Abstract
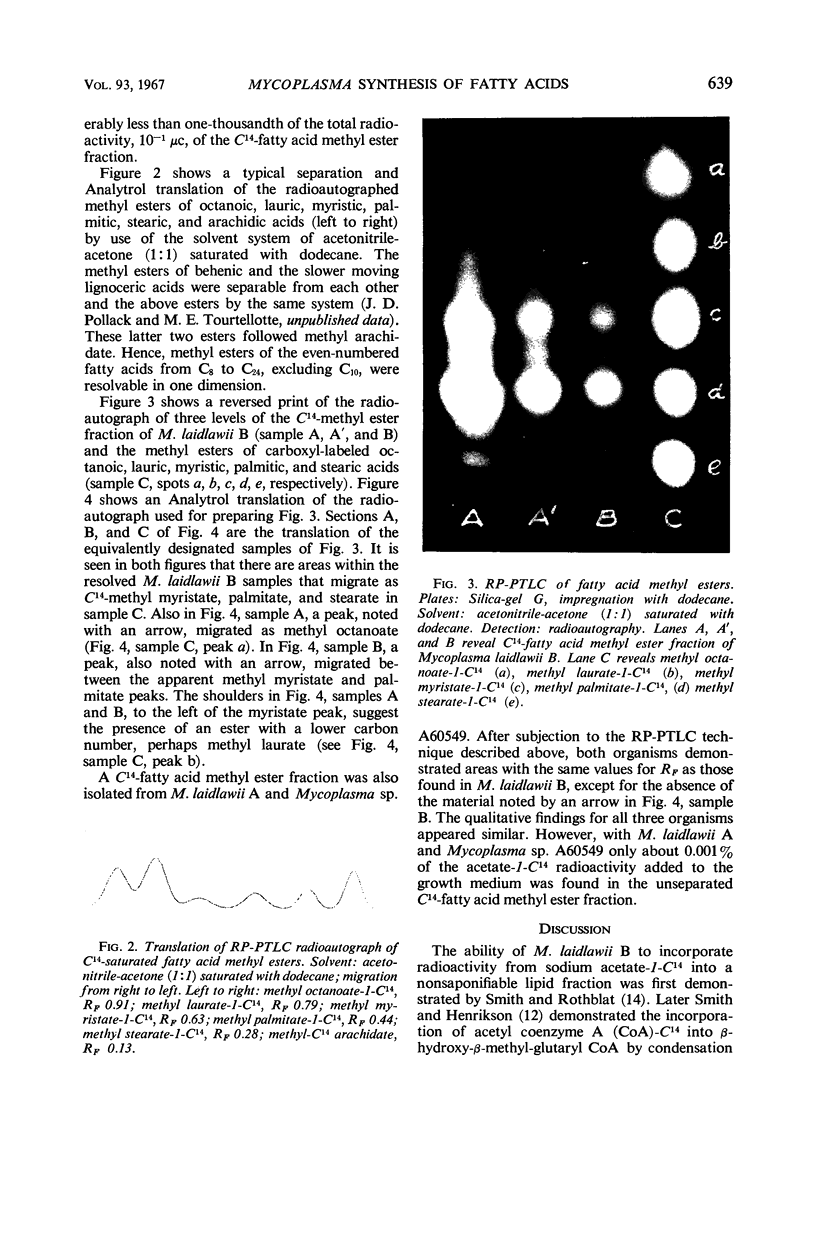
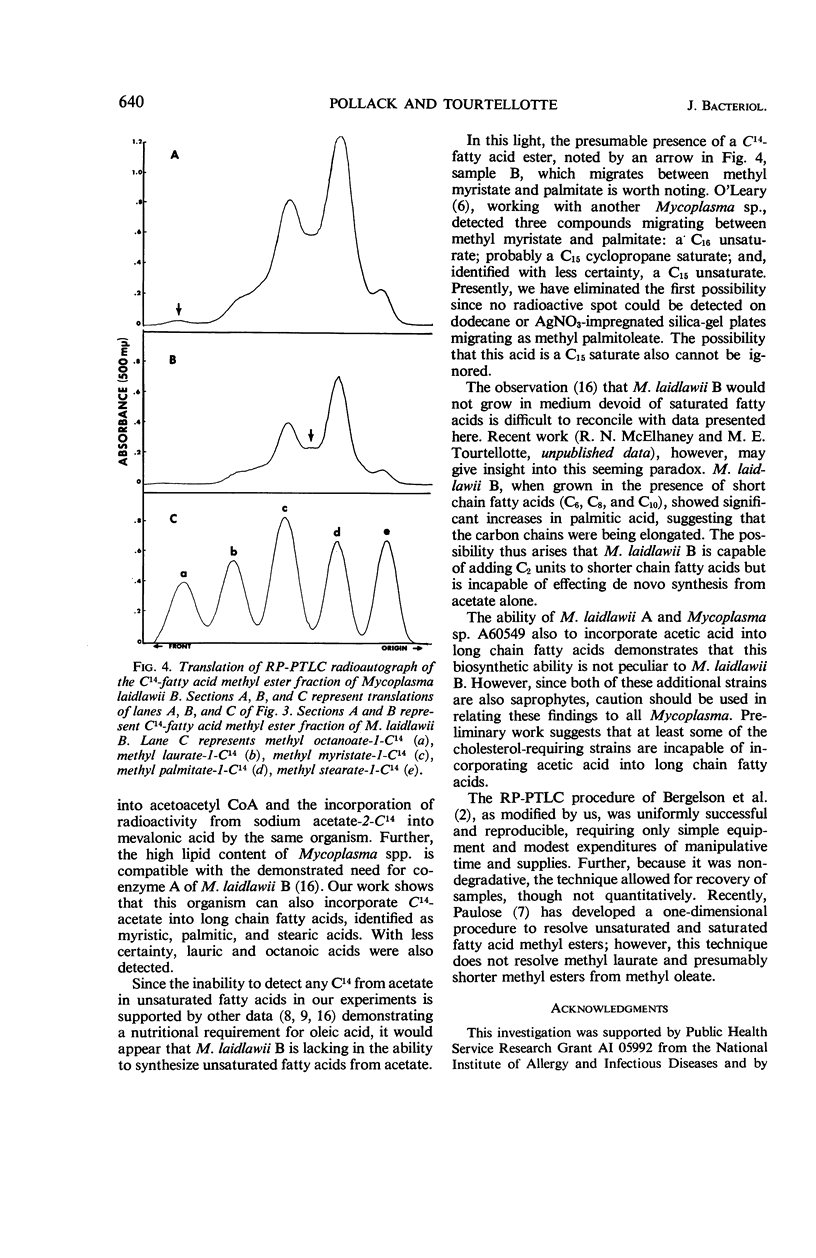
Three strains of Mycoplasma, M. laidlawii A and B, and Mycoplasma sp. A60549, were grown in broth containing sodium acetate-1-C14. The methyl esters of the phospholipid fatty acids of harvested radioactive cells were prepared and identified by comparison of their mobilities to known radioactive fatty acid methyl esters by use of a modified reversed-phase partition-thin layer chromatographic technique. No radioactive methyl oleate or methyl linoleate was detected. Compounds migrating as radioactive methyl myristate, stearate, palmitate, and, with less certainty, laurate and octanoate were detected. The qualitative findings for all three organisms appeared similar. M. laidlawii B synthesized a radioactive substance, presumably a saturated fatty acid detected as the methyl ester derivative, which migrated in a position intermediate to methyl myristate-1-C14 and methyl palmitate-1-C14. This work indicates that M. laidlawii A and B and Mycoplasma sp. A60549 are capable, in a complex medium containing fatty acids, of synthesizing saturated but not unsaturated fatty acids entirely or in part from acetate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGELSON L. D., DYATLOVITSKAYA E. V., VORONKOVA V. V. COMPLETE STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF FATTY ACID MIXTURES BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Chromatogr. 1964 Jul;15:191–199. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82767-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulose M. M. The thin-layer chromatographic separation of fatty acid methyl esters according to both chain length and unsaturation. J Chromatogr. 1966 Jan;21(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ROTTEM S. FATTY ACID REQUIREMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:459–470. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W., ABBOT A. The function of glycerol, cholesterol and long-chain fatty acids in the nutrition of Mycoplasma mycoides. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:201–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W. Nutrition and metabolism of Mycoplasma mycoides var. mycoides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:499–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Tourtellotte M. E., McElhaney R. N., Pollack J. D. Influence of lipid components of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes on osmotic fragility of cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.609-616.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., HENRIKSON C. V. COMPARATIVE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MEVALONIC ACID BY MYCOPLASMA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:146–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.146-153.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., ROTHBLAT G. H. Comparison of lipid composition of pleuropneumonia-like and L-type organisms. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:500–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.500-506.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Koostra W. L., Henrikson C. V. Diphosphatidyl Glycerol in Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):282–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.282-283.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOURTELLOTTE M. E., JENSEN R. G., GANDER G. W., MOROWITZ H. J. LIPID COMPOSITION AND SYNTHESIS IN THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:370–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.370-379.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOURTELLOTTE M. E., MOROWITZ H. J., KASIMER P. DEFINED MEDIUM FOR MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:11–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.11-15.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]