Abstract
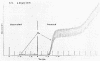
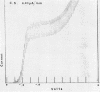
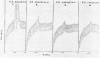
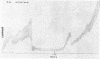
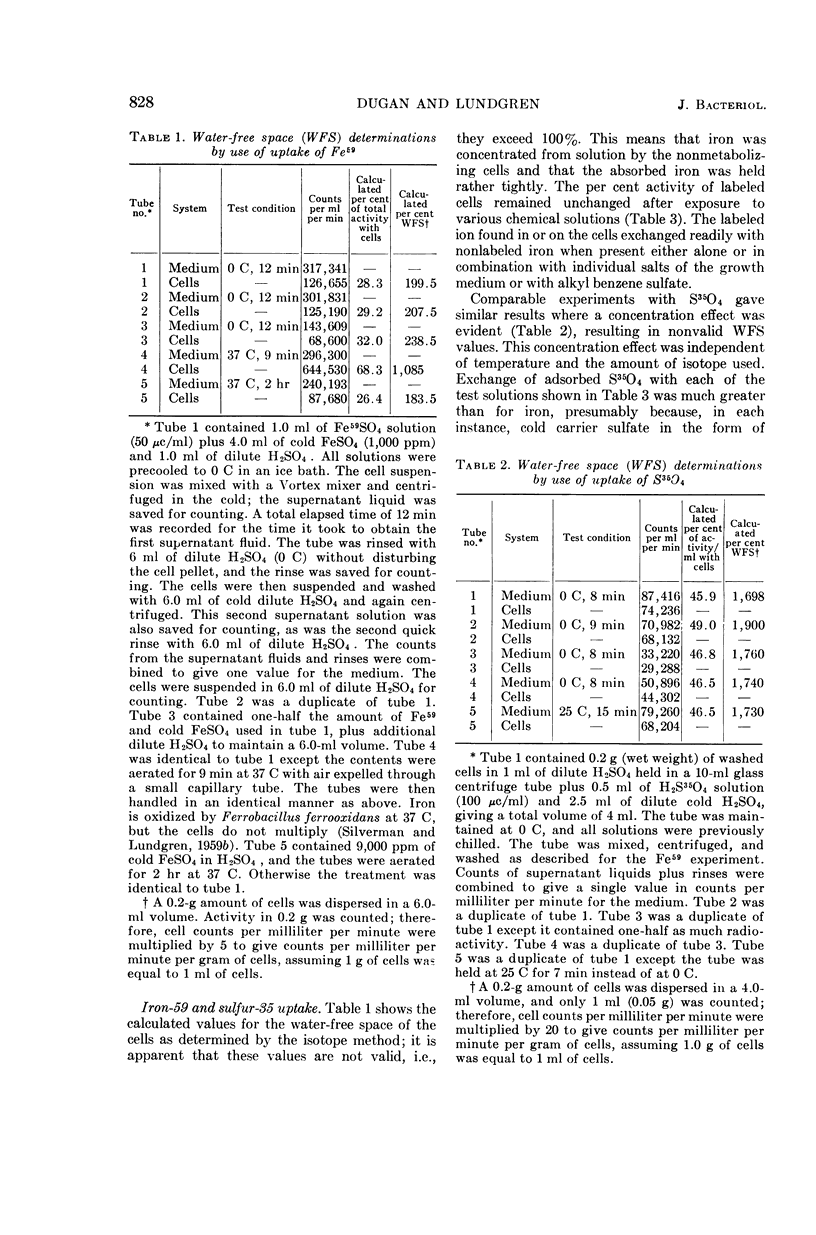
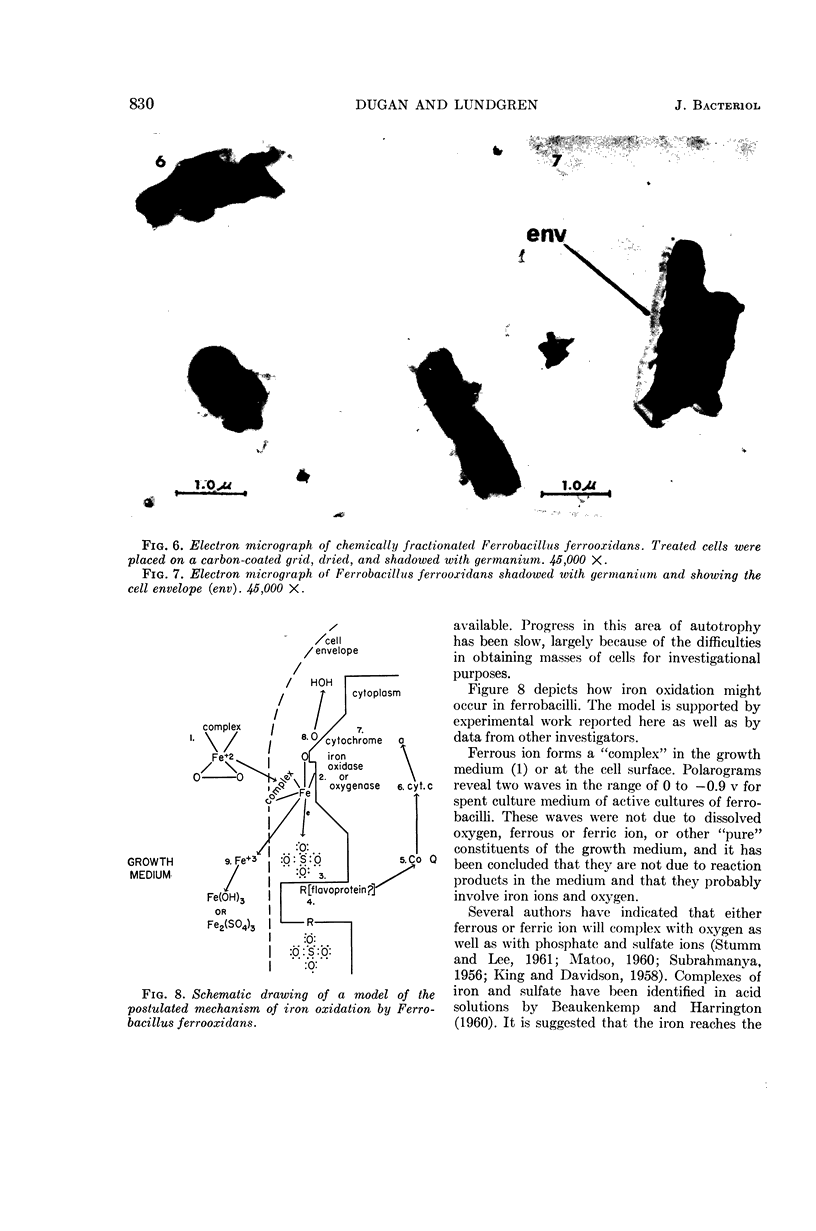
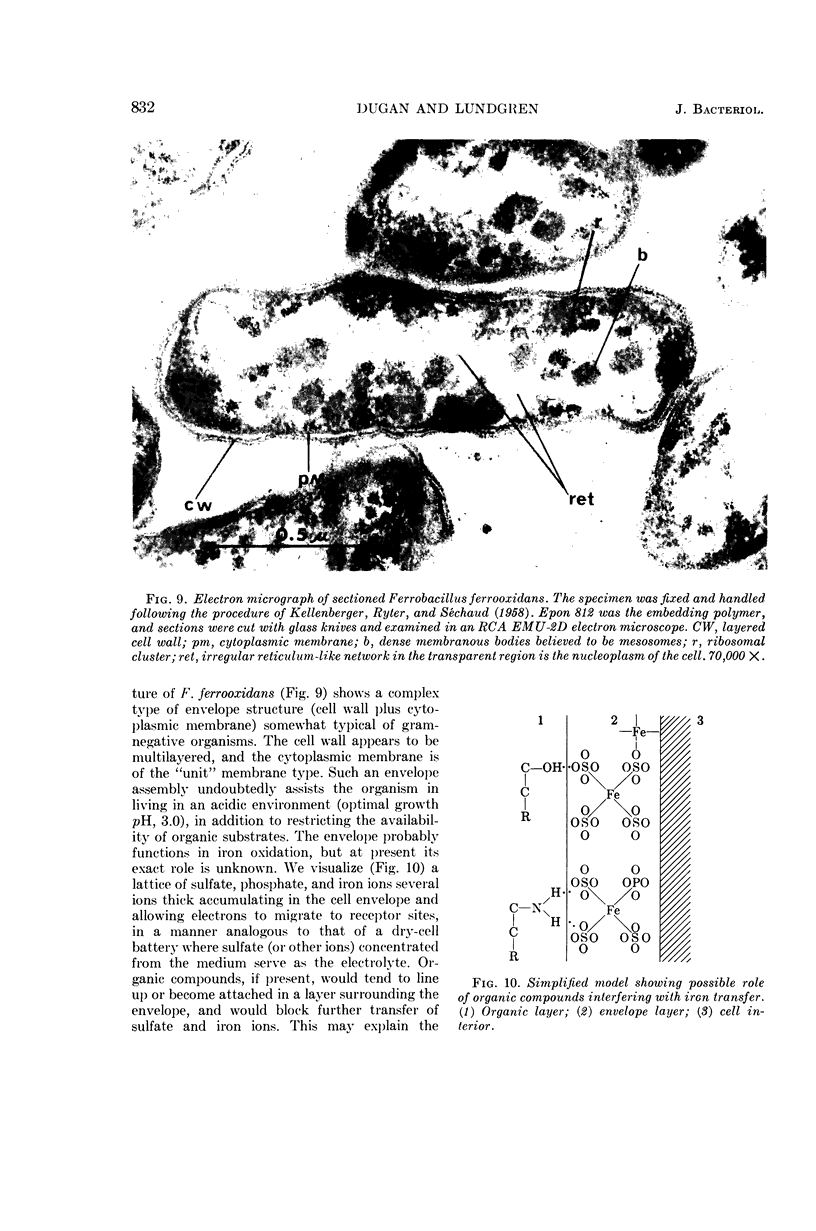
Dugan, Patrick R. (Syracuse University, Syracuse, N.Y.), and Donald G. Lundgren. Energy supply for the chemoautotroph Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Bacteriol. 89:825–834. 1965.—A working model is proposed to explain dissimilatory ferrous iron oxidation by Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans, that is, oxidation linked to an energy source. The model is supported by experimental evidence reported here as well as in the literature. Polarographic assays of the culture medium demonstrated an iron “complex” involving oxygen. The initial “complex” would be oxygenated, but not oxidized because no electron transport has taken place. The “complex” is formed in solution or on the cell surface and is somehow reacted with iron oxidase (or oxygenase), resulting in the release of an electron. Either sulfate or a flavoprotein is suggested as involved in the initial electron-transfer link between iron and the cell. The electron is transported in the cell through a typical electron-transport system involving coenzyme Q6, cytochrome c, and cytochrome a; oxygen is the final electron acceptor. Electron micrographs of intact and sectioned cells are included to show structural detail in support of the model.