Abstract
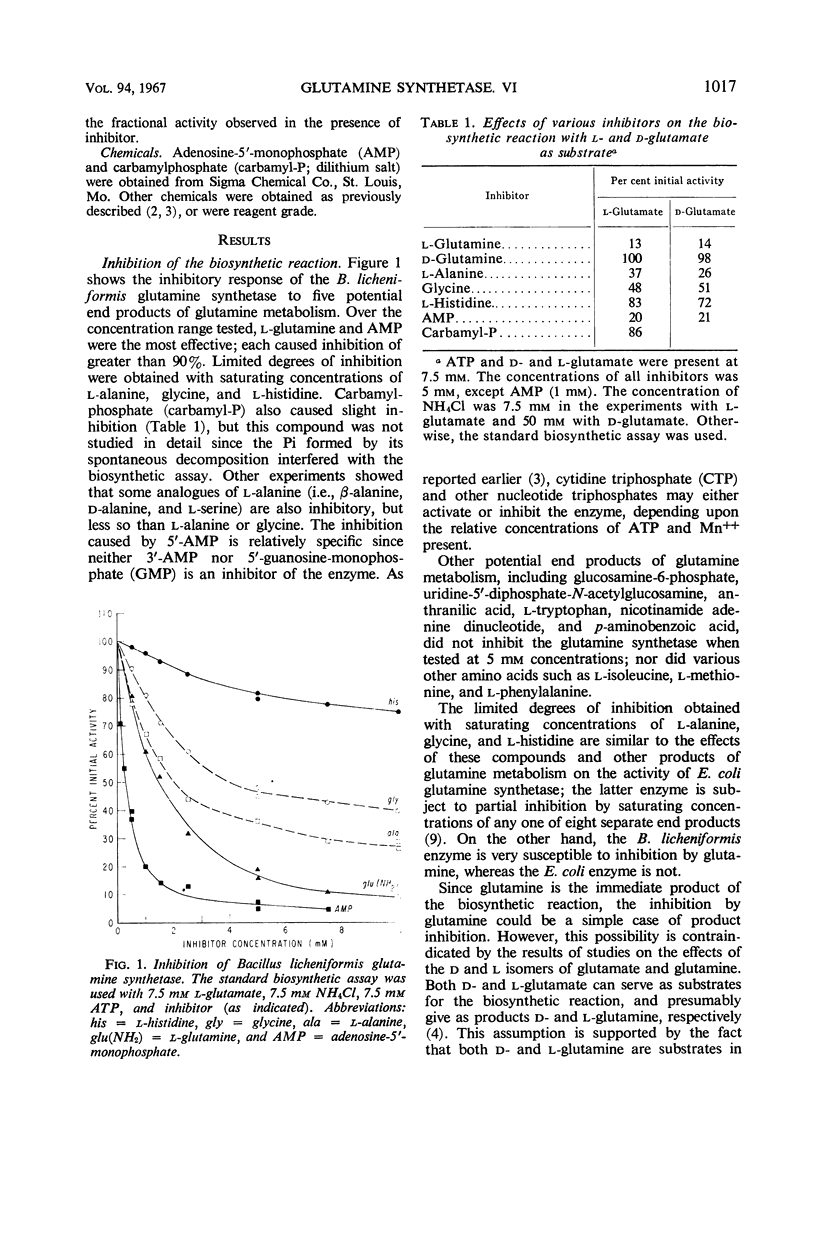
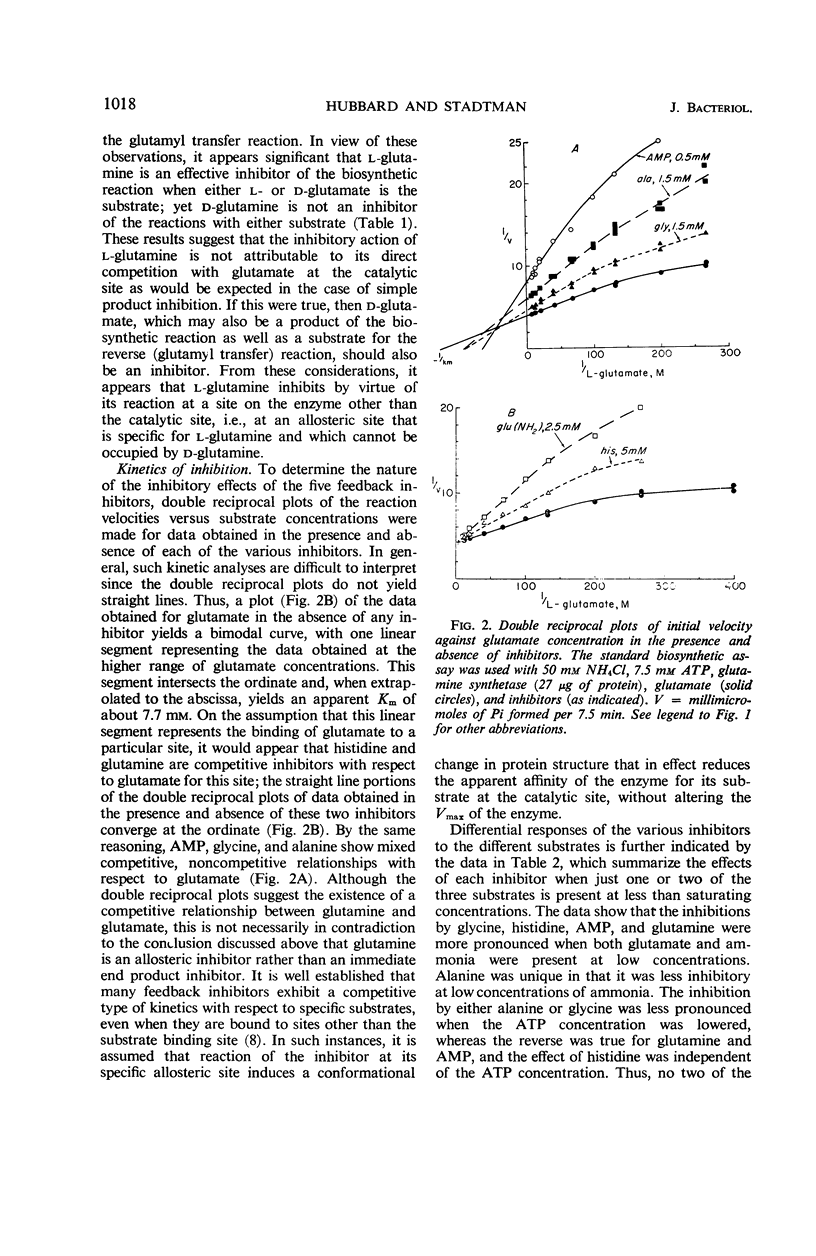
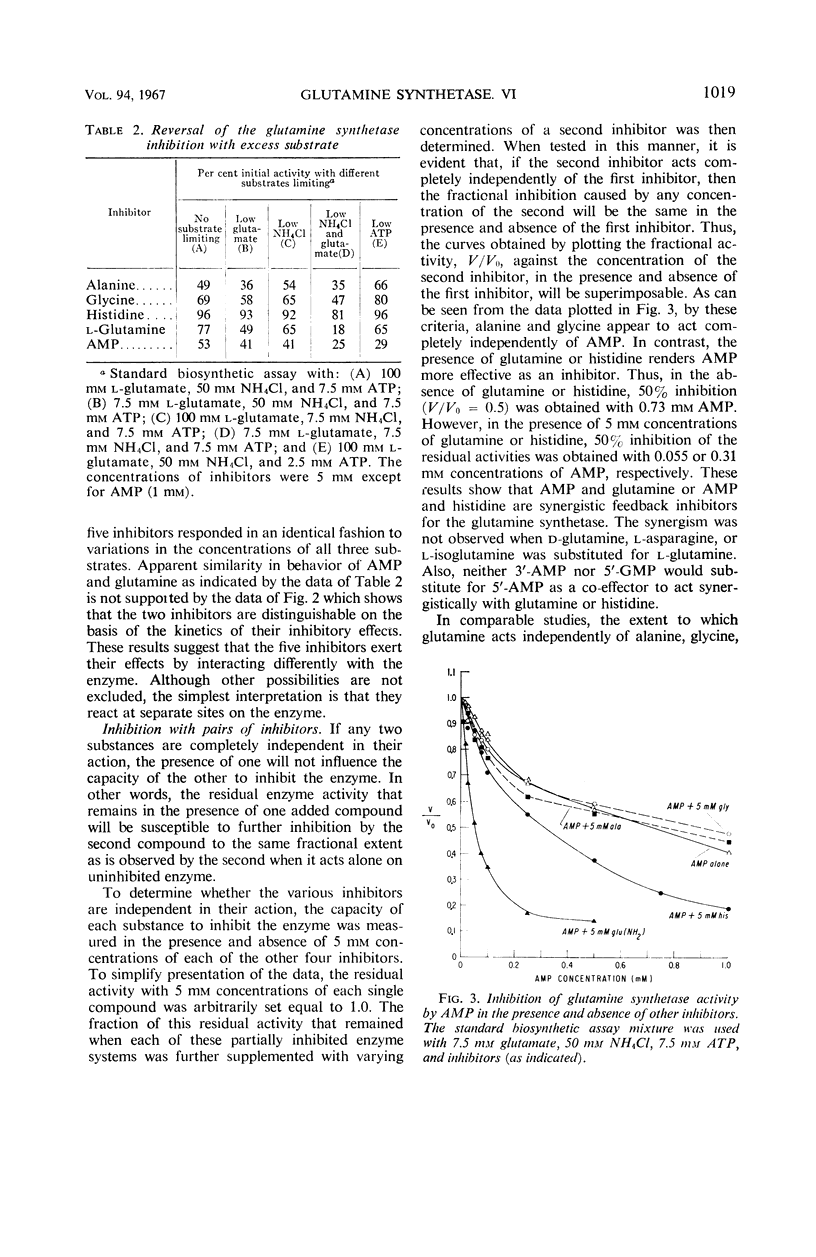
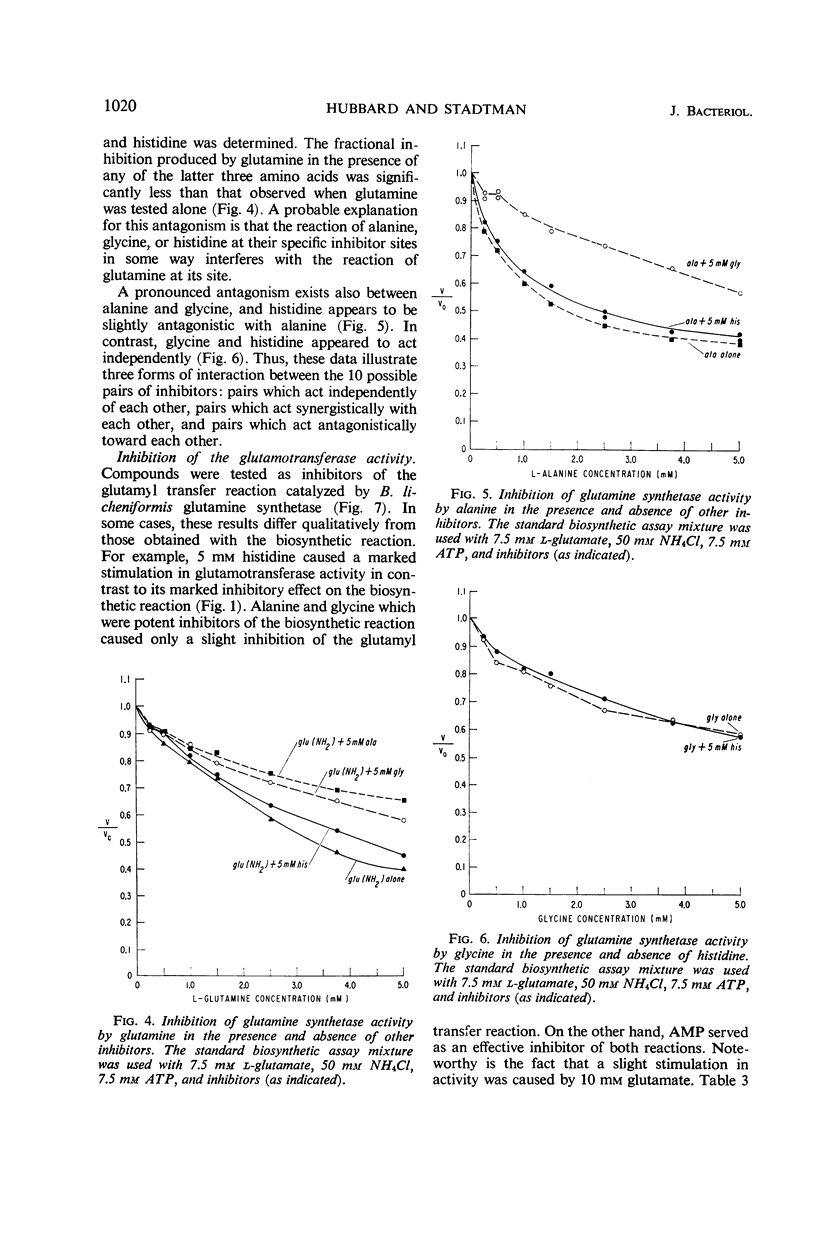
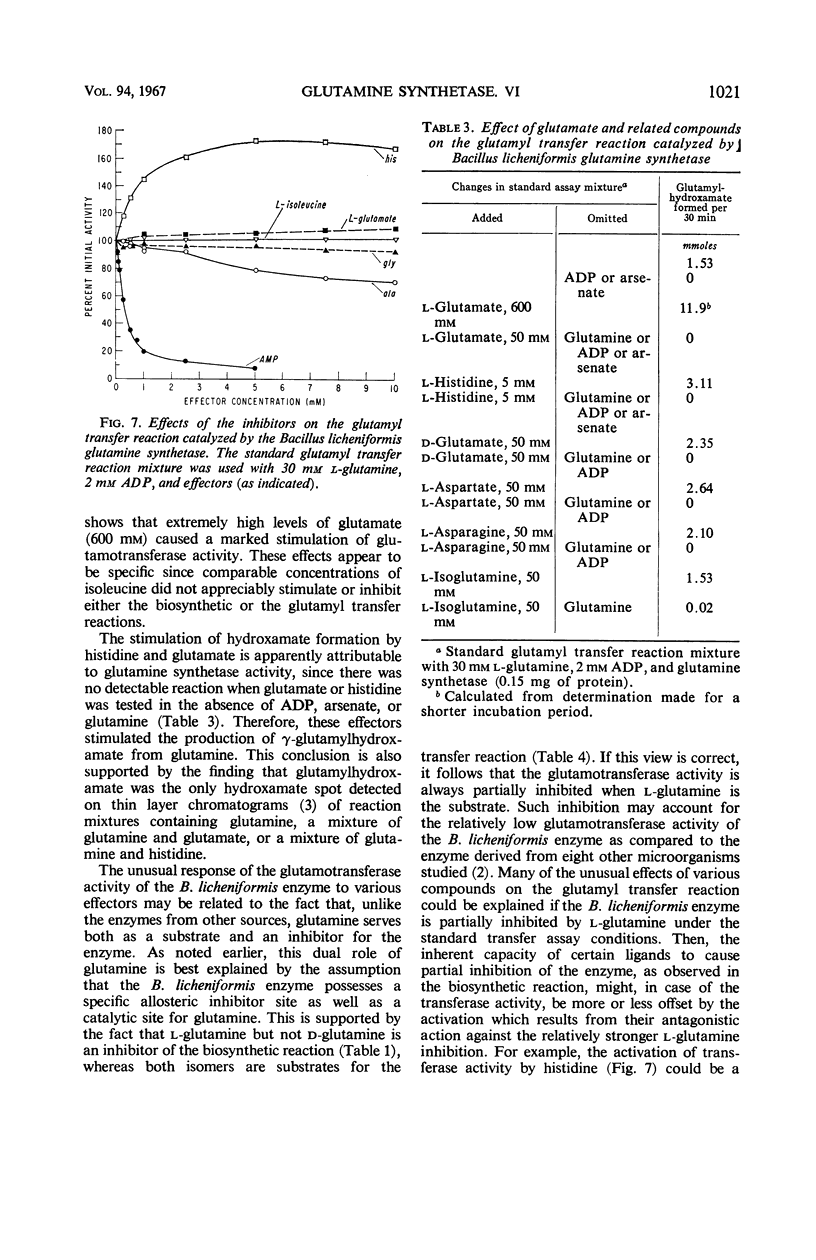
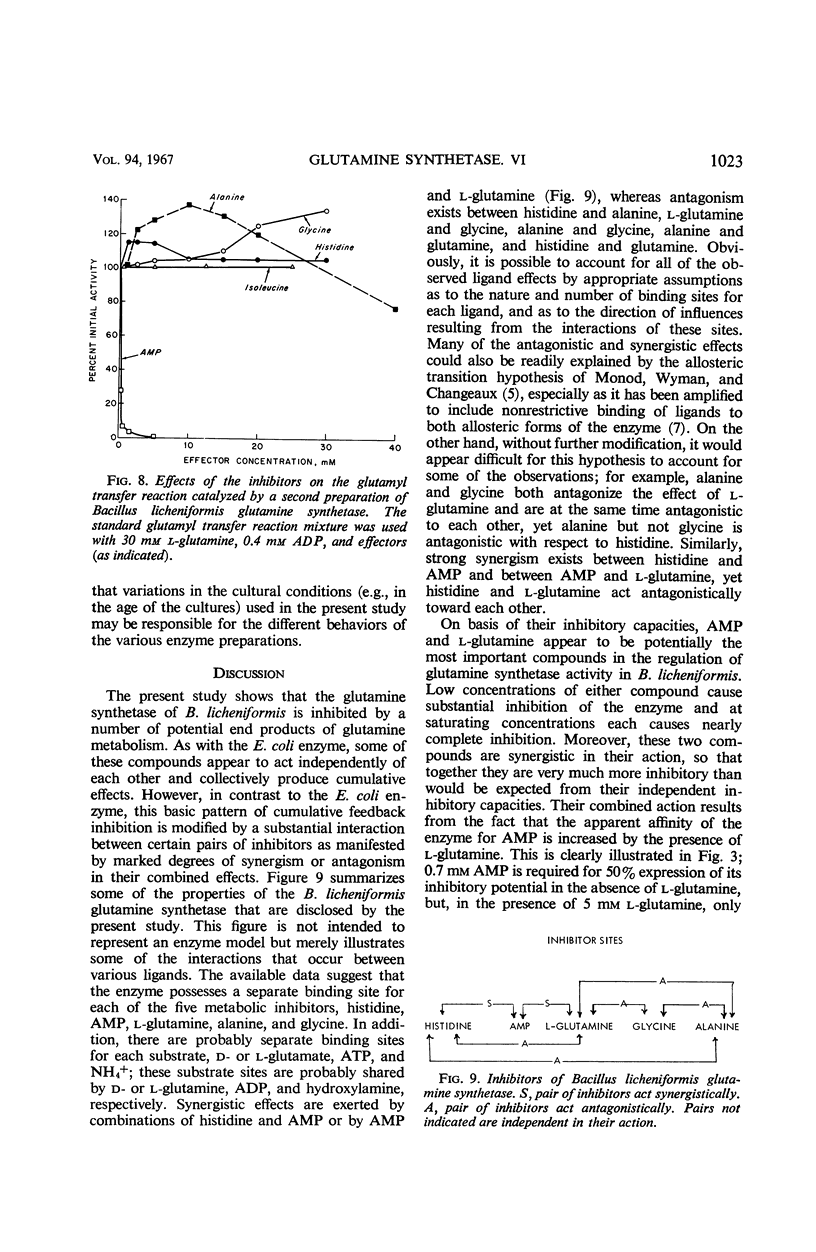
The relationships of five feedback inhibitors for the Bacillus licheniformis glutamine synthetase were investigated. The inhibitors were distinguishable by differences in their competitive relationship for the substrates of the enzyme. Mixtures of l-glutamine and adenosine-5′-monophosphate (AMP) or histidine and AMP caused synergistic inhibition of glutamine synthesis. Histidine, alanine, and glycine acted antagonistically toward the l-glutamine inhibition. Alanine acted antagonistically toward the glycine and histidine inhibitions. Independence of inhibitory action was observed with the other pairs of effectors. Possible mechanisms by which the inhibitors may interact to control glutamine synthesis are discussed. The low rate of catalysis of the glutamyl transfer reaction by the B. licheniformis glutamine synthetase can be attributed to the fact that l-glutamine serves both as a substrate and an inhibitor for the enzyme. Effectors which act antagonistically toward the l-glutamine inhibition stimulated glutamotransferase activity. The stimulation was not observed when d-glutamine was used as substrate for the glutamyl transfer reaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hubbard J. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. II. Patterns of feedback inhibition in microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1045–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1045-1055.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. V. Partial purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1007-1015.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M., Humphreys J. S., Shive W. Control of glutamine synthesis in Lactobacillus arabinosus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Sep;111(3):720–726. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. M., Changeux J. P. On the nature of allosteric transitions: implications of non-exclusive ligand binding. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R. Allosteric regulation of enzyme activity. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:41–154. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


