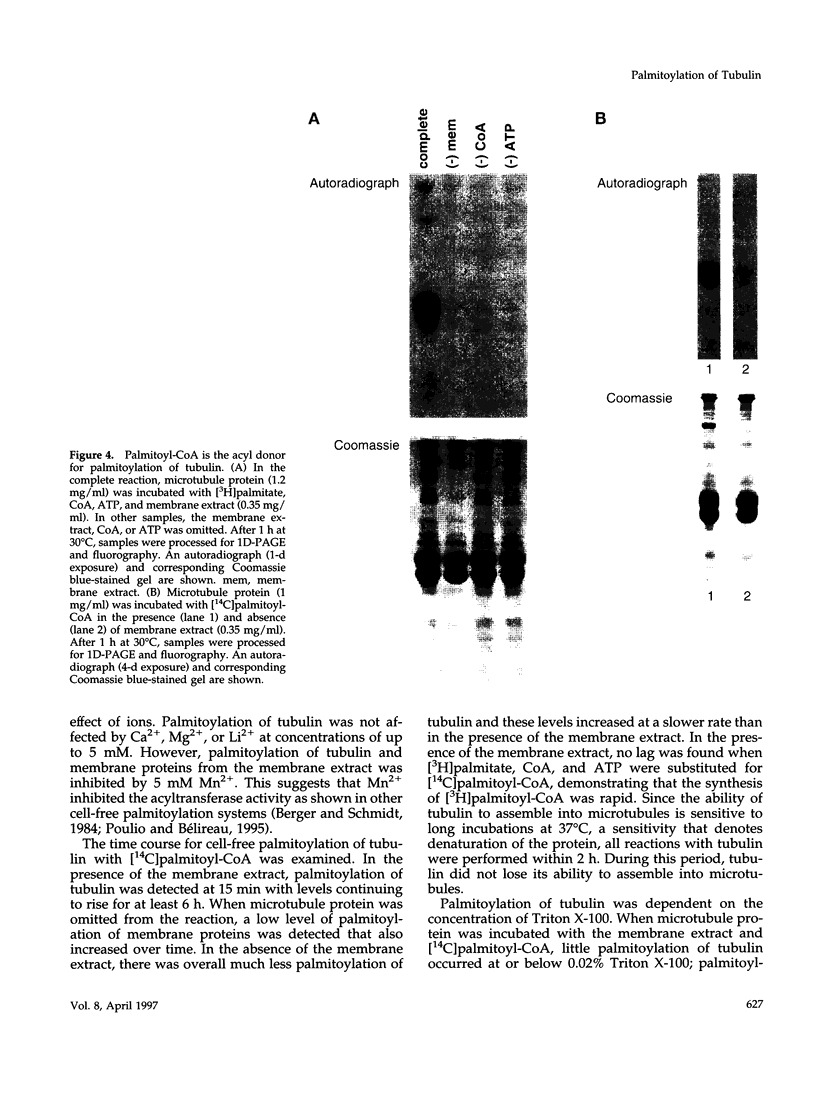
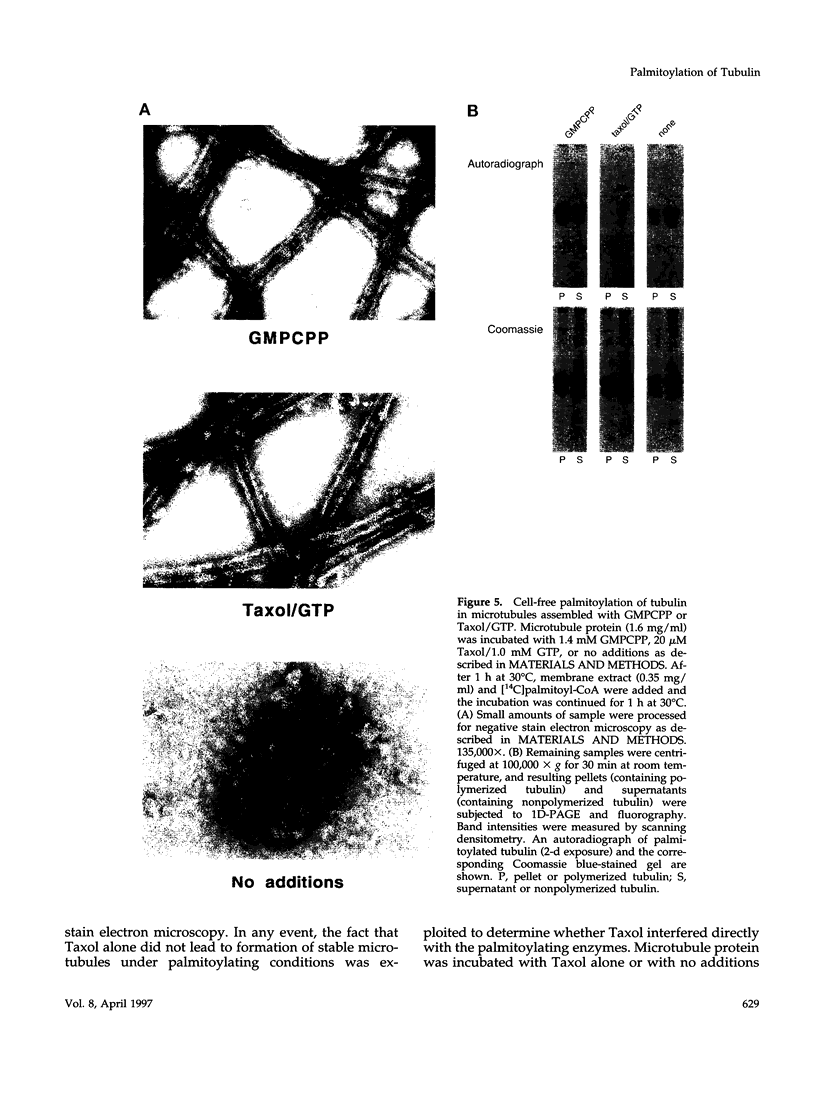
It is well established that microtubules interact with intracellular membranes of eukaryotic cells. There is also evidence that tubulin, the major subunit of microtubules, associates directly with membranes. In many cases, this association between tubulin and membranes involves hydrophobic interactions. However, neither primary sequence nor known posttranslational modifications of tubulin can account for such an interaction. The goal of this study was to determine the molecular nature of hydrophobic interactions between tubulin and membranes. Specifically, I sought to identify a posttranslational modification of tubulin that is found in membrane proteins but not in cytoplasmic proteins. One such modification is the covalent attachment of the long chain fatty acid palmitate. The possibility that tubulin is a substrate for palmitoylation was investigated. First, I found that tubulin was palmitoylated in resting platelets and that the level of palmitoylation of tubulin decreased upon activation of platelets with thrombin. Second, to obtain quantities of palmitoylated tubulin required for protein structure analysis, a cell-free system for palmitoylation of tubulin was developed and characterized. The substrates for palmitoylation were nonpolymerized tubulin and tubulin in microtubules assembled with the slowly hydrolyzable GTP analogue guanylyl-(alpha, beta)-methylene-diphosphonate. However, tubulin in Taxol-assembled microtubules was not a substrate for palmitoylation. Likewise, palmitoylation of tubulin in the cell-free system was specifically inhibited by the antimicrotubule drugs Colcemid, podophyllotoxin, nocodazole, and vinblastine. These experiments identify a previously unknown posttranslational modification of tubulin that can account for at least one type of hydrophobic interaction with intracellular membranes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. E., Hunt D. F., Lee M. K., Shabanowitz J., Michel H., Berlin S. C., MacDonald T. L., Sundberg R. J., Rebhun L. I., Frankfurter A. Characterization of posttranslational modifications in neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4685–4689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Gironès N., Davis R. J. Inhibition of the receptor-mediated endocytosis of diferric transferrin is associated with the covalent modification of the transferrin receptor with palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16644–16655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreu J. M. Interaction of tubulin with non-denaturing amphiphiles. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babitch J. A. Synaptic plasma membrane tubulin may be an integral constituent. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1394–1400. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai R., Pei X. F., Boyé O., Getahun Z., Grover S., Bekisz J., Nguyen N. Y., Brossi A., Hamel E. Identification of cysteine 354 of beta-tubulin as part of the binding site for the A ring of colchicine. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 24;271(21):12639–12645. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.21.12639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Schmidt M. F. Cell-free fatty acid acylation of Semliki Forest viral polypeptides with microsomal membranes from eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7245–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzozero O. A., McGarry J. F., Lees M. B. Acylation of endogenous myelin proteolipid protein with different acyl-CoAs. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2138–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzozero O. A., Tetzloff S. U., Bharadwaj M. Overview: protein palmitoylation in the nervous system: current views and unsolved problems. Neurochem Res. 1994 Aug;19(8):923–933. doi: 10.1007/BF00968702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T. Molecular motors in the nervous system. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt R., Léger J., Lee G. Interaction of tau with the neural plasma membrane mediated by tau's amino-terminal projection domain. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(5):1327–1340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplow M., Shanks J. Evidence that a single monolayer tubulin-GTP cap is both necessary and sufficient to stabilize microtubules. