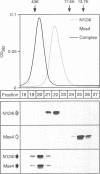
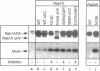
Abstract
Mss4 and its yeast homologue, Dss4, have been proposed to function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for a subset of Rab proteins in the secretory pathway. We have previously shown that Rab1A mutants defective in GTP-binding potently inhibit endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport, presumably by sequestering an unknown GEF regulating its function. We now demonstrate that these mutants stably associate with Mss4 both in vivo and in vitro and that Mss4 effectively neutralizes the inhibitory activity of the Rab1A mutants. An equivalent Rab3A mutant (Rab3A[N135I]), a Rab protein specifically involved in regulated secretion at the cell surface, associates with Mss4 as efficiently as the Rab1A[N124I] mutant. Although Rab3A[N135I] prevents the ability of Mss4 to neutralize the inhibitory effects of Rab1A mutants on transport, it has no effect on Rab1 function or endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. Furthermore, quantitative immunodepletion of Mss4 fails to inhibit transport in vitro. We conclude that Mss4 and its yeast homologue, Dss4, are not GEFs mediating activation of Rab, but rather, they interact with the transient guanine nucleotide-free state, defining a new class of Ras-superfamily GTPase effectors that function as guanine nucleotide-free chaperones (GFCs).
Full text
PDF

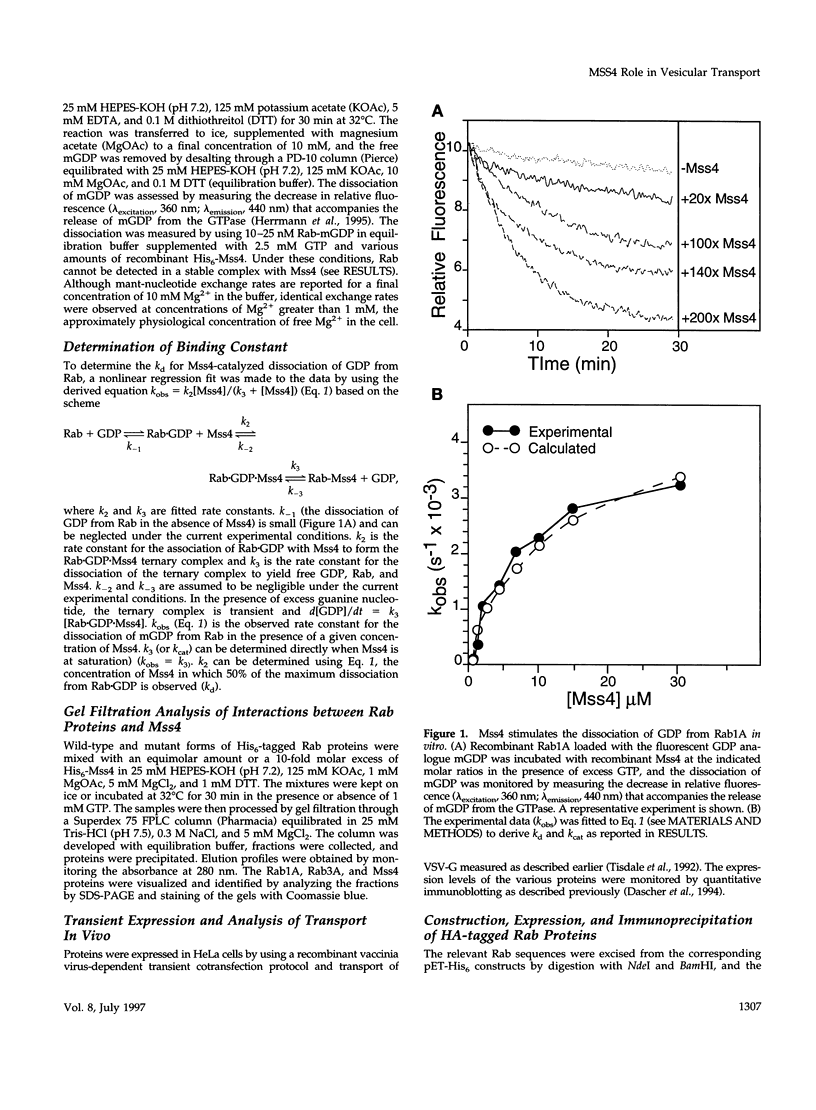

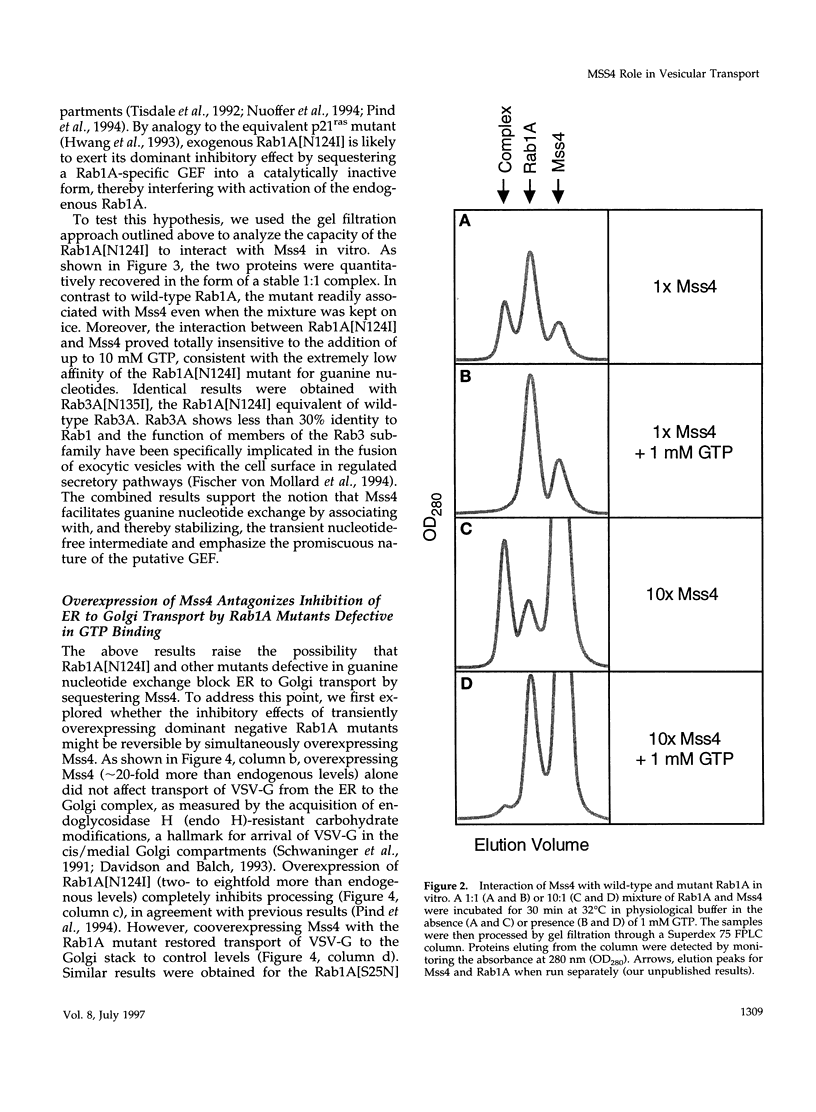




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aridor M., Balch W. E. Membrane fusion: timing is everything. Nature. 1996 Sep 19;383(6597):220–221. doi: 10.1038/383220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., Schekman R. SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):347–349. doi: 10.1038/365347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
