Abstract
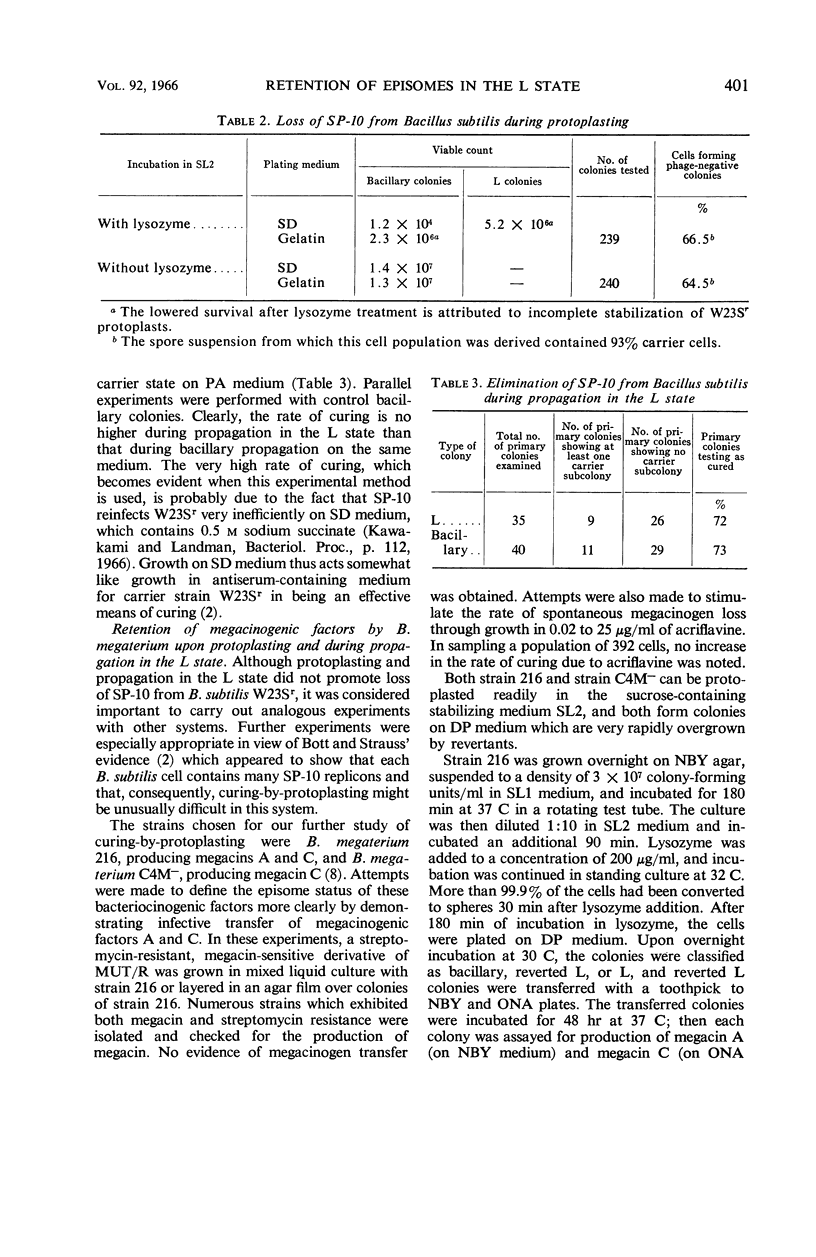
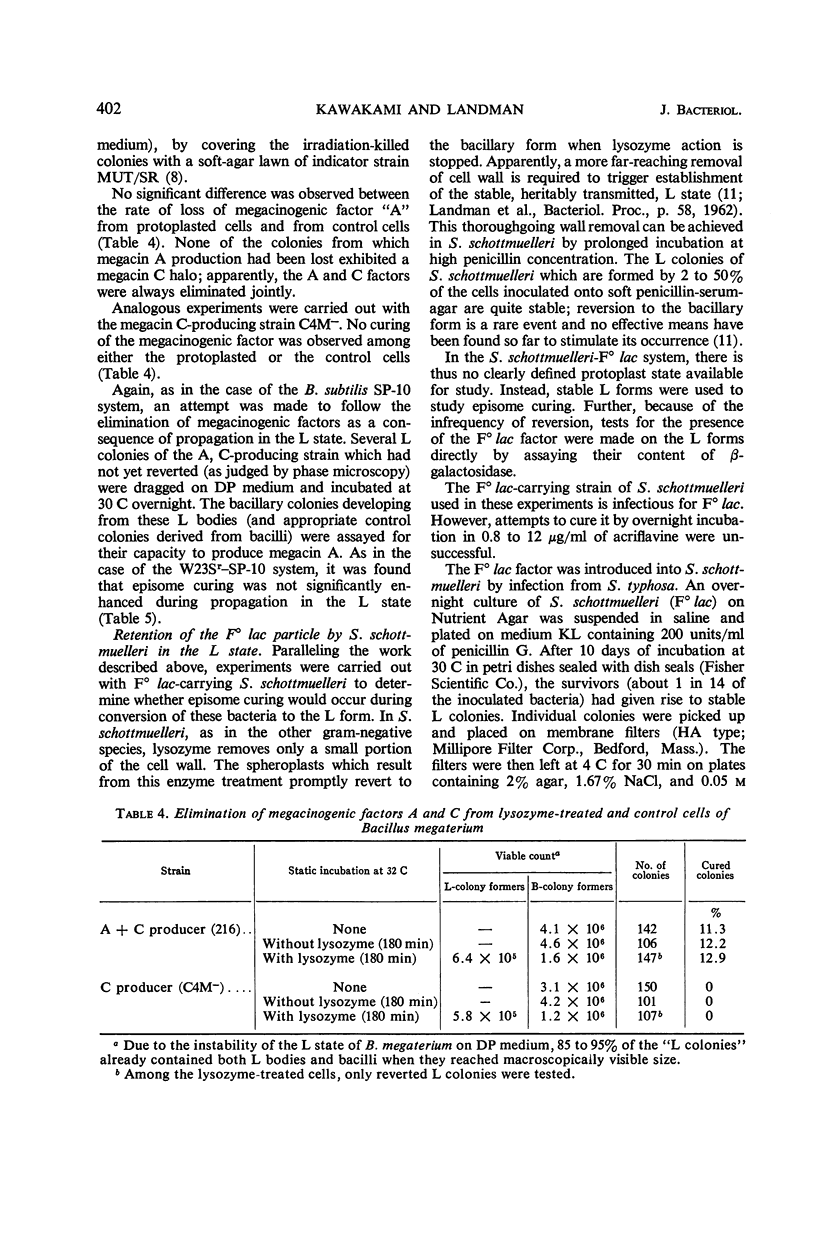
Kawakami, Masaya (Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.), and Otto E. Landman. Retention of episomes during protoplasting and during propagation in the L state. J. Bacteriol. 92:398–404. 1966.—In earlier work, it was observed that the mesosomes of Bacillus magaterium and B. subtilis are expelled from the cell interior during protoplasting and that mesosome fragments are released into the supernatant fluid as the cell wall disintegrates. Since the resultant protoplasts remain intact and capable of reproduction, the expelled contents of the mesosome “bag” are presumably external to the protoplast membrane and nonessential to survival. Accordingly, if episomes (plasmids) were localized in the extramembrane mesosome “bag,” it would be predicted that protoplasting would cure cells of their episomes. This prediction was tested in three different systems: B. subtilis W23 carrying phage SP-10, B. megaterium 216 carrying megacinogenic factors A and C, and B. megaterium C4M− carrying megacinogenic factor C. No curing due to protoplasting was observed. Even during propagation in the L form, when septation is not functioning and the distribution of deoxyribonucleic acid to daughter cells is severely disrupted, curing was not observed in any of the above systems nor in Salmonella L forms carrying F0lac. It is concluded that episomes are located at a position on the interior side of the cell membrane and that their distribution to daughter cells is coordinated with that of the chromosome.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTT K., STRAUSS B. THE CARRIER STATE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS INFECTED WITH THE TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE SP10. Virology. 1965 Feb;25:212–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., ADELBERG E. A. Bacterial conjugation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1962;16:289–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.16.100162.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin F., Jacob F. Existence chez Escherichia coli d'une unité génétique de ségrétion formée de différents réplicons. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 May 17;260(20):5411–5414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P. C., RAY D. S. ISOLATION OF THE GROWING POINT IN THE BACTERIAL CHROMOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:125–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND I. B., ROBERTS C. F. SOME PROPERTIES OF A NEW BACTERIOCIN FORMED BY BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:271–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN O. E., GINOZA H. S. Genetic nature of stable L forms of Salmonella paratyphi. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:875–886. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.875-886.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDMAN O. E., HALLE S. ENZYMICALLY AND PHYSICALLY INDUCED INHERITANCE CHANGES IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Mol Biol. 1963 Dec;7:721–738. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., JACOB F. ETUDE AU MICROSCOPE 'ELECTRONIQUE DE LA LIAISON ENTRE NOYAU ET M'ESOSOME CHEZ BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Sep;107:384–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE C. B. Transduction in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:106–111. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.106-111.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., MARTIN H. H. The rigid layer of the cell wall of Escherichia coli strain B. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:158–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


