Abstract
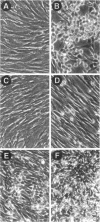
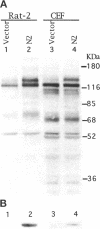
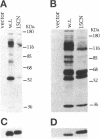
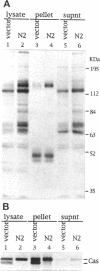
The Src homology (SH2 and SH3) domains of v-Src are required for transformation of Rat-2 cells and for wild-type (morphr) transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEFs). We report herein that the N-terminal domains of v-Src, when expressed in trans, cannot complement the transformation defect of a deletion mutant lacking the "unique," SH3, and SH2 regions. However, the same regions of Src can promote transformation when translocated to the C terminus of v-Src, although the transformation of CEFs is somewhat slower. We conclude that the SH3 and SH2 domains must be present in cis to the catalytic domain to promote transformation but that transformation is not dependent on the precise intramolecular location of these domains. In CEFSs and in Rat-2 cells, the expression of wild-type v-Src results in tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins that bind to the v-Src SH3 and SH2 domains in vitro; mutations in the SH2 or SH3 and SH2 domains prevent the phosphorylation of these proteins. These findings are most consistent with models in which the SH3 and SH2 domains of v-Src directly or indirectly target the catalytic domain to substrates involved in transformation. However, the N-terminal domains of v-Src can promote tyrosine phosphorylation of certain proteins, in particular p130Cas, even when expressed in the absence of the catalytic domain, indicating that the N-terminal domains of v-Src have effects that are independent of the catalytic domain.
Full text
PDF


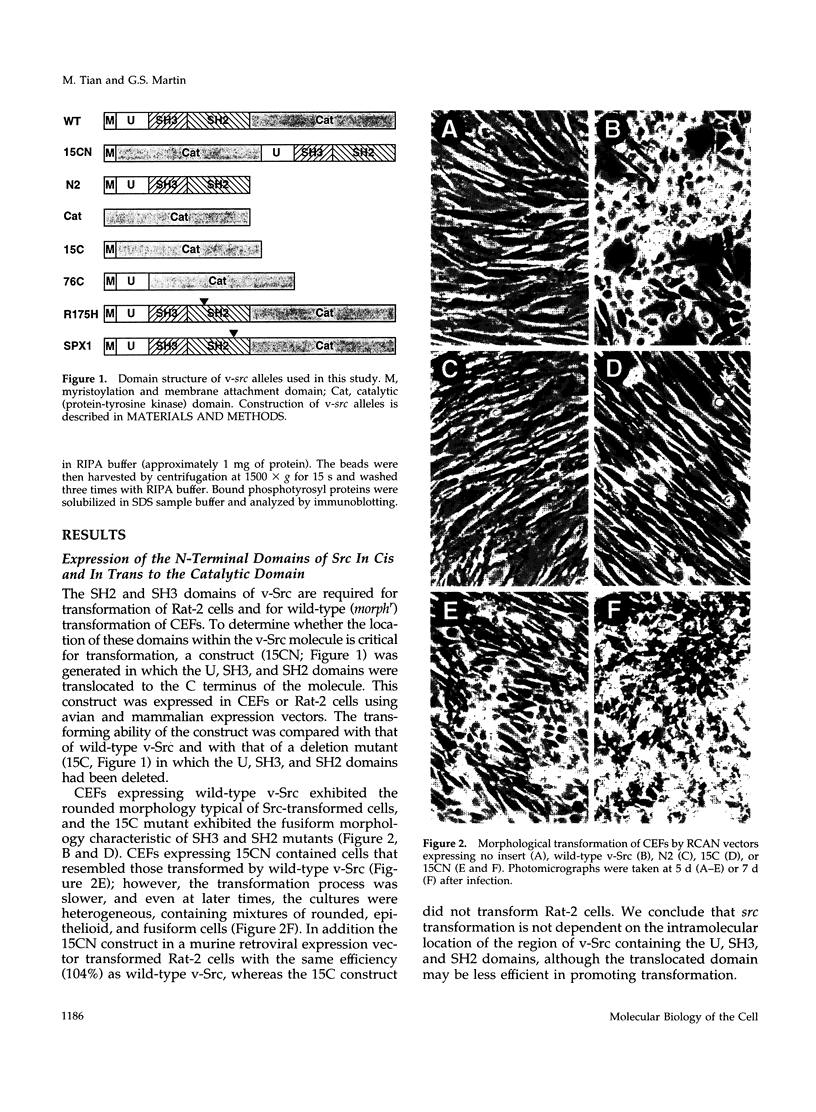





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auvinen M., Paasinen-Sohns A., Hirai H., Andersson L. C., Hölttä E. Ornithine decarboxylase- and ras-induced cell transformations: reversal by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors and role of pp130CAS. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6513–6525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cellular p130 provide high affinity binding substrates to analyze Crk-phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10588–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catling A. D., Fincham V. J., Frame M. C., Haefner B., Wyke J. A. Mutations in v-Src SH3 and catalytic domains that jointly confer temperature-sensitive transformation with minimal temperature-dependent changes in cellular tyrosine phosphorylation. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4392–4399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4392-4399.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Howell B. The when and how of Src regulation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Phosphorylation of talin at tyrosine in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):371–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPHRUSSI B., TEMIN H. M. Infection of chick iris epithelium with the Rous sarcoma virus in vitro. Virology. 1960 Jul;11:547–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide B. L., Turck C. W., Escobedo J. A. Identification of Tyr-397 as the primary site of tyrosine phosphorylation and pp60src association in the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2819–2827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erpel T., Courtneidge S. A. Src family protein tyrosine kinases and cellular signal transduction pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. C., Leu T. H., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. Identification and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding a 110-kilodalton actin filament-associated pp60src substrate. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7892–7900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli S., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., Courtneidge S. A. A target for Src in mitosis. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):871–874. doi: 10.1038/368871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Mutations in src homology regions 2 and 3 of activated chicken c-src that result in preferential transformation of mouse or chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Kosik E. Mutagenesis of the region between env and src of the SR-A strain of Rous sarcoma virus for the purpose of constructing helper-independent vectors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Vande Woude G. F., Robins T. S. Transduction of host cellular sequences by a retroviral shuttle vector. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):750–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.750-753.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Wang H. C., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. The SH2 and SH3 domains of pp60src direct stable association with tyrosine phosphorylated proteins p130 and p110. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1689–1698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. B., Bibbins K. B., Swedlow J. R., Arnaud M., Morgan D. O., Varmus H. E. Association of the amino-terminal half of c-Src with focal adhesions alters their properties and is regulated by phosphorylation of tyrosine 527. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4745–4756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. B., Swedlow J. R., Morgan D. O., Varmus H. E. c-Src enhances the spreading of src-/- fibroblasts on fibronectin by a kinase-independent mechanism. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 15;9(12):1505–1517. