Abstract
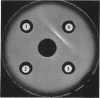
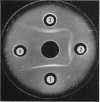
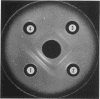
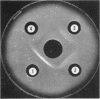
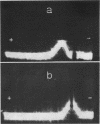
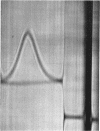
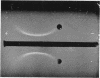
Pirtle, E. C. (National Animal Disease Laboratory, Ames, Iowa), P. A. Rebers, and W. W. Weigel. Nitrogen-containing and carbohydrate-containing antigen from Actinomyces bovis. J. Bacteriol. 89:880–888. 1965.—Water-soluble, heat-stable antigens have been isolated from the supernatant fluids of broth cultures of Actinomyces bovis ATCC 10048 after 8 days of growth in a broth medium composed of Casamino Acids, yeast extract, Tween 80 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate), sodium thioglycolate, dextrose, and sodium chloride. The antigens were precipitated from the culture supernatant fluid with alcohol and purified by fractional precipitation with alcohol in the presence of calcium or zinc and by chromatography on diethylaminoethyl Sephadex. Two serologically active substances which differed in chemical composition and size were characterized. The larger one contained 71% hexose and 2.8% nitrogen, and the smaller one contained 45% hexose and 5.4% nitrogen. Heterogeneity of these fractions could not be demonstrated by electrophoresis in free solution at pH 7.8 or 2, by ultracentrifugal analysis, by double diffusion in agar, or by immunoelectrophoresis. Despite their differences in chemical composition and size, they appeared identical in activity as antigens in complement fixation and in double-diffusion tests in agar. Each was found to contain mannose as its chief component after hydrolysis and paper chromatography with three solvent systems. A small percentage of the total nitrogen may be attributed to the presence of amino sugars but the remainder is as yet unidentified.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERMAN E. R. Isolation of bovine vitreous hyaluronic acid on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 26;58:120–122. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90823-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. Studies on the cell-wall composition and taxonomy of Actinomycetales and related groups. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):173–189. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYER R. L., TAMMES A. R., ROUTH J. I. The determination of phosphorus and phosphatase with N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORG L. K., ROBERTSTAD G. W., BRINKMAN S. A. IDENTIFICATION OF SPECIES OF ACTINOMYCES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:477–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.477-490.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING S., MEYER E. Gel diffusion technique in antigen-antibody reactions of Actinomyces species and "anaerobic diphtheroids". J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:186–190. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.186-190.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KWAPINSKI J. B. Researches on the antigenic structure of Actinomycetales. IV. Chemical and antigenic structure of Actinomyces israeli. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1960;23:158–172. doi: 10.1159/000160928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSON C. F. A procedure for agar gel electrophoresis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1962 Feb;37:143–149. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/37.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M. Filter-paper partition chromatography of sugars: 1. General description and application to the qualitative analysis of sugars in apple juice, egg white and foetal blood of sheep. with a note by R. G. Westall. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):238–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0420238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. A complement fixation test for poliomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1955 Aug 1;102(2):133–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLACK J. M., SPEARS R. G., SNODGRASS W. G., KUCHLER R. J. Studies with microaerophilic actinomycetes. II. Serological groups as determined by the reciprocal agglutinin adsorption technique. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.400-404.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Winger A., Moore D. W. SEROLOGICAL GROUPING OF ACTINOMYCES BY MEANS OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODIES. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82(1):54–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.54-65.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]