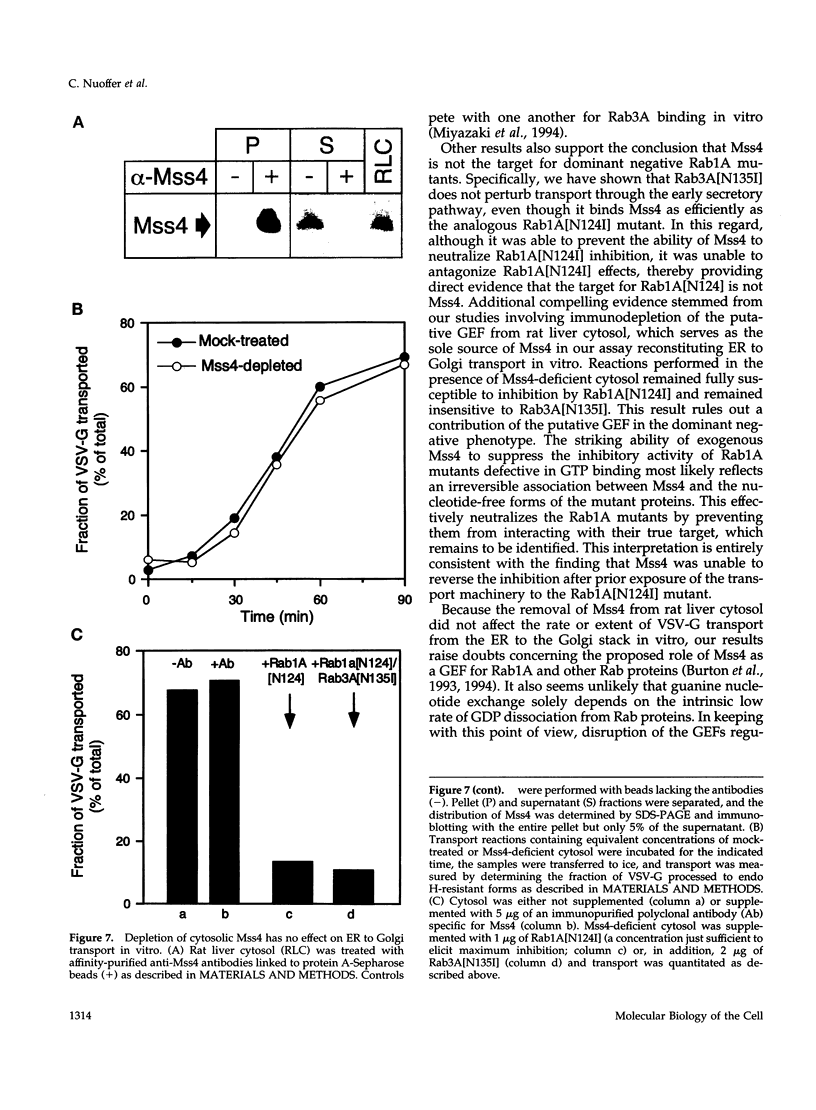
- Burton J. L., Burns M. E., Gatti E., Augustine G. J., De Camilli P. Specific interactions of Mss4 with members of the Rab GTPase subfamily. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5547–5558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton J., Roberts D., Montaldi M., Novick P., De Camilli P. A mammalian guanine-nucleotide-releasing protein enhances function of yeast secretory protein Sec4. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):464–467. doi: 10.1038/361464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascher C., Matteson J., Balch W. E. Syntaxin 5 regulates endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29363–29366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Balch W. E. Differential inhibition of multiple vesicular transport steps between the endoplasmic reticulum and trans Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4216–4226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Novick P. The role of GTP-binding proteins in transport along the exocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:575–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Stahl B., Li C., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Rab proteins in regulated exocytosis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C., Martin G. A., Wittinghofer A. Quantitative analysis of the complex between p21ras and the Ras-binding domain of the human Raf-1 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):2901–2905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.2901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Zhong J. M., Poullet P., Parmeggiani A. Inhibition of SDC25 C-domain-induced guanine-nucleotide exchange by guanine ring binding domain mutants of v-H-ras. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24692–24698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Litt R. J., Richardson C. J., Segev N. Requirement of nucleotide exchange factor for Ypt1 GTPase mediated protein transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1051–1061. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe C., Prinz H., Wittinghofer A., Goody R. S. The kinetic mechanism of Ran--nucleotide exchange catalyzed by RCC1. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 3;34(39):12543–12552. doi: 10.1021/bi00039a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki A., Sasaki T., Araki K., Ueno N., Imazumi K., Nagano F., Takahashi K., Takai Y. Comparison of kinetic properties between MSS4 and Rab3A GRF GDP/GTP exchange proteins. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya M., Roberts D., Novick P. DSS4-1 is a dominant suppressor of sec4-8 that encodes a nucleotide exchange protein that aids Sec4p function. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):460–463. doi: 10.1038/361460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomanbhoy T. K., Cerione R. Characterization of the interaction between RhoGDI and Cdc42Hs using fluorescence spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 26;271(17):10004–10009. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.17.10004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Balch W. E. GTPases: multifunctional molecular switches regulating vesicular traffic. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:949–990. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
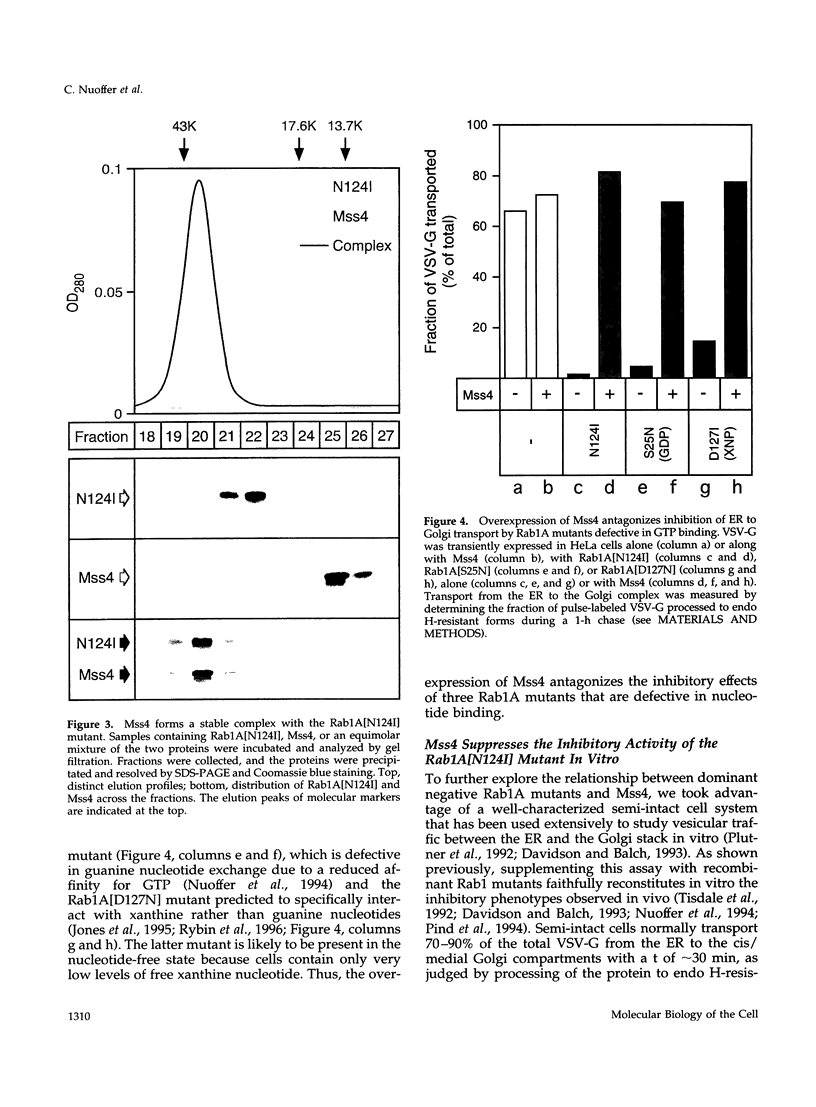
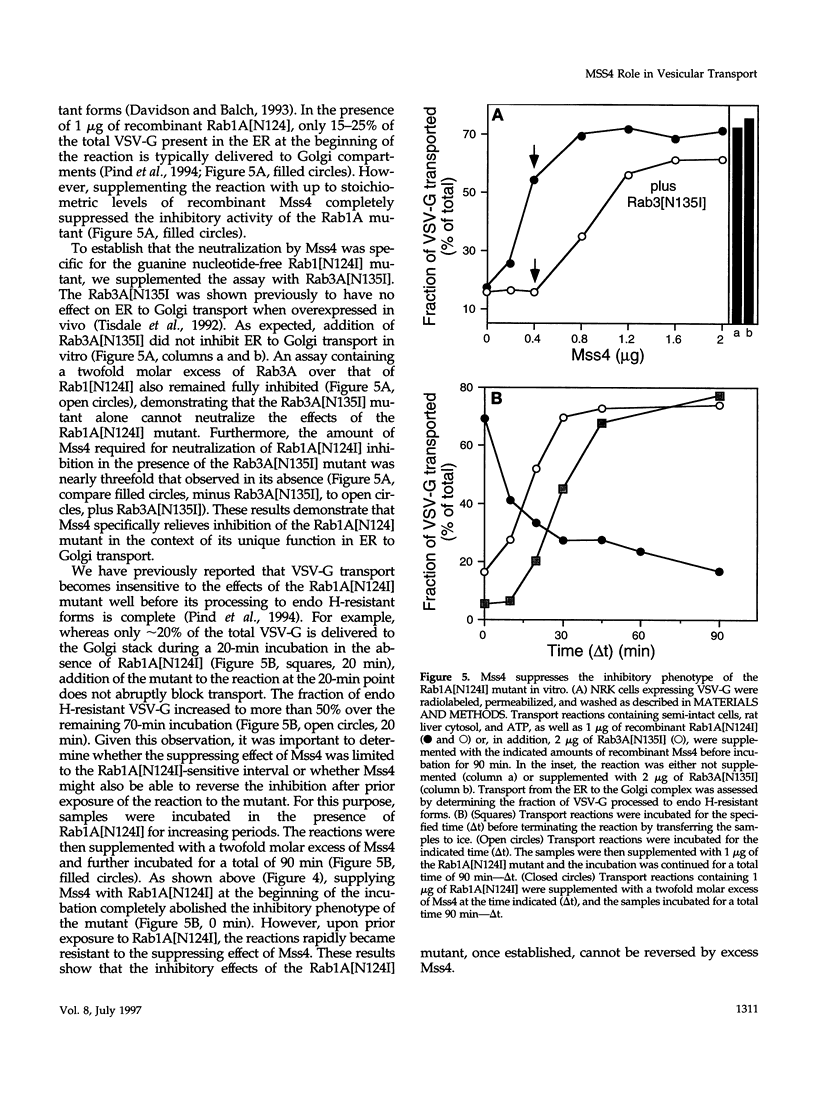
- Nuoffer C., Davidson H. W., Matteson J., Meinkoth J., Balch W. E. A GDP-bound of rab1 inhibits protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport between Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):225–237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Peter F., Balch W. E. Purification of His6-tagged Rab1 proteins using bacterial and insect cell expression systems. Methods Enzymol. 