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.12.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Subcellular localization of pp60src in RSV-transformed cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:51–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebl E. C., England L. J., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Host range mutants of v-src: alterations in kinase activity and substrate interactions. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4315–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4315-4324.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebl E. C., England L. J., Martin G. S. Reactivation of host-dependent src kinase activity by co-expression with a heterologous tyrosine kinase. Virology. 1993 Jul;195(1):265–267. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Pawson T. Biochemistry of the Src protein-tyrosine kinase: regulation by SH2 and SH3 domains. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1994;49:149–160. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571149-4.50011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock P., Fumagalli S., Polakis P., McCormick F., Courtneidge S. A. The human p62 cDNA encodes Sam68 and not the RasGAP-associated p62 protein. Cell. 1996 Jan 12;84(1):23–24. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80989-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Baltimore D. Mutagenic analysis of the roles of SH2 and SH3 domains in regulation of the Abl tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2883–2894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hirai H., Sakai R. Evidence that SH2 domains promote processive phosphorylation by protein-tyrosine kinases. Curr Biol. 1995 Mar 1;5(3):296–305. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura H., Resh M. D. Differential binding of pp60c-src and pp60v-src to cytoskeleton is mediated by SH2 and catalytic domains. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2293–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. Circularly permuted DNA, RNA and proteins--a review. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90317-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains in signal transduction. Adv Cancer Res. 1994;64:87–110. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60835-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Membrane interactions of pp60v-src: a model for myristylated tyrosine protein kinases. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1437–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Myristylation and palmitylation of Src family members: the fats of the matter. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):411–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R., Iwamatsu A., Hirano N., Ogawa S., Tanaka T., Mano H., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. A novel signaling molecule, p130, forms stable complexes in vivo with v-Crk and v-Src in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3748–3756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M. D., Parsons J. T. Focal adhesion kinase and associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharenberg A. M., Lin S., Cuenod B., Yamamura H., Kinet J. P. Reconstitution of interactions between tyrosine kinases and the high affinity IgE receptor which are controlled by receptor clustering. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3385–3394. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07344.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Broome M. A., Hunter T. Fibronectin-stimulated signaling from a focal adhesion kinase-c-Src complex: involvement of the Grb2, p130cas, and Nck adaptor proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Mar;17(3):1702–1713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.3.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Hanks S. K., Hunter T., van der Geer P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):786–791. doi: 10.1038/372786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMIN H. M. The control of cellular morphology in embryonic cells infected with rous sarcoma virus in vitro. Virology. 1960 Feb;10:182–197. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Shalloway D. An RNA-binding protein associated with Src through its SH2 and SH3 domains in mitosis. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):867–871. doi: 10.1038/368867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Martin G. S. Reduced phosphotyrosine binding by the v-Src SH2 domain is compatible with wild-type transformation. Oncogene. 1996 Feb 15;12(4):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner C. E. Paxillin: a cytoskeletal target for tyrosine kinases. Bioessays. 1994 Jan;16(1):47–52. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Varmus H. E. Highly conserved amino acids in the SH2 and catalytic domains of v-src are altered in naturally occurring, transformation-defective alleles. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F. pp60v-src transformation of rat cells but not chicken cells strongly correlates with low-affinity phosphopeptide binding by the SH2 domain. Mol Biol Cell. 1997 May;8(5):843–854. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.5.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. M., Verderame M. F. Autophosphorylation is required for high kinase activity and efficient transformation ability of proteins encoded by host range alleles of v-src. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7267–7274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7267-7274.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]