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Apr;7(4):663–675. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J. M., Berlin R. D. Interaction of microtubule proteins with phospholipid vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):665–671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J. Protein lipidation in cell signaling. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):221–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7716512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cierniewski C. S., Krzeslowska J., Pawlowska Z., Witas H., Meyer M. Palmitylation of the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex in human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12158–12164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Sullivan K. F. Molecular biology and genetics of tubulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:331–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole N. B., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Organization of organelles and membrane traffic by microtubules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;7(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Vallee R. B. Temperature-dependent reversible assembly of taxol-treated microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2847–2854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese F., Bhattacharyya B., Wolff J. Podophyllotoxin as a probe for the colchicine binding site of tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1134–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Preston S. F., Hanson R. K., Gordon M. W. On the mechanism of turnover of the carboxy-terminal tyrosine of the alpha chain of tubulin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):207–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degtyarev M. Y., Spiegel A. M., Jones T. L. The G protein alpha s subunit incorporates [3H]palmitic acid and mutation of cysteine-3 prevents this modification. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8057–8061. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derry W. B., Wilson L., Jordan M. A. Substoichiometric binding of taxol suppresses microtubule dynamics. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2203–2211. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deselnicu M., Lange P. M., Heidermann E. Versuche über die Spaltung der alpha2-Kollagenkette mit Hydroxylamin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Feb;354(2):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel D. N., Kirschner M. W. The minimum GTP cap required to stabilize microtubules. Curr Biol. 1994 Dec 1;4(12):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. A., Gilman A. G. Autoacylation of G protein alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1996 Sep 20;271(38):23594–23600. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.38.23594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy J. T., Greentree W. K., Manahan C. L., Linder M. E. G-protein palmitoyltransferase activity is enriched in plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):7154–7159. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.7154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddé B., Rossier J., Le Caer J. P., Desbruyères E., Gros F., Denoulet P. Posttranslational glutamylation of alpha-tubulin. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.1967194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Identification of actin-binding protein as the protein linking the membrane skeleton to glycoproteins on platelet plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11970–11977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Stroud E., Whatley R. E., Prescott S. M., Muszbek L., Laposata M., McEver R. P. P-selectin is acylated with palmitic acid and stearic acid at cysteine 766 through a thioester linkage. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11394–11400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Kirschner M. W. A polymer-dependent increase in phosphorylation of beta-tubulin accompanies differentiation of a mouse neuroblastoma cell line. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):764–774. