Abstract
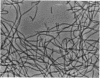
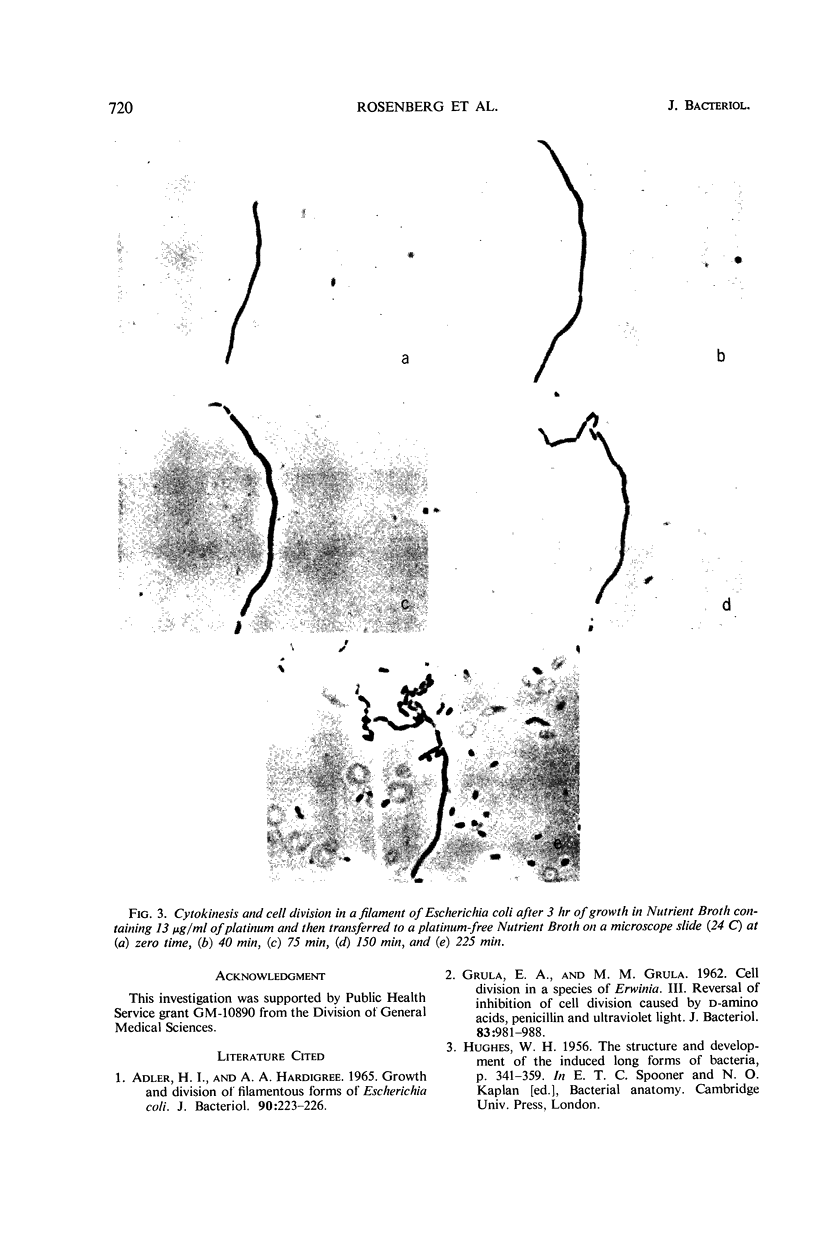
Certain group VIIIB transition metal compounds were found to inhibit cell division in Escherichia coli, causing marked filamentous growth. Gram-negative bacilli were the most sensitive to this effect, whereas gram-positive bacilli responded only at near-toxic levels of the metal. None of the cocci tested showed any apparent effect. Cytokinesis (cross-septation) can be initiated by removal or decrease of platinum, but not by treatment with pantoyl lactone, divalent cations, or a temperature of 42 C.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Hardigree A. A. Growth and Division of Filamentous Forms of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):223–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.223-226.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A., GRULA M. M. Cell division in a species of Erwinia III. Reversal of inhibition of cell division caused by D-amino acids, penicillin, and ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:981–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.981-988.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG B., VANCAMP L., KRIGAS T. INHIBITION OF CELL DIVISION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI BY ELECTROLYSIS PRODUCTS FROM A PLATINUM ELECTRODE. Nature. 1965 Feb 13;205:698–699. doi: 10.1038/205698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B., Blow D. M. A means of promoting heavy-atom binding in protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):640–644. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]