Abstract
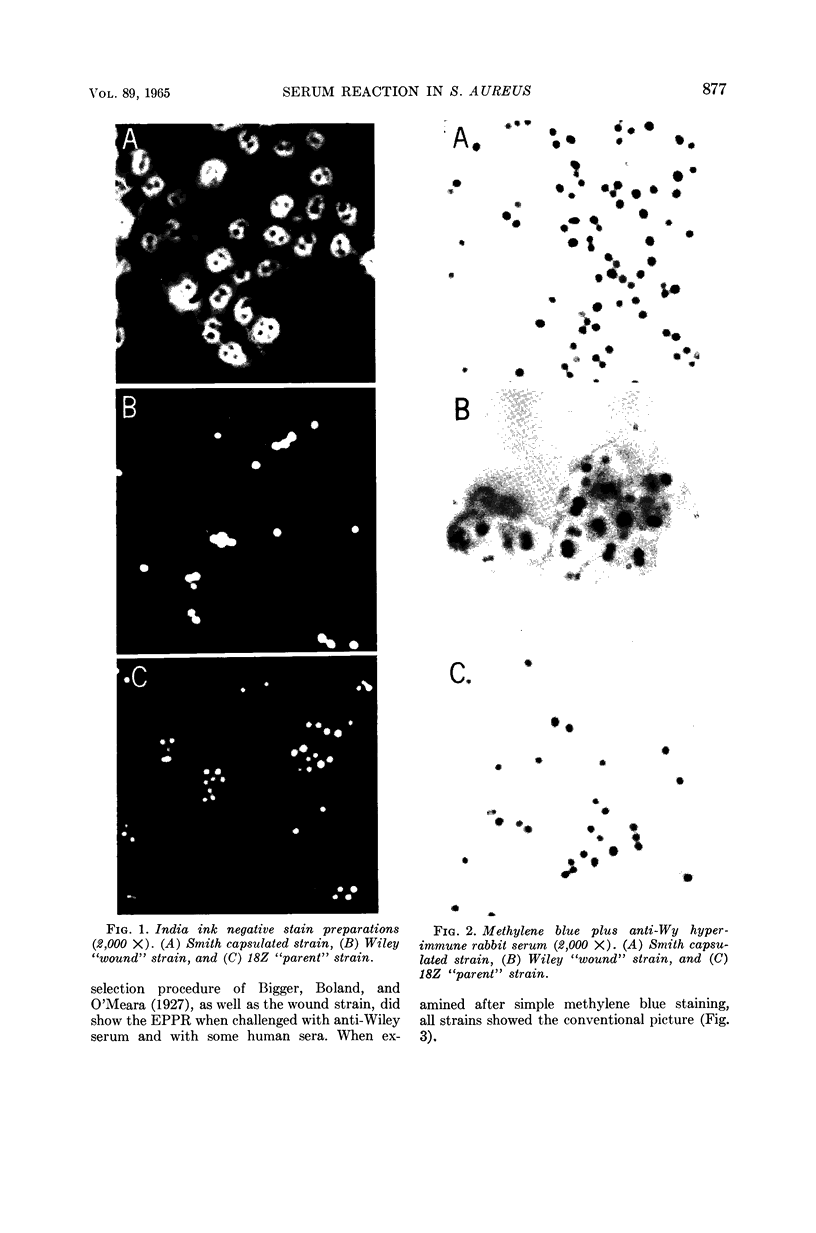
Mudd, Stuart (U.S. Veterans Administration Hospital, Philadelphia, Pa.), and Samuel J. DeCourcy, Jr. Interaction of viscid material of Staphylococcus aureus with specific immune serum. J. Bacteriol. 89:874–879. 1965.—Re-examination of the phenomenon of Price and Kneeland and of Wiley revealed the following. (i) The prototype “wound strain” of Wiley, and viscid-colony strains obtained by aging and selection of laboratory or field strains, differed in growth characteristics in liquid and solid media from the Smith encapsulated strain and from ordinary, unselected laboratory and field strains of coagulase-positive staphylococci. (ii) The wound strain and ordinary unselected strains, unlike the Smith encapsulated strain, did not exhibit capsules when examined in thin films of Pelikan Waterproof Drawing Ink. (iii) The phenomenon of Price and Kneeland and of Wiley is exhibited when the wound strain and other viscid-colony strains interact with anti-Wiley immune sera or various human sera. In our experience, this phenomenon was not exhibited by the Smith or by ordinary, unselected strains. (iv) The staphylococcal polysaccharide antigen previously characterized as the capsular substance of a Smith-like strain was completely different chemically and serologically from extracellular material prepared from the Wiley wound strain. We conclude that the viscid-colony strains are not, in fact, encapsulated, and that the phenomenon in question is a precipitation of extracellular material about the periphery of the cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKELL T. H., HANESSIAN S. THE PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A NEW ACTIVE IMMUNIZING POLYSACCHARIDE PREPARED FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 2;83:35–41. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT G. A., MOSES A. J. Acute infection of mice with Smith strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1958 Dec 19;128(3338):1574–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3338.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPRAL F. A., LI I. W. Virulence and coagulases of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:151–153. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. II. Observations on four mouse-pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:589–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. III. Antibacterial versus antioxic immunity. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:601–610. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENHART N. A., LI I. W., DECOURCY S. J., Jr, MUDD S. Nonmucoid mutant of the encapsulated Smith strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:1165–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1165-1166.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENHART N. A., MUDD S., YOSHIDA A., LI I. W. THE COMMON PROTEIN AGGLUTINOGEN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. I. DISTRIBUTION IN INTERNATIONAL SEROTYPES AND CORRESPONDING ANTIBODY IN HUMAN POPULATIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:771–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI I. W., MUDD S., KAPRAL F. A. DISSOCIATION OF PHAGOCYTOSIS AND INTRACELLULAR KILLING OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY HUMAN BLOOD LEUKOCYTES. J Immunol. 1963 May;90:804–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation and properties of a surface antigen of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:295–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S., Heinmets F., Anderson T. F. Bacterial Morphology as Shown by the Electron Microscope: VI. Capsule, Cell-Wall and Inner Protoplasm of Pneumococcus, Type III. J Bacteriol. 1943 Aug;46(2):205–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.2.205-211.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE K. M., KNEELAND Y., Jr A mucoid form of Micrococcus pyogenes var aureus which shows capsular swelling with specific immune serum. J Bacteriol. 1954 Apr;67(4):472–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.4.472-475.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE K. M., KNEELAND Y., Jr Further studies of the phenomenon of capsular swelling of Micrococcus pyogenes var. aureus in the presence of immune serum. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):229–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.229-230.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. The formation of extracellular enzymes by staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. The rate of formation of hyaluronidase, coagulase and total extracellular protein by strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Apr;10(2):209–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. Variant populations within a hyaluronidase-producing culture of Staphylococcus aureus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):545–551. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALL T. Interrelationship of extracellular enzymes and pseudocapsulation in a strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1238–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1238-1243.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALL T., MUDD S., TAUBLER J. Concerning the surfaces of cells of Staphylococcus pyogenes. I. A pseudocapsulation phenomenon under certain experimental conditions. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:693–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B. A new virulence test for Staphylococcus aureus and its application to encapsulated strains. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Dec;7:933–943. doi: 10.1139/m61-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B., WONNACOTT J. C. Isolation and partial characterization of a capsular material from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1169–1176. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1169-1176.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