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L., Magee A. I. Characterization of an acyltransferase acting on p21N-ras protein in a cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 24;1078(2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)99003-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoebeke J., Van Nijen G., De Brabander M. Interaction of oncodazole (R 17934), a new antitumoral drug, with rat brain tubulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M. Agonist-enhanced palmitoylation of platelet proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 10;1011(2-3):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. A., Chrétien D., Arnal I., Wade R. H. Structural changes accompanying GTP hydrolysis in microtubules: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue guanylyl-(alpha,beta)-methylene-diphosphonate. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. A., Salser S., Drechsel D. N., Unwin N., Mitchison T. J. Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule dynamics: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue, GMPCPP. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1155–1167. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G., Olson E. N. Fatty acylated proteins as components of intracellular signaling pathways. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2623–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Matus A. I. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Associations between microtubules and intracellular organelles. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;2(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly W. G., Passaniti A., Woods J. W., Daiss J. L., Roth T. F. Tubulin as a molecular component of coated vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1191–1199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Kumar N., Weinstein J. N., Blumenthal R., Flavin M. Interaction of tubulin with phospholipid vesicles. I. Association with vesicles at the phase transition. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5879–5885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N., Blumenthal R., Flavin M. Interaction of tubulin with phospholipid vesicles. II. Physical changes of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5886–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. Taxol-induced polymerization of purified tubulin. Mechanism of action. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10435–10441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Hernault S. W., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas alpha-tubulin is posttranslationally modified by acetylation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysine. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):473–478. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. L., Haimo L. T. Cytoplasmic dynein is a vesicle protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4793–4798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDizet M., Piperno G. Detection of acetylated alpha-tubulin by specific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:264–274. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96025-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L., Dudler T., Gelb M. H. Purification of a protein palmitoyltransferase that acts on H-Ras protein and on a C-terminal N-Ras peptide. J Biol Chem. 1996 Sep 20;271(38):23269–23276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.38.23269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Fisher D. A., Storm D. R. Analysis of the palmitoylation and membrane targeting domain of neuromodulin (GAP-43) by site-specific mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 12;32(40):10714–10719. doi: 10.1021/bi00091a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña R. F., Roach M. C. Interaction of tubulin with drugs and alkylating agents. 2. Effects of colchicine, podophyllotoxin, and vinblastine on the alkylation of tubulin. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4444–4450. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Parenti M., Magee A. I. The dynamic role of palmitoylation in signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 May;20(5):181–187. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muszbek L., Laposata M. Covalent modification of platelet proteins by palmitate. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1339–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., St Jules R. S., Reddy T. S., Bazan N. G., Zatz M. Acylation of disc membrane rhodopsin may be nonenzymatic. