Abstract
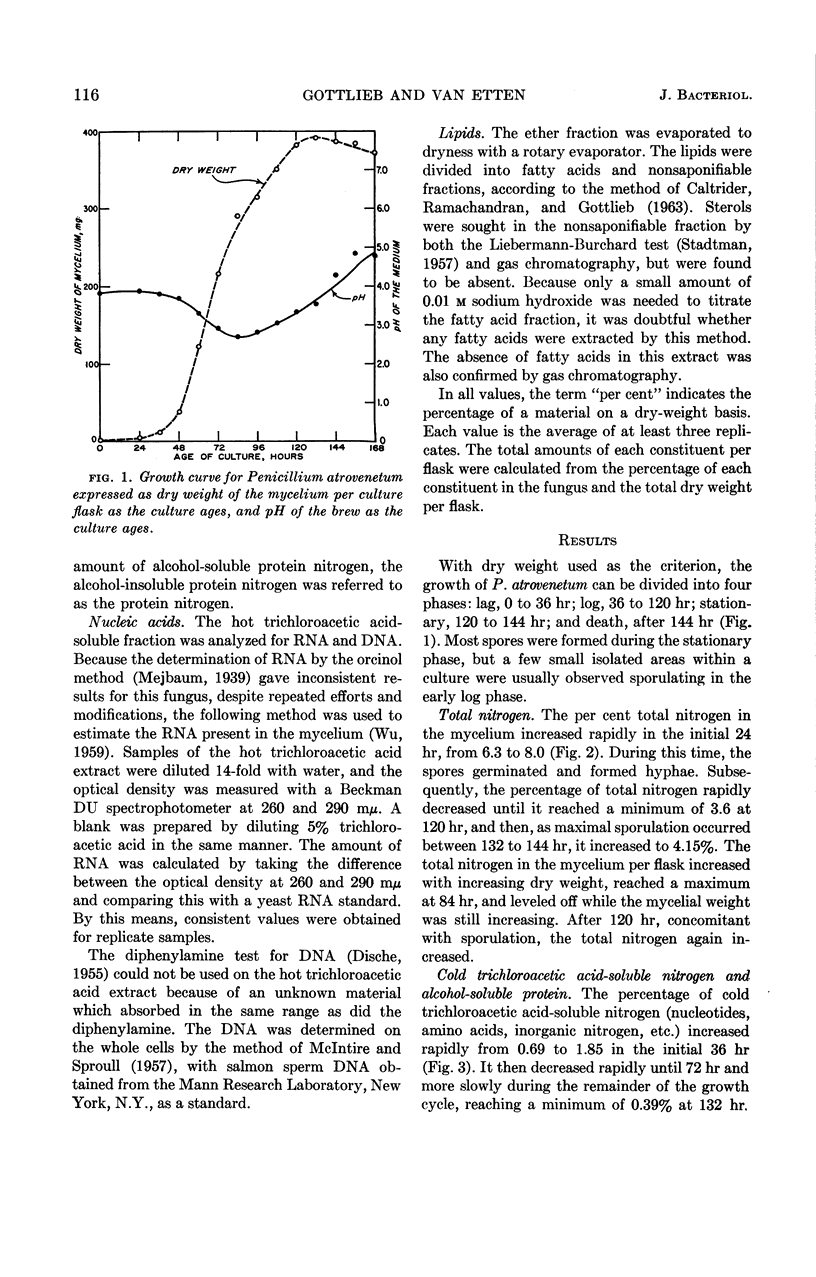
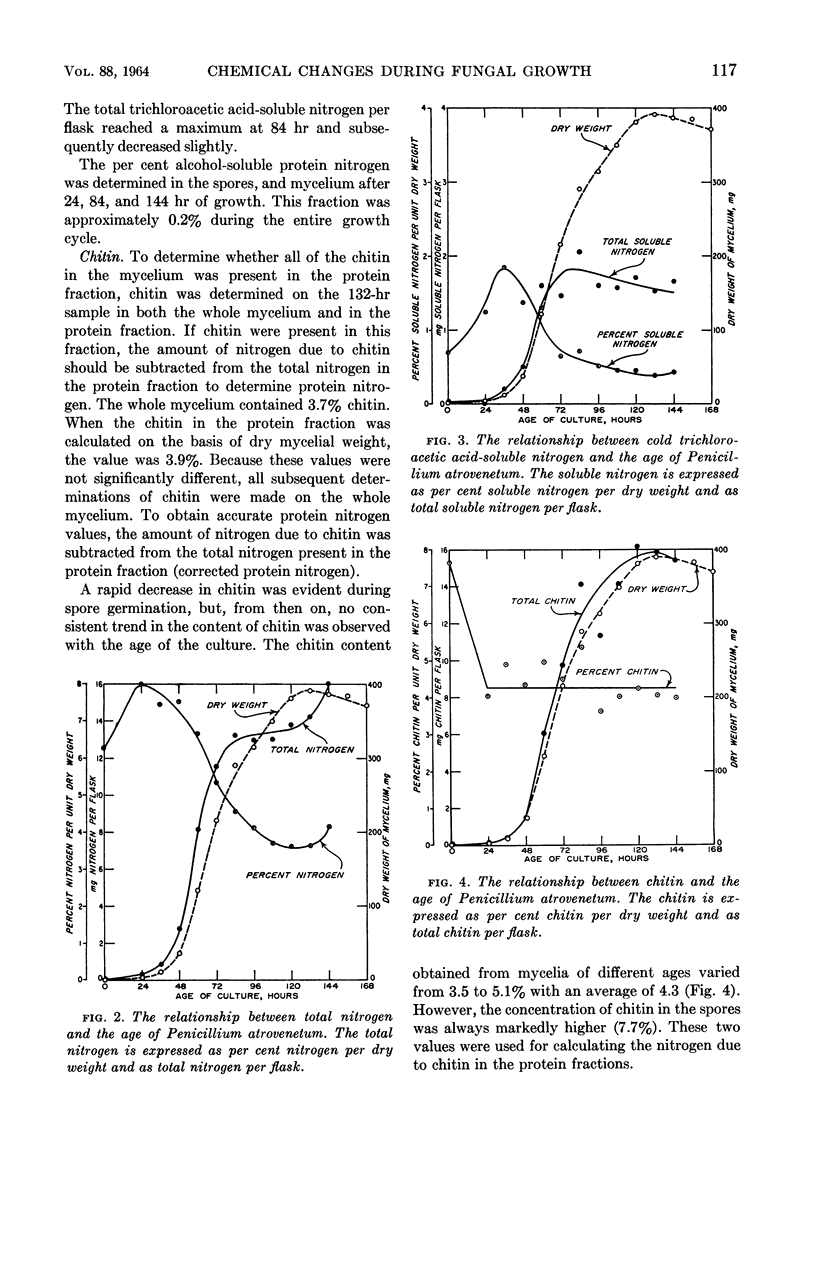
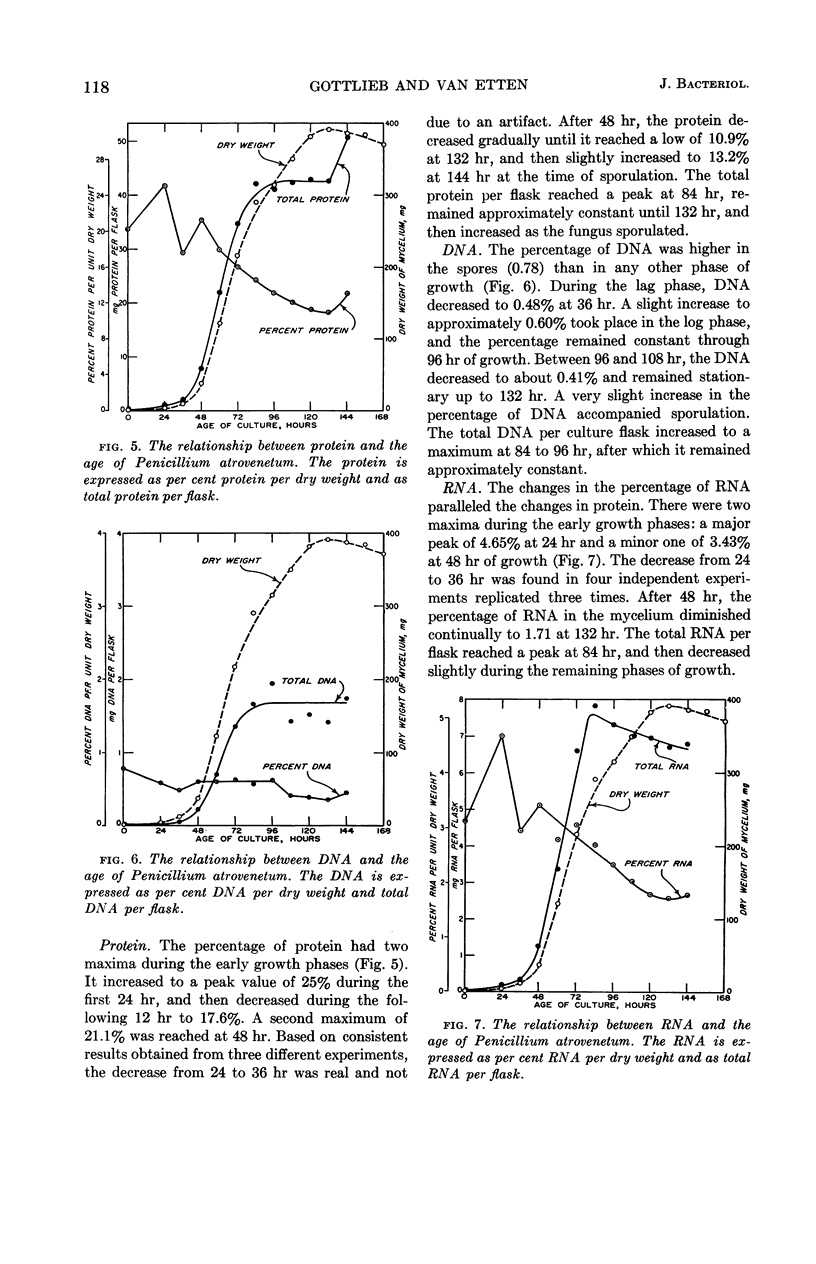
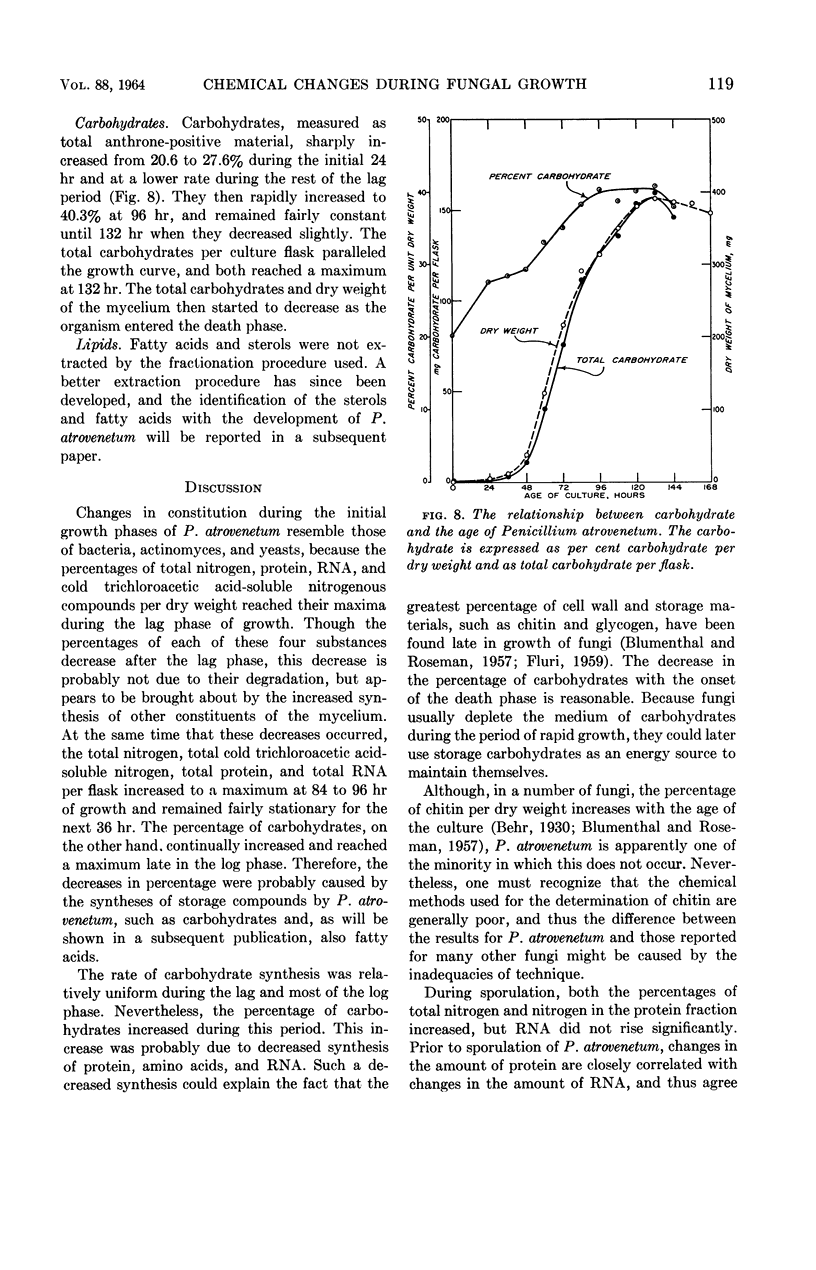
Gottlieb, David (University of Illinois, Urbana), and James L. Van Etten. Biochemical changes during the growth of fungi. I. Nitrogen compounds and carbohydrate changes in Penicillium atrovenetum. J. Bacteriol. 88:114–121. 1964.—Changes in the biochemical constituents of cells were studied during the growth and development of Penicillium atrovenetum. Growth of the fungus, as measured by the dry weight, could be divided into four phases: lag, log, stationary, and death. The percentages of total nitrogen, cold trichloroacetic acid-soluble nitrogen, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and protein increased to a maximum during the lag phase, and subsequently decreased as the fungus aged. The percentage of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was always slightly higher in the spores than in the mycelium. The