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEEM M. I., LEES H. ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT REDUCTION OF NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE BY FERRO-CYTOCHROME C IN CHEMOAUTOTROPHIC BACTERIA. Nature. 1963 Nov 23;200:759–761. doi: 10.1038/200759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAYLOCK B. A., NASON A. ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEMS OF THE CHEMOAUTOTROPH FERROBACILLUS FERROOXIDANS. I. CYTOCHROME C-CONTAINING IRON OXIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3453–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRALEY S. A., Sr, KINSEL N. A., LEATHEN W. W. Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans: a chemosynthetic autotrophic Bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):700–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.700-704.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLMER A. R., TEMPLE K. L., HINKLE M. E. An iron-oxidizing bacterium from the acid drainage of some bituminous coal mines. J Bacteriol. 1950 Mar;59(3):317–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.3.317-328.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGAN P., LUNDGREN D. MICRODETECTION OF MENADIONE, COENZYME Q6, AND CERTAIN RELATED QUINOID COMPOUNDS IN BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS USING ELECTRON CAPTURE-GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jul;8:312–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDLER P., RAJAGOPALAN K. V., ALEMAN V. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF IRON-FLAVOPROTEINS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaroff N. SULFATE REQUIREMENT FOR IRON OXIDATION BY THIOBACILLUS FERROOXIDANS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85(1):78–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.78-83.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. II. Manometric studies. J Bacteriol. 1959 Sep;78:326–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.3.326-331.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMPLE K. L., COLMER A. R. The autotrophic oxidation of iron by a new bacterium, thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1951 Nov;62(5):605–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.5.605-611.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNON L. P., MANGUM J. H., BECK J. V., SHAFIA F. M. Studies on a ferrous-ion-oxidizing bacterium. II. Cytochrome composition. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Jun;88:227–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]