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5210–5215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Bierer B. E. Association of CD2 with tubulin. Evidence for a role of the cytoskeleton in T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4979–4988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Caron J. M. Posttranslational modification of tubulin by palmitoylation: II. Identification of sites of palmitoylation. Mol Biol Cell. 1997 Apr;8(4):637–645. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti M., Viganó M. A., Newman C. M., Milligan G., Magee A. I. A novel N-terminal motif for palmitoylation of G-protein alpha subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2910349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. D., Furlong M. T., Asai D. J., Harrison M. L., Geahlen R. L. Syk, activated by cross-linking the B-cell antigen receptor, localizes to the cytosol where it interacts with and phosphorylates alpha-tubulin on tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4755–4762. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Drubin D. G., Kelly R. B. Identification of three coated vesicle components as alpha- and beta-tubulin linked to a phosphorylated 50,000-dalton polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):40–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre P., Scheel J., Rickard J. E., Kreis T. E. CLIP-170 links endocytic vesicles to microtubules. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):887–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90240-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popova J. S., Johnson G. L., Rasenick M. M. Chimeric G alpha s/G alpha i2 proteins define domains on G alpha s that interact with tubulin for beta-adrenergic activation of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21748–21754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulio J. F., Béliveau R. Palmitoylation of brain capillary proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;27(11):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/1357-2725(95)00095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S., Krauss N. E., Heerding J. M., Swindell C. S., Ringel I., Orr G. A., Horwitz S. B. 3'-(p-azidobenzamido)taxol photolabels the N-terminal 31 amino acids of beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3132–3134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S., Orr G. A., Chaudhary A. G., Kingston D. G., Horwitz S. B. Characterization of the taxol binding site on the microtubule. 2-(m-Azidobenzoyl)taxol photolabels a peptide (amino acids 217-231) of beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20235–20238. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasenick M. M., Wang N. Exchange of guanine nucleotides between tubulin and GTP-binding proteins that regulate adenylate cyclase: cytoskeletal modification of neuronal signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):300–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybin D., Flavin M. Enzyme which specifically adds tyrosine to the alpha chain of tubulin. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2189–2194. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riendeau D., Guertin D. ATP- and coenzyme A-dependent fatty acid incorporation into proteins of cell-free extracts from mouse tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):976–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M. Protein modification. Palmitoylation in G-protein signaling pathways. Curr Biol. 1995 Feb 1;5(2):107–109. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross N. W., Braun P. E. Acylation in vitro of the myelin proteolipid protein and comparison with acylation in vivo: acylation of a cysteine occurs nonenzymatically. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Sep;21(1):35–44. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Bhattacharyya B., Wolff J. Local unfolding and the stepwise loss of the functional properties of tubulin. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 1;33(43):12868–12878. doi: 10.1021/bi00209a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L. Vinca site agents induce structural changes in tubulin different from and antagonistic to changes induced by colchicine site agents. Biochemistry. 