Abstract
Morton, Harry E. (University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia). Mycoplasma-latex agglutination reaction. J. Bacteriol. 92:1196–1205. 1966.—The building up of Mycoplasma cell mass through adsorption to carrier particles as a method for enhancing the agglutination reaction to identify Mycoplasma is described. Mycoplasma cells of human, avian, swine, goat, sewage, and tissue-culture origin were adsorbed to latex particles (0.81 μ) and then were agglutinated by immune sera. The adsorption was demonstrated by electron microscopy. Either the cells or their antibodies, depending on which came into contact with the latex particles first, were adsorbed. The test, completed in less than 2 hr, consisted of serially diluting immune sera with buffered saline, adding the antigen, incubating in a water bath, centrifuging, and reading the reaction under 50 × microscope magnification. The antigen in each reaction tube, representing the growth from about 1.6 ml of culture, was estimated to contain 23 μg of protein (approximately one-tenth the amount of Mycoplasma cells needed for a direct agglutination reaction). In the sera from rabbits undergoing immunization with Mycoplasma antigens, the presence of anti-Mycoplasma antibodies was detected much sooner in the Mycoplasma-latex agglutination reaction test than in the agar-gel diffusion reaction and the growth inhibition tests. Four different lots of latex particles showed excellent uniformity of behavior and stability during storage and testing.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
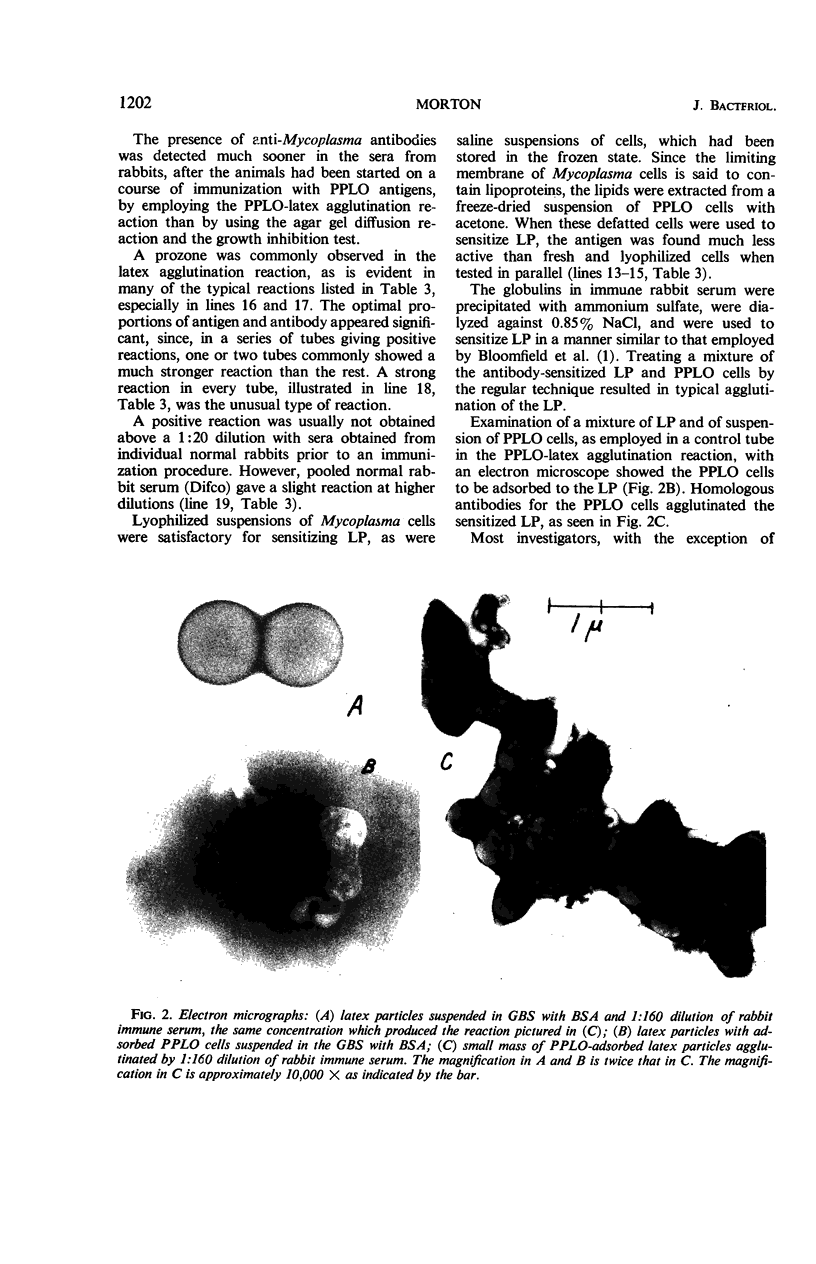
- BLOOMFIELD N., GORDON M. A., ELMENDORF D. F., Jr DETECTION OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS ANTIGEN IN BODY FLUIDS BY LATEX PARTICLE AGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:64–67. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLISLE H. N., SASLAW S. A histoplasmin-latex agglutination test. I. Results with animal sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 May;51(5):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN C. L., MENDEZ-BRYAN R., LARSON D. L. Latex agglutination test for disseminated lupus erythematosus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIVITO G., FRE B., ANDRI L. LA SIEROAGGLUTINAZIONE CON LATEX-ISTAMINANELLA DIAGNOSI DI ALLERGOPATIA. G Clin Med. 1963 Oct;44:1028–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON P., PENNINGTON K. AGGLUTINATION OF LATEX PARTICLES WITHOUT ANTIGEN ADSORPTION. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWDLE W. R., ROBINSON R. Q. AN INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION TEST FOR DIAGNOSIS OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE INFECTIONS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:947–950. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHMAN A. Flocculation tests in hydatid disease. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Jan;13:72–75. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHMAN A. REACTIVITY OF LATEX AND COMPLEMENT FIXATION TESTS IN HYDATID DISEASE. J Parasitol. 1965 Aug;51:497–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK L., EVENCHIK Z. Latex agglutination test with Brucella antigen and antiserum. Nature. 1962 May 12;194:548–550. doi: 10.1038/194548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLORMAN A. L., SCOMA J. L. A latex agglutination test for anaerobic diphtheroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Aug-Sep;104:683–685. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL G. B., CAMPBELL C. C. Commercially available histoplasmin sensitized latex particles in an agglutination test for histoplasmosis. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1962 Nov 10;18:160–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02051586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURIEZ C., DESMONS F., AGACHE P., MARTIN P., BAELDEN J., DUQUESNE J. P. UTILITE EN DERMATO-ALLERGOLOGIE DU TEST AU LATEX-HISTAMINE (1.004 TESTS) ET DE LA MESURE DU POUVOIR HISTAMINOPEXIQUE DU SERUM (3.088 DETERMINATIONS) Arch Belg Dermatol Syphiligr. 