Abstract
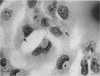
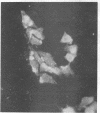
Eaton, Monroe D. (Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass.), Ann E. Farnham, Jeana D. Levinthal, and Anthony R. Scala. Cytopathic effect of the atypical pneumonia organism in cultures of human tissue. J. Bacteriol. 84:1330–1337. 1962.—Three strains of the atypical pneumonia agent were adapted to grow in continuous cell cultures of human amnion or human embryonic lung, with production of initial increased acidity followed by destruction of the cells. Evidence is presented that cytopathic effects of the organism were associated with intracellular growth and formation of microcolonies. Clumps of organisms stained specifically with fluorescein-labeled antibody, and showed distinctive tinctorial reactions with the May Grünwald-Giemsa stain. The cytopathic effect was prevented by fresh serum from a rabbit immunized with an egg-passage strain of the atypical pneumonia agent. Heating the immune serum to 56 C for 30 min abolished the neutralizing effect. The significance of heat-labile serum constituents in killing or inhibition of mycoplasma is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARSKI T. R., SHEPARD C. C. Pleuropneumonia-like (mycoplasma) infections of tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:626–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.626-635.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., FOX H. H., JAMES W. D., BLOOM H. H., MUFSON M. A. Growth of laboratory and naturally occurring strains of Eaton agent in monkey kidney tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Nov;105:371–375. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr Demonstration of Eaton's agent in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Aug-Sep;107:715–718. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EATON M. D., LIU C. Studies on sensitivity to streptomycin of the atypical pneumonia agent. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):784–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.784-787.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FITZGERALD W. A. Inhibition of growth of pleuropneumonia-like organisms by antibody. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):23–30. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS G. A., FOGH J. Fine structure of pleuropneumonia-like organisms in pure culture and in infected tissue culture cells. J Bacteriol. 1960 Feb;79:267–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.2.267-276.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON F. B., QUAN A. L., COOK K., CHANOCK R. M., FOX H. H. Growth of the Eaton agent of primary atypical pneumonia in chick entodermal tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Nov;105:375–377. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., STINEBRING W. R. Intracellular growth of pleuropneumonialike organisms (PPLO) in tissue culture and in ovo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:433–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Studies on primary atypical pneumonia. I. Localization, isolation, and cultivation of a virus in chick embryos. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):455–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Studies on primary atypical pneumonia. III. A factor in normal serum which enhances the reaction between PAP virus and convalescent serum. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:111–123. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMION B. P., GOODBURN G. M. Effect of an organic gold salt on Eaton's primary atypical pneumonia agent and other observations. Nature. 1961 Jan 21;189:247–248. doi: 10.1038/189247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD M. C. Visualization and morphology of pleuropneumonialike organisms in clinical material. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):162–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.162-171.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTLER R. G., CARY S. G., LINDBERG R. B. Reversion of a pleuropneumonia-like organism to a Corynebacterium during tissue culture passage. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):763–774. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]