Abstract
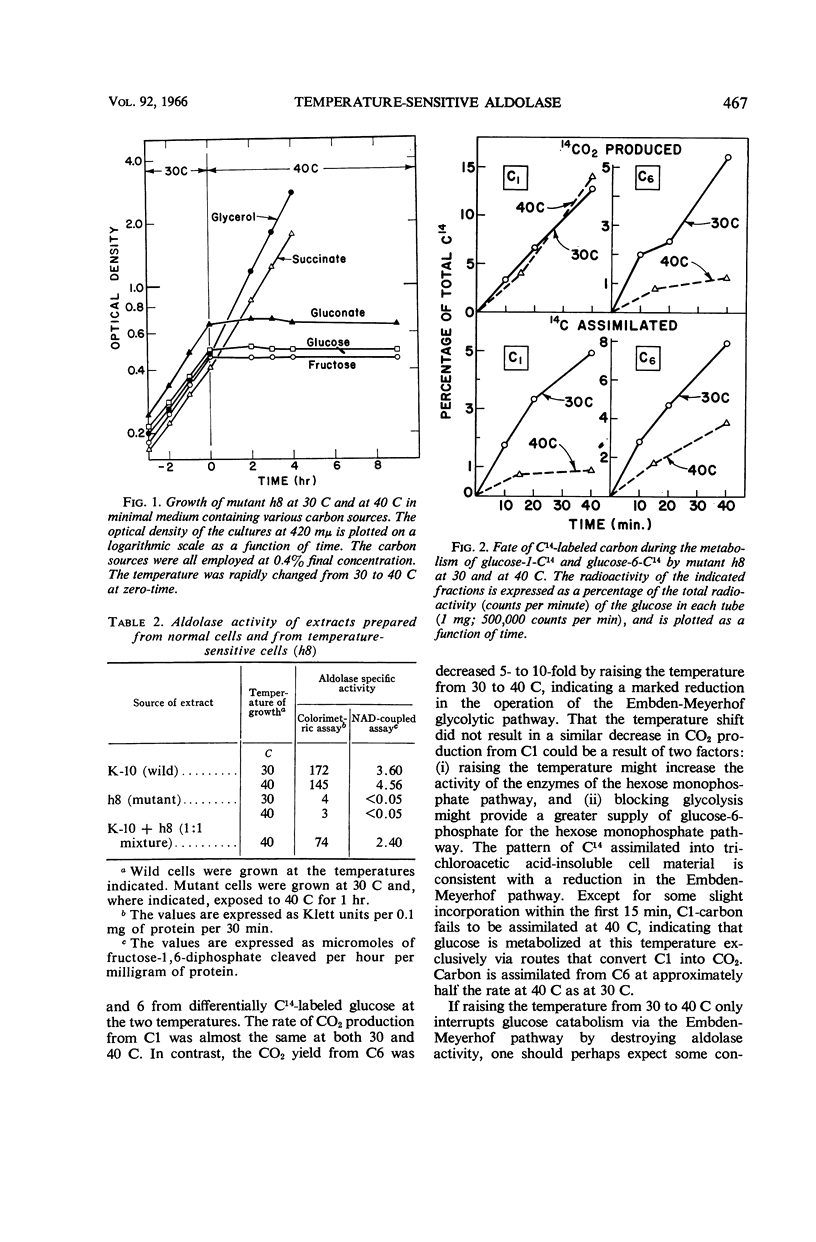
Böck, August (Purdue University, Lafayette, Ind.), and Frederick C. Neidhardt. Isolation of a mutant of Escherichia coli with a temperature-sensitive fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase activity. J. Bacteriol. 92:464–469. 1966.—A mutant of Escherichia coli was isolated which was able to grow in rich medium at 30 C but not at 40 C. Upon exposure to 40 C, the cells immediately stopped ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, but protein synthesis continued at a diminished rate for a short time. Addition of chloramphenicol did not release RNA synthesis from inhibition at 40 C. Synthesis of β-galactosidase could be induced at high temperature despite the presence of glucose in the medium, indicating a lesion in glucose catabolism. Of many catabolic enzymes tested in cell-free extracts, only fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase activity appeared to be altered in the mutant cells. No activity was demonstrable in extracts of mutant cells grown at either 30 or 40 C, but determination of glucose-oxidation patterns revealed that the enzyme is probably active in vivo at 30 C. Temperature-resistant secondary mutants were found to have partially or fully restored aldolase activity, and temperature-resistant recombinants had normal aldolase activity, indicating that the growth pattern and the altered aldolase had a common genetic basis. Linkage data permitted the assignment of an approximate map location for the mutated aldolase gene.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EIDLIC L., NEIDHARDT F. C. PROTEIN AND NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN TWO MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH TEMPERATURE-SENSITIVE AMINOACYL RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHETASES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:706–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.706-711.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Horecker B. L. Fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase and acid hexose phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):837–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.837-842.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZENBERG L. A. Studies on the induction of beta-galactosidase in a cryptic strain of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):525–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. Mutant of Aerobacter aerogenes lacking glucose repression. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:536–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.536-543.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C. The regulation RNA synthesis in bacteria. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:145–181. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60741-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L., THOMAN M. S. THE GENETIC MAP OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12. Genetics. 1964 Oct;50:659–677. doi: 10.1093/genetics/50.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. H., STERN I., GILMOUR C. M., KLUNGSOYR S., REED D. J., BIALY J. J., CHRISTENSEN B. E., CHELDELIN V. H. Comparative study of glucose catabolism by the radiorespirometric method. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.207-216.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. T., Kaney A. R., Atwood K. C. Genetic mapping off fructose-1,6-diphosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1150–1152. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1150-1152.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