1964 Sep;20:65–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INNELLA F., REDNER W. J. Latex-agglutination serologic test for trichinosis. Preliminary report. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Oct 17;171:885–887. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.73010250001006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEELE D. K., WEBSTER J. Latex agglutination by the reaction of human growth hormone with its antiserum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jan;106:168–170. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. E., SMITH P. F., LEBERMAN P. R. Investigation of the cultivation of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from man. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1951 Jul;35(4):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURASCHI T. F., BLOOMFIELD N., NEWMAN R. B. A slide latex-particle agglutination test for trichinosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1962 Feb;37:227–231. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/37.2_ts.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURASCHI T. F. Latex-leptospiral agglutination test. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Oct;99(1):235–238. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magwood S. E., Annau E. The Adsorption of Somatic Antigens of Salmonella by Polystyrene Latex Particles. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1961 Mar;25(3):69–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORESKES I., SINGER J. M. The mechanism of particulate carrier reactions. I. Adsorption of human gamma-globulin to polystyrene latex particles. J Immunol. 1961 Mar;86:338–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILP J. R., WEIR D. M., STUART A. E., IRVINE W. J. A latex particle precipitation test in the diagnosis of thyroid disease. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Mar;15:148–152. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. L., HILL G. A., CARLE B. N., CARLQUIST J. H., MARCUS S. Latex agglutination reactions between human chorionic gonadotropin and rabbit antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Feb;109:321–325. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASLAW S., CARLISLE H. N. Histoplasmin-latex agglutination test. II. Results with human sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Mar;97(3):700–703. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER J. M., PLOTZ C. M., PADER E., ELSTER S. K. The latex-fixation test. III. Agglutination test for C-reactive protein and comparison with the capillary precipitin method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Dec;28(6):611–617. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.6.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., MORTON H. E. The separation and characterization of the growth factor in serum and ascitic fluid which is required by certain pleuropneumonia-like organisms. J Bacteriol. 1951 Apr;61(4):395–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.4.395-405.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYFRES B., KAGAN I. G. A modified slide latex screening test for hydatid disease. J Parasitol. 1963 Feb;49:69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., CHANOCK R. M. CHARACTERIZATION OF A NEWLY IDENTIFIED MYCOPLASMA FROM THE HUMAN OROPHARYNX. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:180–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., LUDWIG W. M., PURCELL R. H., MUFSON M. A., CHANOCK R. M. SIGNIFICANCE OF ANTIBODY TO MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS TYPE 1 AS MEASURED BY INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1073–1083. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]