Abstract
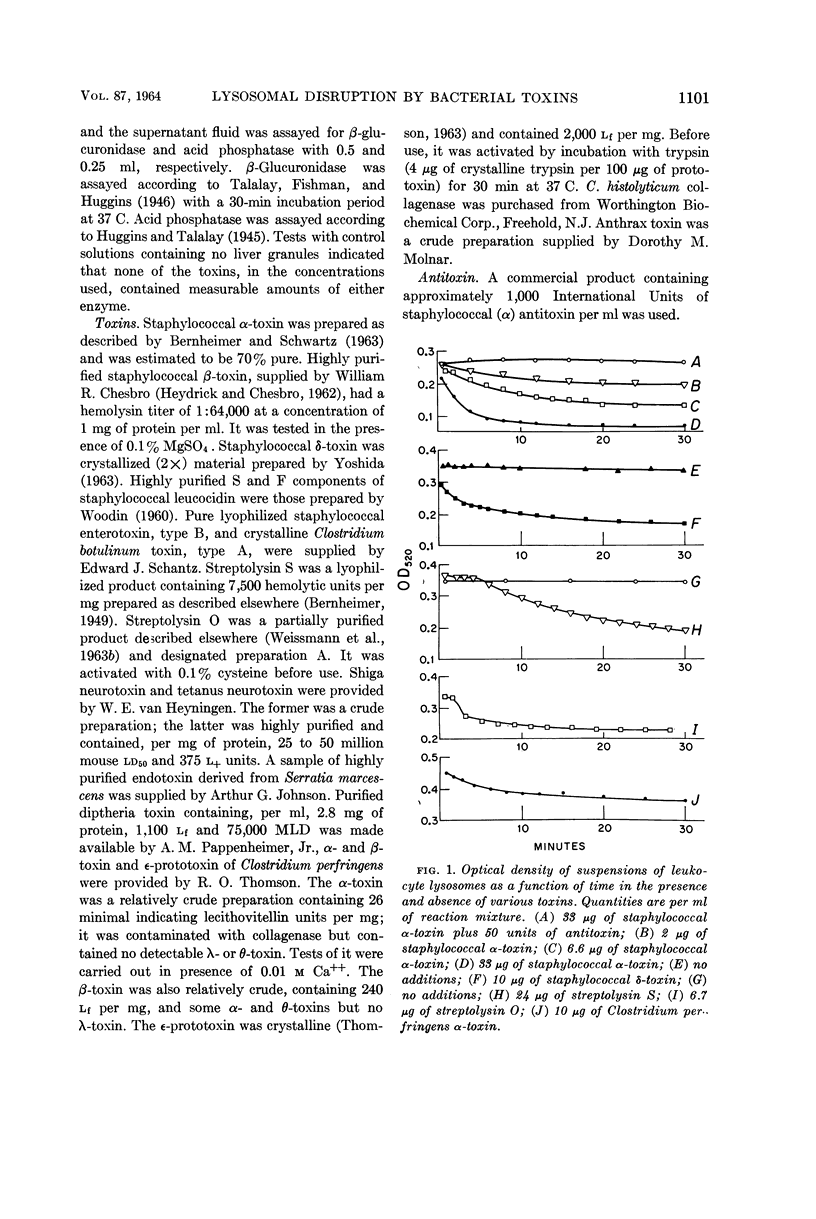
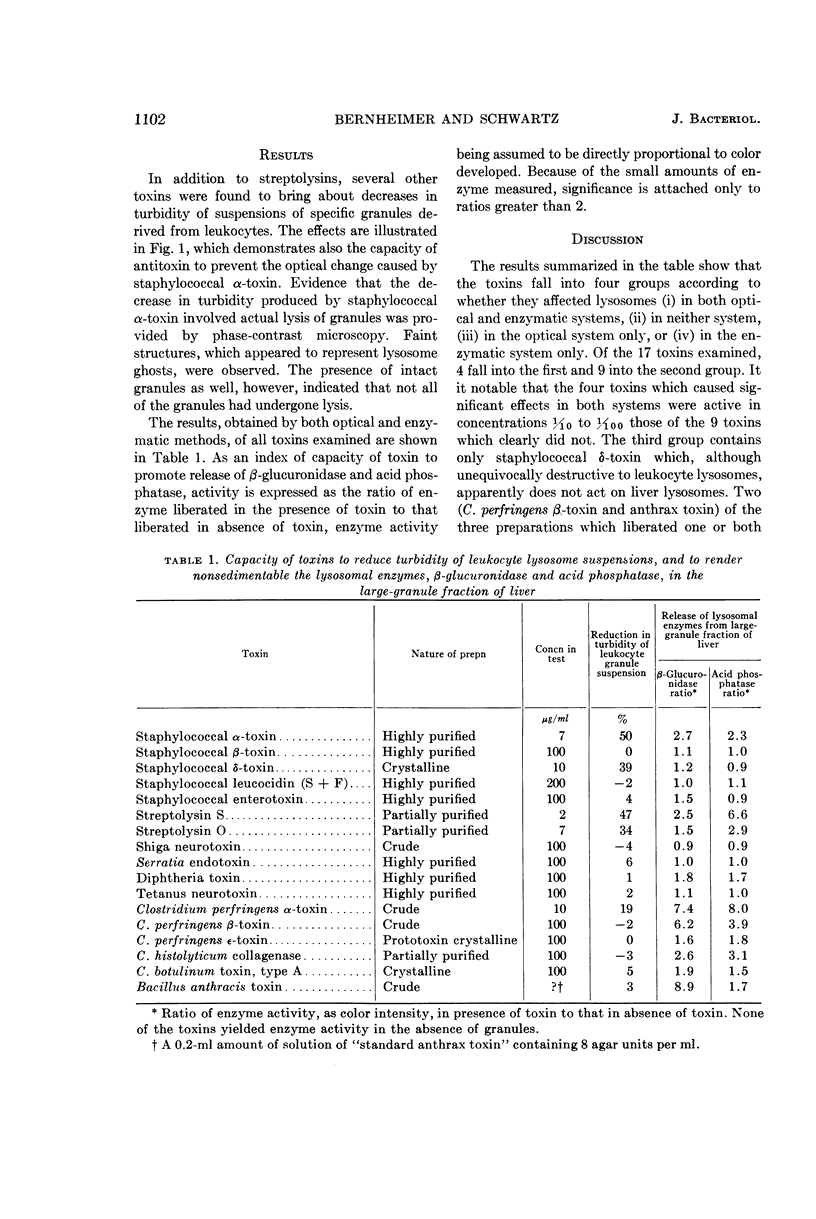
Bernheimer, Alan W. (New York University School of Medicine, New York), and Lois L. Schwartz. Lysosomal disruption by bacterial toxins. J. Bacteriol. 87:1100–1104. 1964.—Seventeen bacterial toxins were examined for capacity (i) to disrupt rabbit leukocyte lysosomes as indicated by decrease in turbidity of lysosomal suspensions, and (ii) to alter rabbit liver lysosomes as measured by release of β-glucuronidase and acid phosphatase. Staphylococcal α-toxin, Clostridium perfringens α-toxin, and streptolysins O and S affected lysosomes in both systems. Staphylococcal β-toxin, leucocidin and enterotoxin, Shiga neurotoxin, Serratia endotoxin, diphtheria toxin, tetanus neurotoxin, C. botulinum type A toxin, and C. perfringens ε-toxin were not active in either system. Staphylococcal δ-toxin, C. histolyticum collagenase, crude C. perfringens β-toxin, and crude anthrax toxin caused lysosomal damage in only one of the test systems. There is a substantial correlation between the hemolytic property of a toxin and its capacity to disrupt lysosomes, lending support to the concept that erythrocytes and lysosomes are bounded by similar membranes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., BERNHEIMER A. W., WEISSMANN G. MOTION PICTURE STUDY OF THE TOXIC ACTION OF STREPTOLYSINS ON LEUCOCYTES. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:223–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE M. G., DATTA N. Observations on the immunological and biochemical properties of liver mitochondria with reference to the action of Clostridium welchii toxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):191–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON R. O. The fractionation of Clostridium welchii epsilon-antigen on cellulose ion exchangers. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Apr;31:79–90. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., KEISER H., BERNHEIMER A. W. STUDIES ON LYSOSOMES. III. THE EFFECTS OF STREPTOLYSINS O AND S ON THE RELEASE OF ACID HYDROLASES FROM A GRANULAR FRACTION OF RABBIT LIVER. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:205–222. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Studies on lysosomes. I. The effects of endotoxin, endotoxin tolerance, and cortisone on the release of acid hydrolases from a granular fraction of rabbit liver. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:433–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Studies on lysosomes. II. The effect of cortisone on the release of acid hydrolases from a large granule fraction of rabbit liver induced by an excess of vitamin A. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:661–669. doi: 10.1172/JCI104757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODIN A. M. Purification of the two components of leucocidin from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:158–165. doi: 10.1042/bj0750158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A. Staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. I. Purification and chemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 4;71:544–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


