Abstract
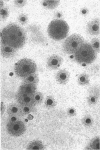
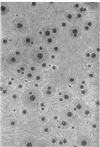
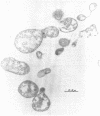
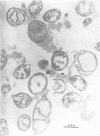
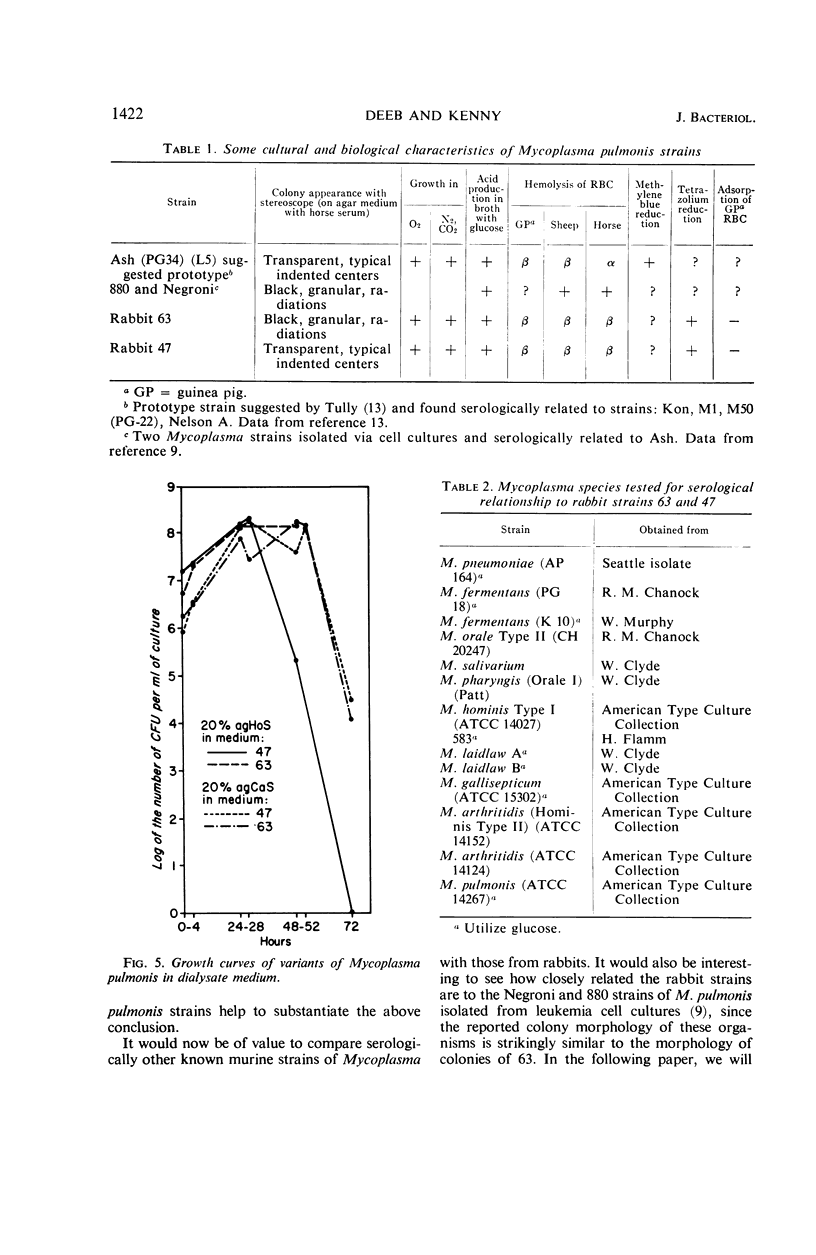
Mycoplasma showing at least two colony types were isolated from the nares and oropharynx of New Zealand white rabbits. Two strains were purified by single-colony passages and characterized. Morphology by phase-contrast and electron microscopy was typical of Mycoplasmataceae. Both grew anaerobically as well as aerobically, caused hemolysis of guinea pig, sheep, and horse red blood cells, and fermented glucose. These characteristics are shared by members of the species M. pulmonis, commonly isolated from the respiratory tracts of laboratory rats and mice. By use of the growth-inhibition test and agar-gel double-diffusion tests, the two strains were found to be serologically related to each other and to M. pulmonis ATCC 14267 but not to other representative Mycoplasma species from man and animals.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. R., Manaker R. A. Electron microscopic studies of Mycoplasma (PPLO strain 880) in artificial medium and in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Jan;36(1):139–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
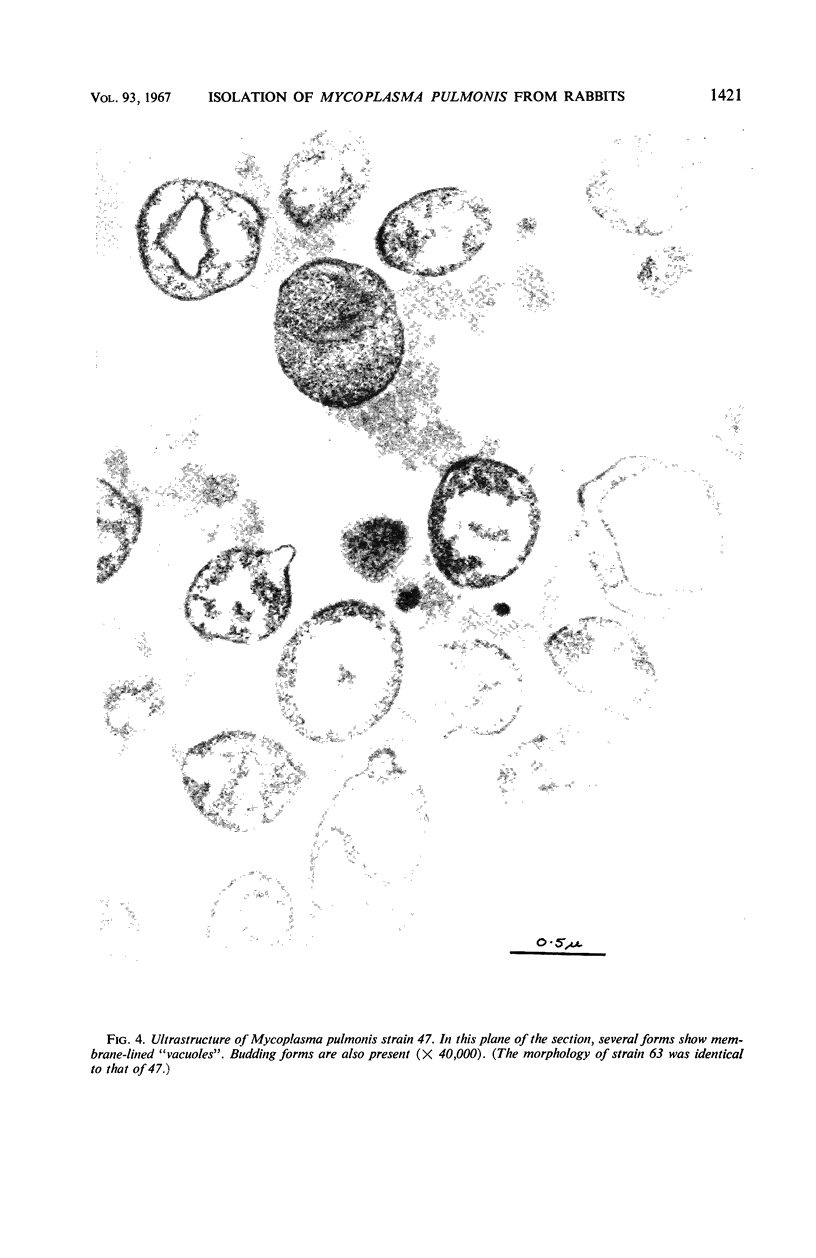
- DOMERMUTH C. H., NIELSEN M. H., FREUNDT E. A., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF MYCOPLASMA SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:727–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.727-744.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDT E. A. Morphology and classification of the PPLO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:312–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. Electron microscopic study of the phagocytosis process in lung. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Apr;7:357–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. A SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF VARIOUS SPECIES OF MYCOPLASMA BY AN AGAR GEL DOUBLE-DIFFUSION TECHNIQUE. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:91–100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. H., Butler M. Compraison of mycoplasmas associated with human tumors, leukemia, and tissue cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):934–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.934-941.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G. BIOCHEMICAL, MORPHOLOGICAL, AND SEROLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MYCOPLASMA OF MURINE ORIGIN. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:171–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]