Abstract
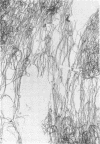
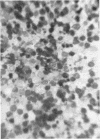
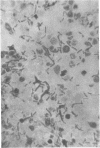
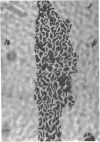
Chang, Te-Wen (Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Mass.), and Louis Weinstein. Morphological changes in gram-negative bacilli exposed to cephalothin. J. Bacteriol. 88:1790–1797. 1964.—Exposure of gram-negative bacteria to cephalothin (7-[thiophene-2-acetamido]-cephalosporanic acid) revealed the formation of long filaments and large bodies, which were capable of reverting to normal cells when removed from contact with the drug. The degree of morphological change was found to be related to the concentration of antibiotic in which the organisms were suspended. The large bodies were altered by contact with solutions of varying osmolarity. Different species showed variation in the ability to develop large bodies. A relationship between antibiotic sensitivity and the capacity to resist morphological alteration was observed. Though most sensitive gram-negative bacilli were strikingly changed by exposure to cephalothin, naturally resistant ones were unaffected. Organisms made drug-resistant in vitro underwent changes in cellular form which were qualitatively the same but less intense than those which developed in parent strains originally sensitive to cephalothin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOND J. M., BRIMBLECOMBE R. W., CODNER R. C. Biological assay of cephalosporin C. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jan;27:11–19. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG T. W., WEINSTEIN L. IN VITRO BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF CEPHALOTHIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1022–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1022-1027.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG T. W., WEINSTEIN L. INHIBITION OF SYNTHESIS OF THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY CEPHALOTHIN. Science. 1964 Feb 21;143(3608):807–808. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3608.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIAK J., HAHN F. E. Concurrent morphological and chemical events in Staphylococcus aureus exposed to penicillin. Science. 1962 Sep 21;137(3534):982–983. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3534.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIAK J., HAHN F. E. Penicillin-induced lysis of Escherichia coli. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):119–120. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., WEINBERGER H. J. The L forms of bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1951 Dec;15(4):245–288. doi: 10.1128/br.15.4.245-288.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L. THE DEVELOPMENT OF PROTEUS CULTURES IN THE PRESENCE OF PENICILLIN. J Bacteriol. 1949 May;57(5):529–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.5.529-546.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING A., VOUREKA A., KRAMER I. R. H., HUGHES W. H. The morphology and motility of Proteus vulgaris and other organisms cultured in the presence of penicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 May;4(2):257–269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEBICKI J. M., JAMES A. M. The preparation and properties of spheroplasts of Aerobacter aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:9–18. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGO W. B., RUSSELL A. D. Action of 6-aminopenicillanic acid on gram-negative bacteria. Nature. 1960 Dec 3;188:875–875. doi: 10.1038/188875a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDLER O., HUND A., ZEHENDER C. Cell wall composition in bacterial and L forms of Proteus vulgaris. Nature. 1958 Feb 22;181(4608):572–573. doi: 10.1038/181572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Mechanism of action of penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):144–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.144-144.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., ST CLAIR J. Protoplasts and L-type growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):143–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.143-160.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., FRANCOMBE W. H., MAYALL B. H. The effect of penicillin on the structure of staphylococcal cell walls. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Dec;5:641–648. doi: 10.1139/m59-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., STROMINGER J. L. Mode of action of penicillin. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):99–101. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]