1995;257:3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(95)57003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter F., Nuoffer C., Pind S. N., Balch W. E. Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor is essential for Rab1 function in budding from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport through the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1393–1406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyroche A., Paris S., Jackson C. L. Nucleotide exchange on ARF mediated by yeast Gea1 protein. Nature. 1996 Dec 5;384(6608):479–481. doi: 10.1038/384479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Dirac-Svejstrup A. B., Soldati T. Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor: putting rab GTPases in the right place. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17057–17059. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pind S. N., Nuoffer C., McCaffery J. M., Plutner H., Davidson H. W., Farquhar M. G., Balch W. E. Rab1 and Ca2+ are required for the fusion of carrier vesicles mediating endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):239–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Cox A. D., Pind S., Khosravi-Far R., Bourne J. R., Schwaninger R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):31–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Davidson H. W., Saraste J., Balch W. E. Morphological analysis of protein transport from the ER to Golgi membranes in digitonin-permeabilized cells: role of the P58 containing compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1097–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybin V., Ullrich O., Rubino M., Alexandrov K., Simon I., Seabra M. C., Goody R., Zerial M. GTPase activity of Rab5 acts as a timer for endocytic membrane fusion. Nature. 1996 Sep 19;383(6597):266–269. doi: 10.1038/383266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalk I., Zeng K., Wu S. K., Stura E. A., Matteson J., Huang M., Tandon A., Wilson I. A., Balch W. E. Structure and mutational analysis of Rab GDP-dissociation inhibitor. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):42–48. doi: 10.1038/381042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaninger R., Beckers C. J., Balch W. E. Sequential transport of protein between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments in semi-intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13055–13063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati T., Shapiro A. D., Svejstrup A. B., Pfeffer S. R. Membrane targeting of the small GTPase Rab9 is accompanied by nucleotide exchange. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):76–78. doi: 10.1038/369076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale E. J., Bourne J. R., Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):749–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Horiuchi H., Bucci C., Zerial M. Membrane association of Rab5 mediated by GDP-dissociation inhibitor and accompanied by GDP/GTP exchange. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):157–160. doi: 10.1038/368157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Nakanishi H., Satoh A., Hirano H., Obaishi H., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. Isolation and characterization of a GDP/GTP exchange protein specific for the Rab3 subfamily small G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 14;272(7):3875–3878. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.7.3875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. K., Zeng K., Wilson I. A., Balch W. E. Structural insights into the function of the Rab GDI superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Dec;21(12):472–476. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]