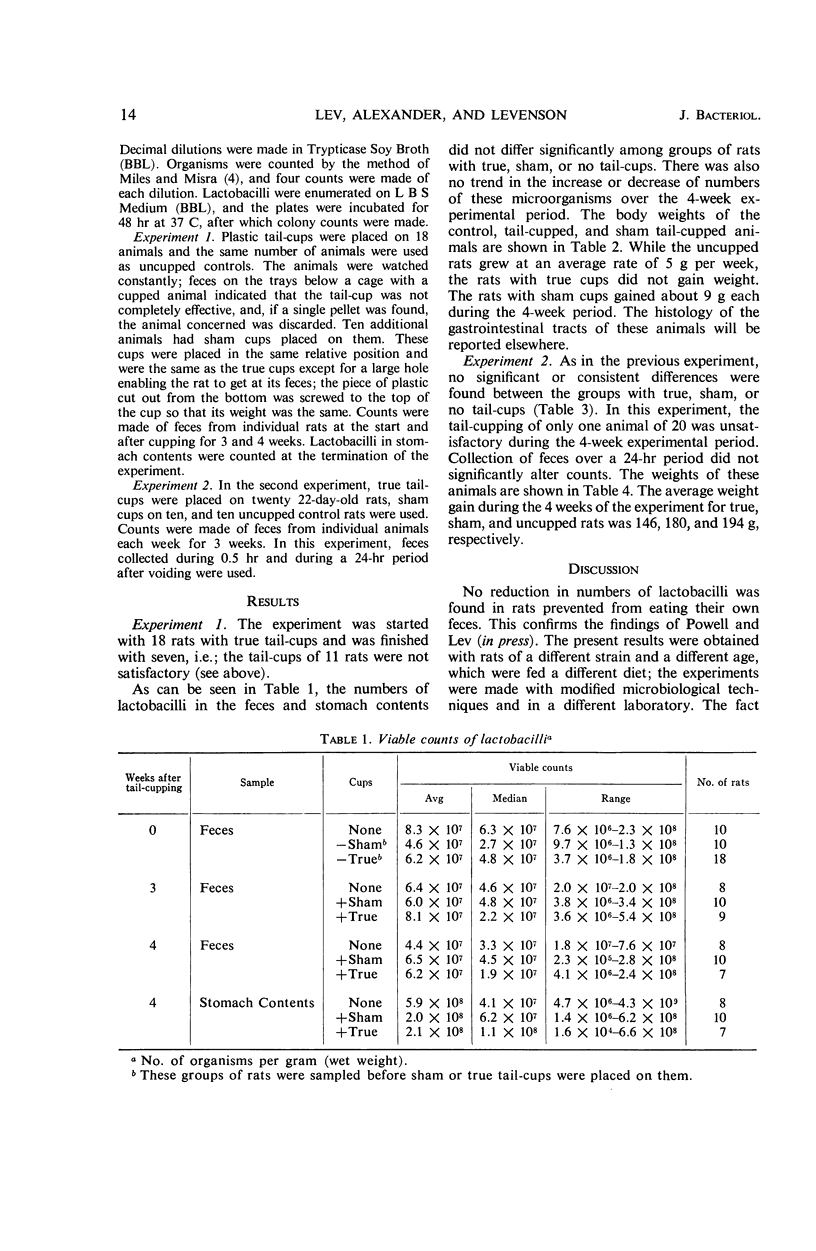
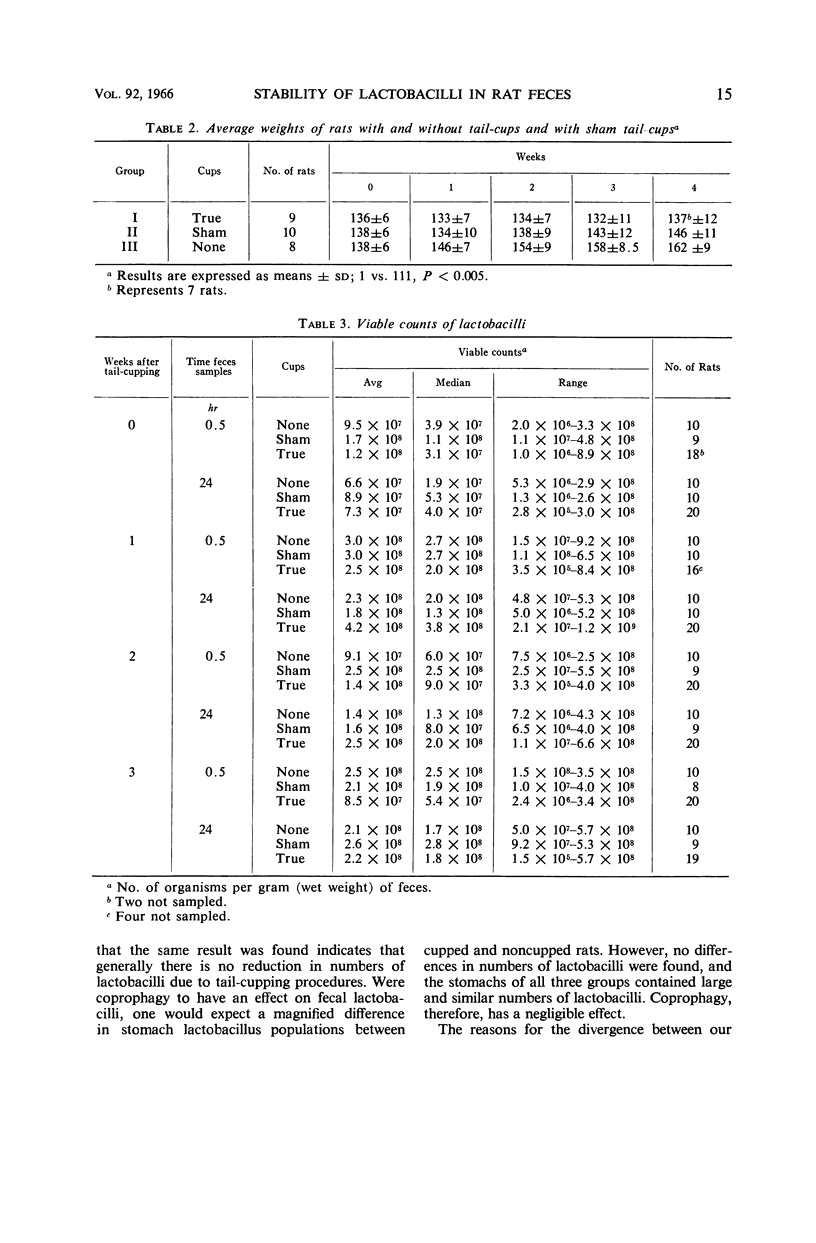
Abstract
Lev, Meir (Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, N.Y.), Raymond H. Alexander, and Stanley M. Levenson. Stability of the Lactobacillus population in feces and stomach contents of rats prevented from coprophagy. J. Bacteriol. 92: 13–16. 1966.—Lactobacilli were enumerated in the feces of rats prevented from coprophagy by tail-cupping. No differences were found when numbers of these organisms were compared with lactobacilli in feces of control rats, without tail-cups. High and similar numbers of lactobacilli were found in the stomachs of rats with and without tail-cups. The effect of coprophagy on fecal lactobacilli was therefore negligible.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES R. H., FIALA G., KWONG E. Decreased growth rate resulting from prevention of coprophagy. Fed Proc. 1963 Jan-Feb;22:125–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., FITZGERALD R. J. Alteration in intestinal microbial flora of rats with tail cups to prevent coprophagy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jun;104:319–322. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


