Abstract
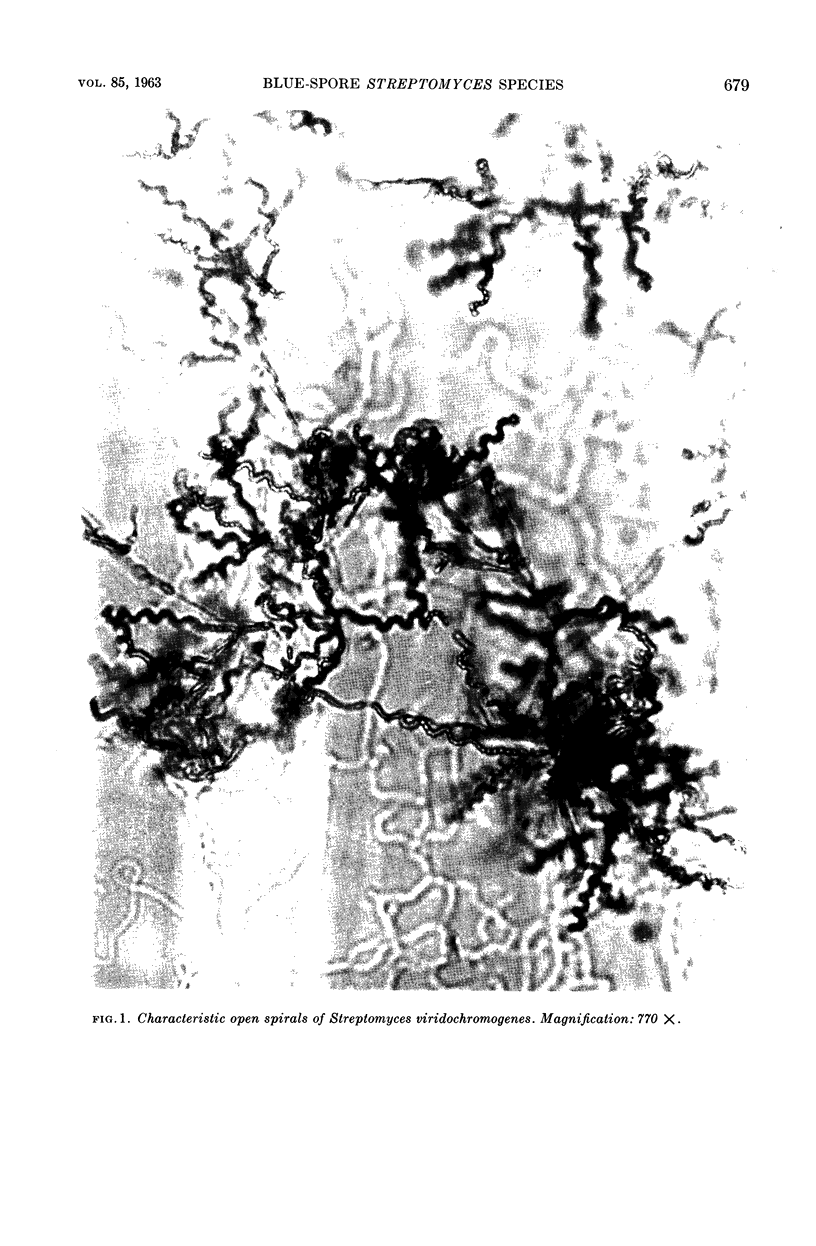
