Abstract
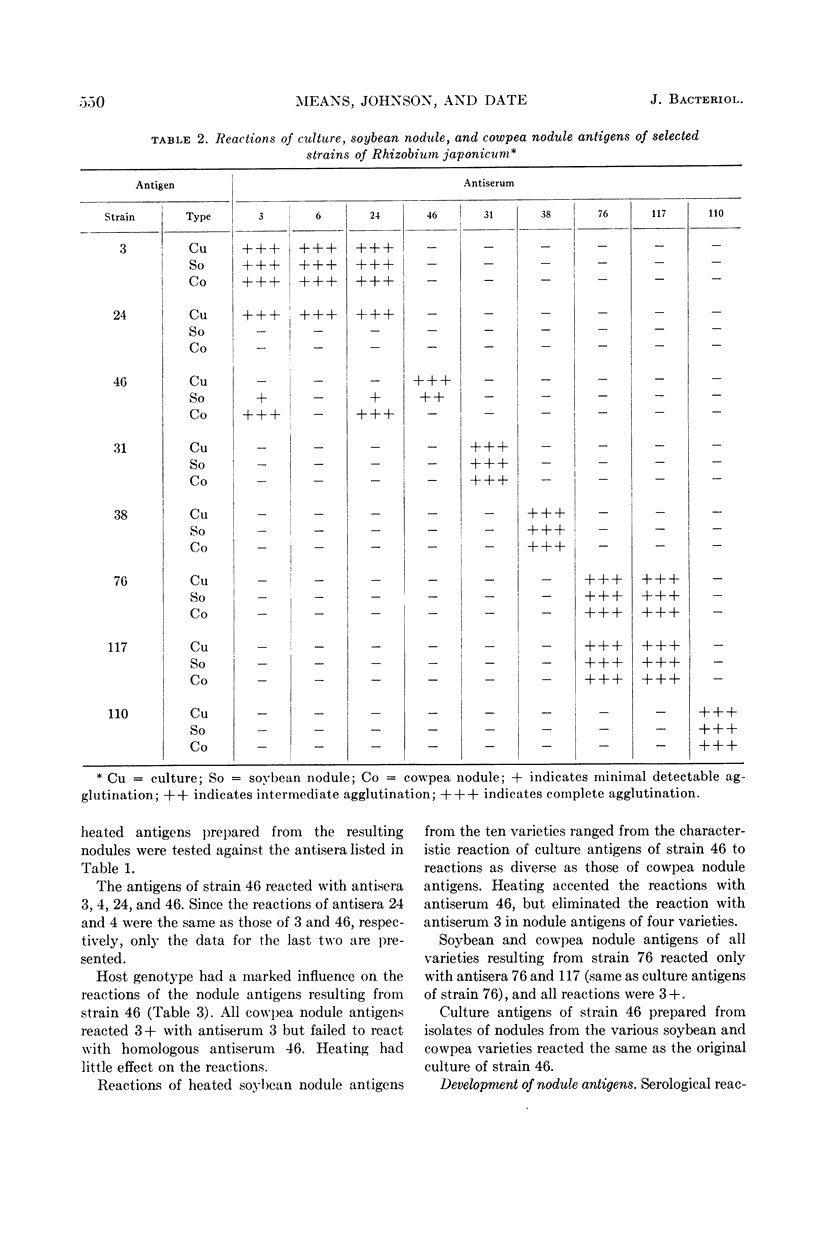
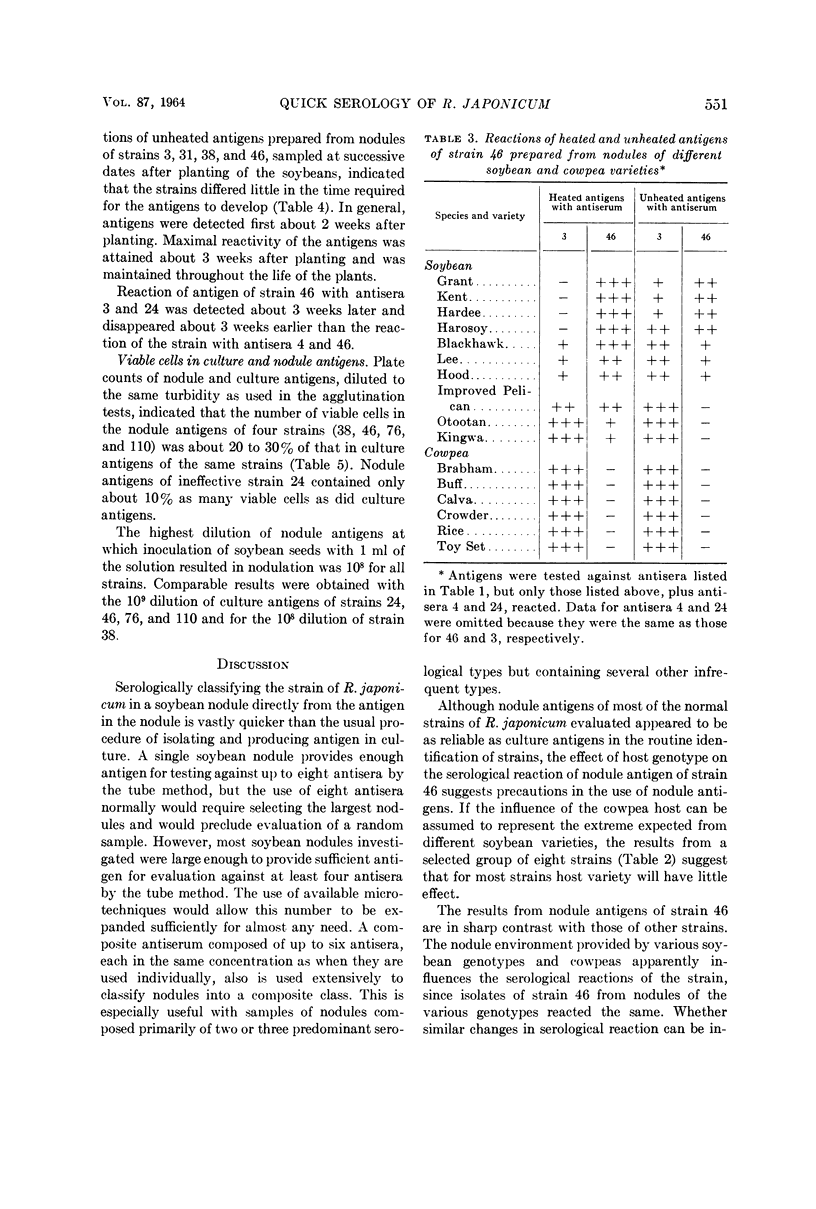
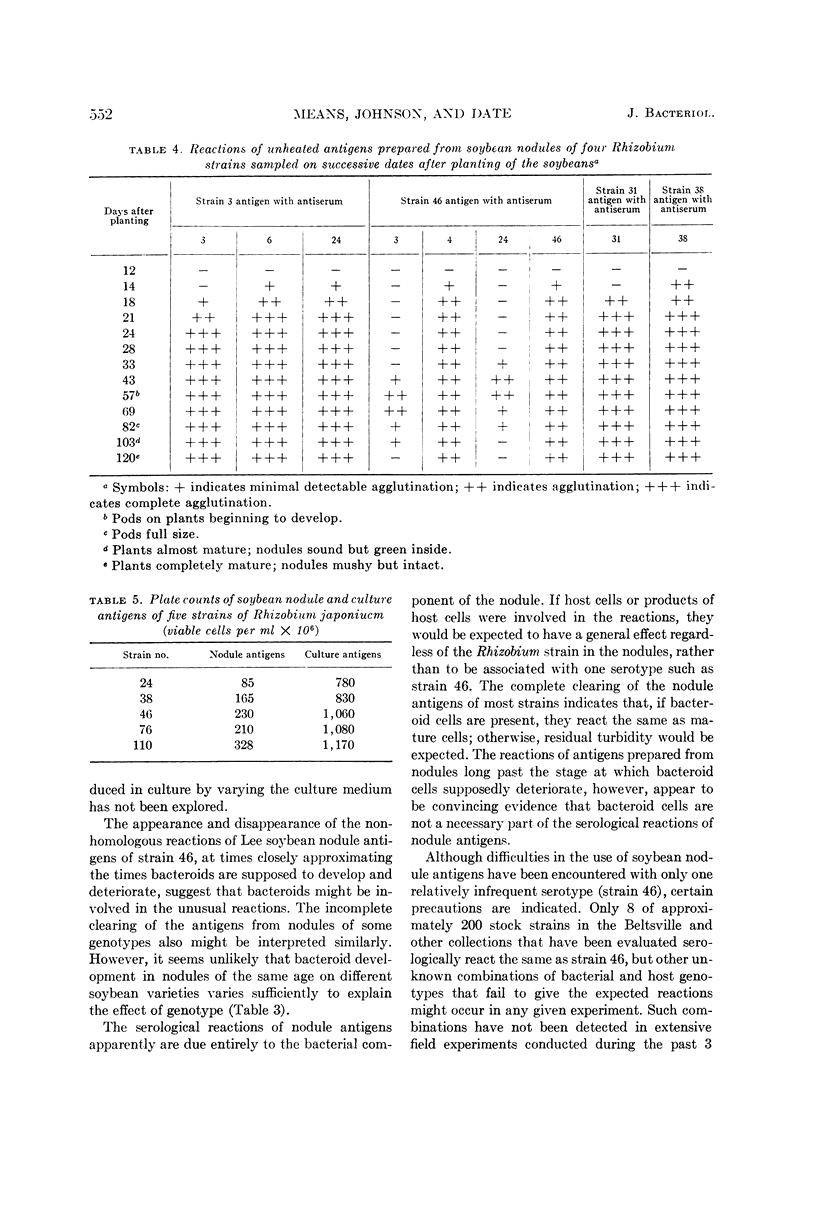
Means, Ura M. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, Beltsville, Md.), Herbert W. Johnson, and R. A. Date. Quick serological method of classifying strains of Rhizobium japonicum in nodules. J. Bacteriol. 87:547–553. 1964.—A new method of classifying strains of Rhizobium japonicum serologically by utilizing the contents of nodules as antigens is described. The method differs from standard procedures only in the preparation of antigens, but it is less time-consuming. Agglutination reactions of culture and nodule antigens were identical for 15 of the 17 strains investigated. Nodule antigens of ineffective strain 24 failed to agglutinate with any of the 17 antisera employed, and nodule antigens of strain 46 reacted with two antisera in addition to the two with which the culture antigens reacted. Host genotypes affected the reactions of nodule antigens of strain 46, with the reactions ranging from those typical for culture antigens for some soybean (Glycine max) varieties to reactions with heterologous antisera only for other soybean varieties and six cowpea (Vigna sinensis) varieties. Although nodule antigens of most strains of R. japonicum reacted the same as culture antigens, the inconsistent reactions of nodule antigens of strain 46 suggest precautions in the general use of nodule antigens. Indicated precautions are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JORDAN D. C. The bacteroids of the genus Rhizobium. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26:119–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


