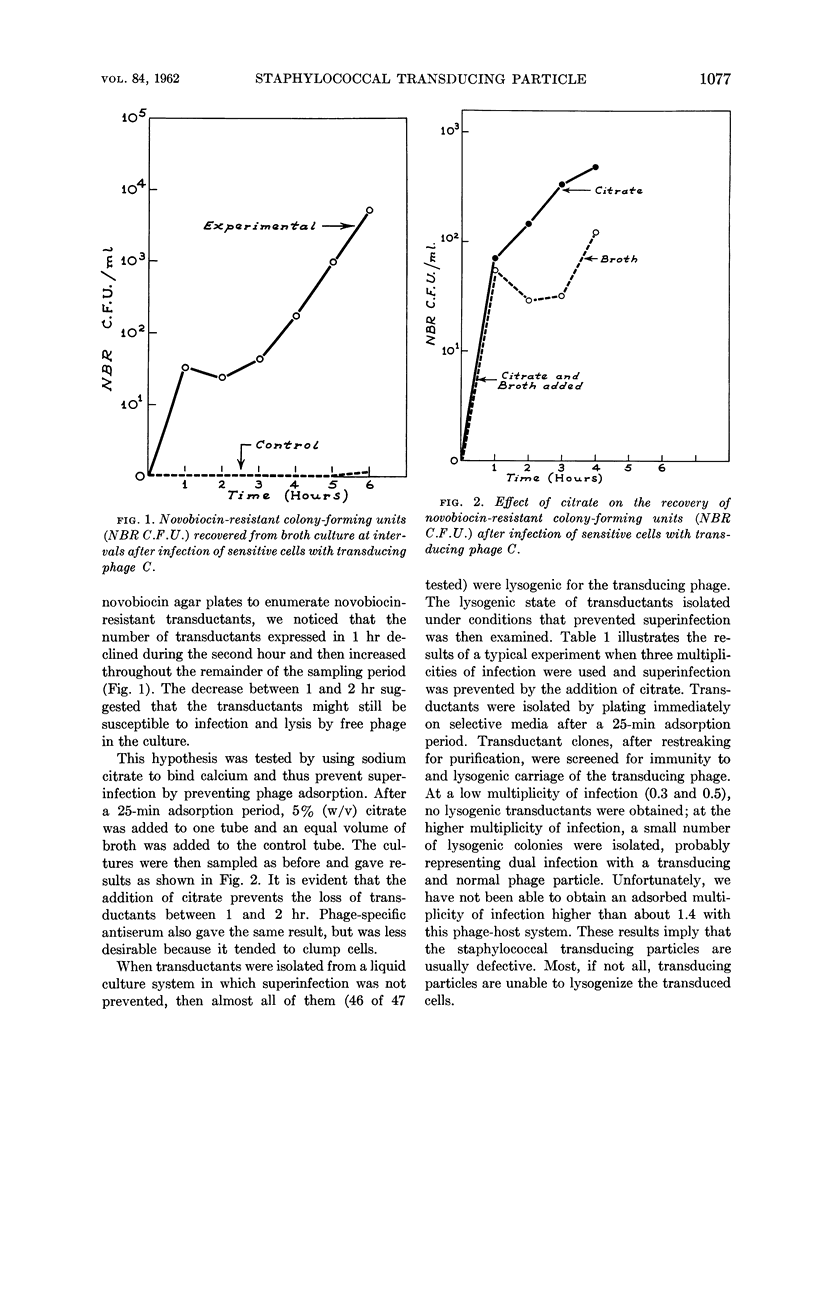
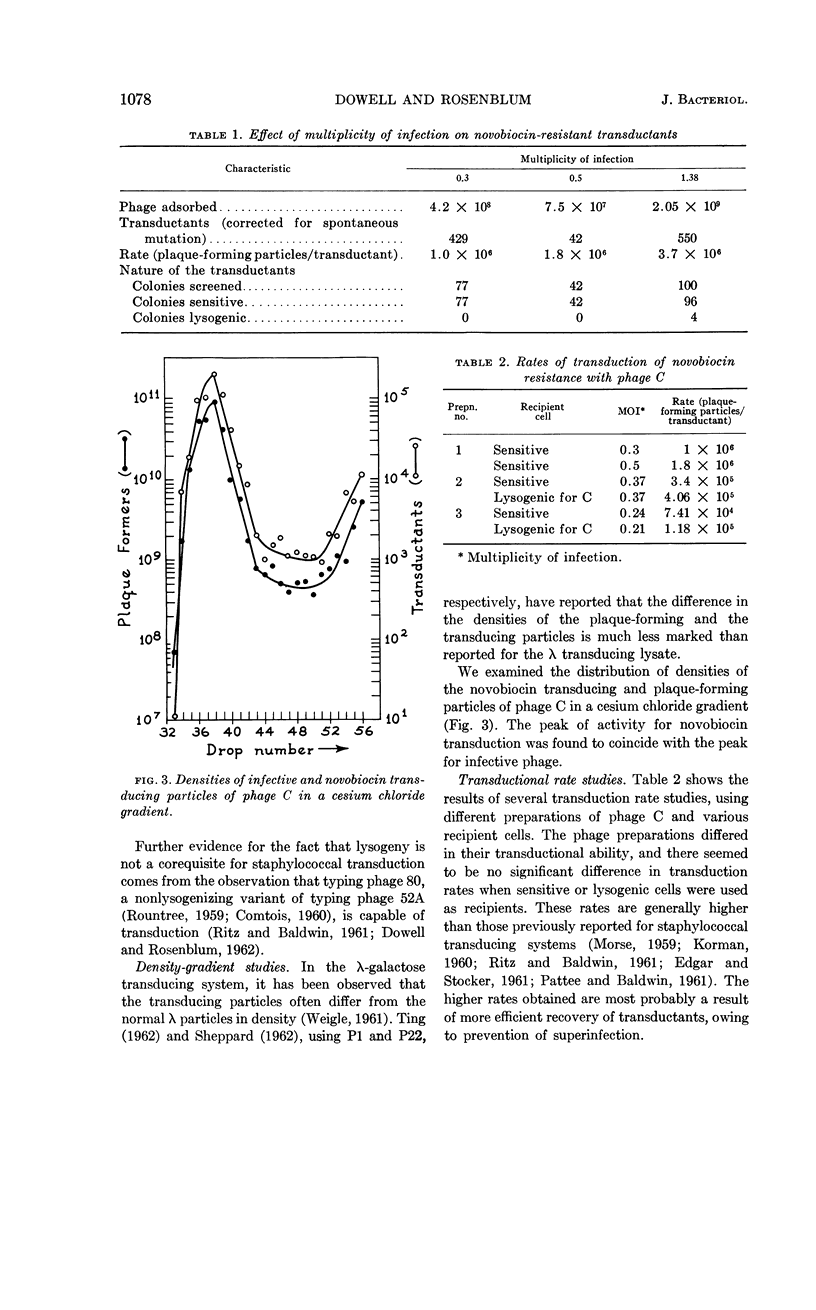
Abstract
Dowell, C. E. (The University of Texas, Dallas) and E. D. Rosenblum. Staphylococcal transducing particle. J. Bacteriol. 84:1076–1079. 1962.—When novobiocin-resistant transductants were isolated under conditions that permitted superinfection, almost all the clones were lysogenic for the transducing phage. If superinfection was prevented, then the transductants isolated were nonlysogenic, suggesting the defective nature of the transducing particle. It was noted that the transducing and plaque-forming particles showed no appreciable difference in buoyant density. No difference was found in transduction rates when either sensitive or lysogenic cells were used as recipients. Transduction rates as high as one transductant per 7 × 104 phage particles were obtained for novobiocin resistance.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARBER W., KELLENBERGER G., WEIGLE J. La défectuosité du phage lambda transducteur. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1957;20(5):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMTOIS R. D. Changes in the phage-typing patterns of Staphlococci following lysogenization with a related group of Staphylococcus bacteriophages. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Oct;6:491–502. doi: 10.1139/m60-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowell C. E., Rosenblum E. D. SEROLOGY AND TRANSDUCTION IN STAPHYLOCOCCAL PHAGE. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84(5):1071–1075. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1071-1075.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDGAR J. B., STOCKER B. A. Metabolic and genetic investigations of nutritionally exacting strains of Staphylococcus pyogenes. Nature. 1961 Sep 9;191:1121–1122. doi: 10.1038/1911121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L. TRANSDUCTION BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 May;45(5):722–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTEE P. A., BALDWIN J. N. Transduction of resistance to chlortetracycline and novobiocin in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:875–881. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.875-881.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITZ H. L., BALDWIN J. N. Transduction of capacity to produce staphylococcal penicillinase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:678–680. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUNTREE P. M. Changes in the phage-typing patterns of staphylococci following lysogenization. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):620–633. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPPARD D. E. Density gradient centrifugation of bacteriophage P22. Virology. 1962 May;17:212–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TING R. C. The specific gravity of transducing particles of bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:115–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE J. Densities of transducing lambda bacteriophages. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:393–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