1995 May 30;34(21):7010–7019. doi: 10.1021/bi00021a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol assembles tubulin in the absence of exogenous guanosine 5'-triphosphate or microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3247–3252. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Functions of microtubule-based motors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:629–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkowitz P., Ellis L., Pfenninger K. H. Membrane proteins of the nerve growth cone and their developmental regulation. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):1004–1017. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-01004.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skene J. H., Virág I. Posttranslational membrane attachment and dynamic fatty acylation of a neuronal growth cone protein, GAP-43. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):613–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoufias D. A., Scholey J. M. Cytoplasmic microtubule-based motor proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany A., Liau Y. H., Takagi A., Laszewicz W., Slomiany B. L. Characterization of mucus glycoprotein fatty acyltransferase from gastric mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13304–13308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Packman L. C., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Fatty acylation of two internal lysine residues required for the toxic activity of Escherichia coli hemolysin. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1992–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.7801126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M. Membrane-bound tubulin in human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 23;729(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Membrane tubulin. Biol Cell. 1986;57(2):95–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1986.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo Y., Valenzuela D., Beck-Sickinger A. G., Fishman M. C., Strittmatter S. M. Palmitoylation alters protein activity: blockade of G(o) stimulation by GAP-43. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2095–2102. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. C., Wilson L., Purich D. L. Taxol induces microtubule assembly at low temperature. Cell Motil. 1981;1(4):445–454. doi: 10.1002/cm.970010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uppuluri S., Knipling L., Sackett D. L., Wolff J. Localization of the colchicine-binding site of tubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11598–11602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Coppin C. M., Malik F., Kull F. J., Milligan R. A. Tubulin GTP hydrolysis influences the structure, mechanical properties, and kinesin-driven transport of microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23769–23775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkruyse L. A., Hofmann S. L. Lysosomal targeting of palmitoyl-protein thioesterase. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 28;271(26):15831–15836. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.26.15831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman-Storer C. M., Gregory J., Parsons S. F., Salmon E. D. Membrane/microtubule tip attachment complexes (TACs) allow the assembly dynamics of plus ends to push and pull membranes into tubulovesicular networks in interphase Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1161–1169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Bourne H. R. Activation and depalmitoylation of Gs alpha. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Detrich H. W., 3rd Separation of tubulin from microtubule-associated proteins on phosphocellulose. Accompanying alterations in concentrations of buffer components. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 12;18(12):2499–2503. doi: 10.1021/bi00579a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng F. Y., Weigel P. H. Hydroxylamine treatment differentially inactivates purified rat hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptors and distinguishes two receptor populations. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 8;270(36):21388–21395. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.36.21388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]