DNA in the mycelium decreased in the lag phase, and then increased slightly to a plateau for the duration of the log phase, followed by a decrease to a constant percentage during the stationary and death phases. Carbohydrates were present in higher concentration in the mycelium than in the spores. The percentage of carbohydrates in the mycelium increased continually until it reached a maximum late in the log phase, and then decreased as the fungus entered the death phase. The results reported for this fungus are, in general, in agreement with those reported for other microorganisms. Namely, the percentages of enzyme-forming compounds, such as amino acids, nucleotides, RNA, and protein, were highest in the lag phase, whereas storage compounds such as carbohydrates increased to a maximum near the end of the log phase. The definition of log phase in fungi depends on the criteria that are used. If, instead of using the linear increase in dry weight to delimit this growth period, one uses the end of net protein, RNA, and DNA synthesis, a more realistic concept of growth emerges.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUMENTHAL H. J., ROSEMAN S. Quantitative estimation of chitin in fungi. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):222–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.222-224.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLURI R. [Carbohydrate metabolism of a fungus (Phycomyces blakesleeanus) in dependence on culture conditions. The influence of carbon sources, vitamin B1 and 2 and their antagonists (pyrithiamine and oxythiamine)]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1959;33:195–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISHNAN P. S., DAMLE S. P., BAJAJ V. Studies on the role of metaphosphate in molds. II. The formation of soluble and insoluble metaphosphates in Aspergillus niger. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):35–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTIRE F. C., SPROULL M. F. A simple method for determination of desoxypentose nucleic acid in tissue cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jul;95(3):458–462. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLAI N. C., SRINIVASAN K. S. The amino acid metabolism of Aspergillus flavus. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Apr;14(2):248–255. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-2-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAISTRICK H., STOSSL A. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms. 104. Metabolites of Penicillium atrovenetum G. Smith: beta-nitropropionic acid, a major metabolite. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):647–653. doi: 10.1042/bj0680647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E. Variation in the phosphorus content of Escherichia coli during cultivation. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Aug;7(1-2):24–30. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-1-2-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