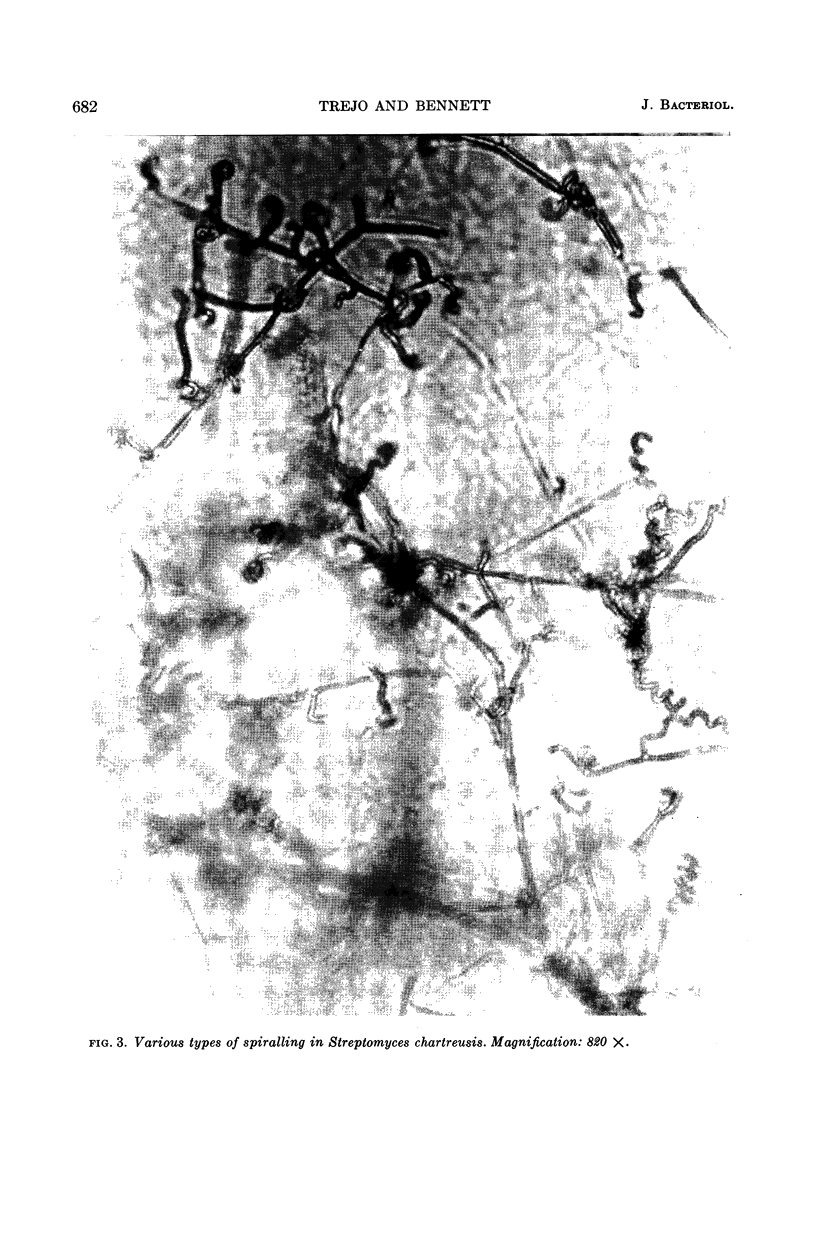
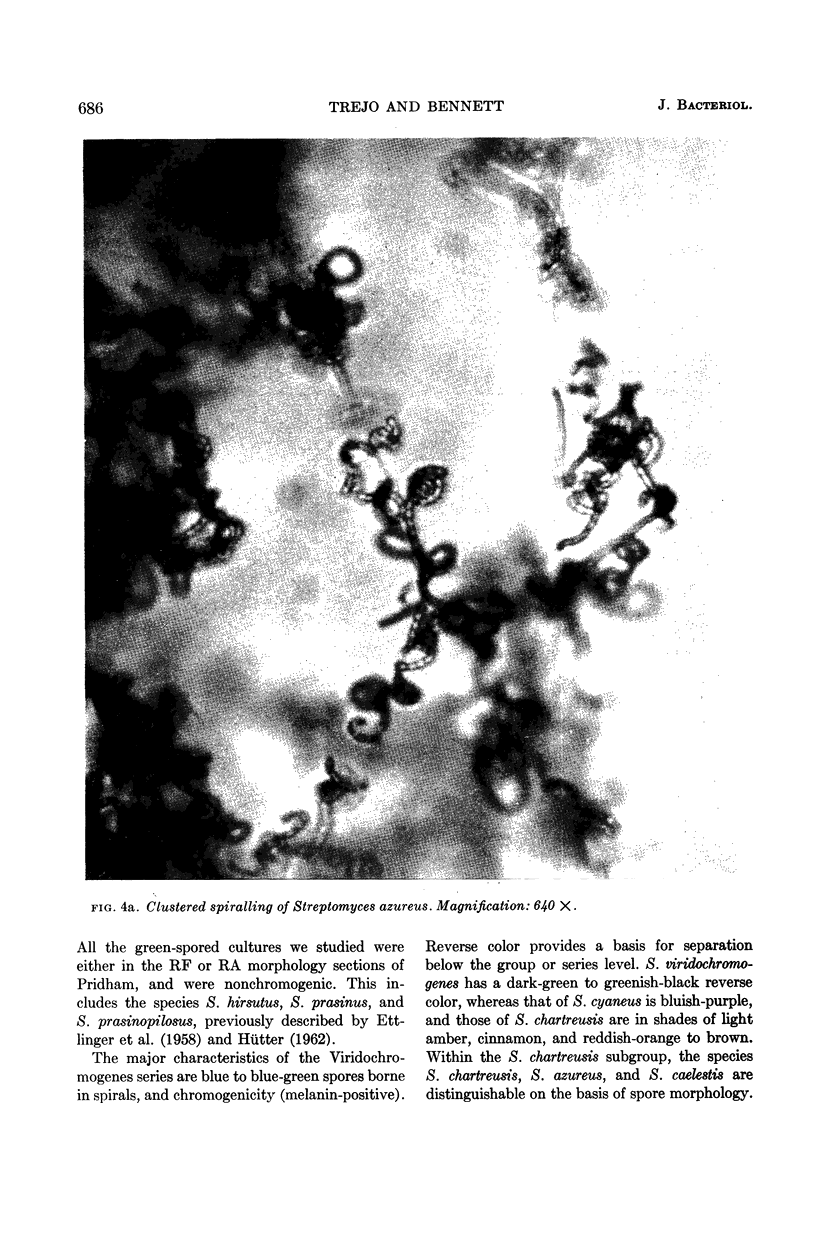
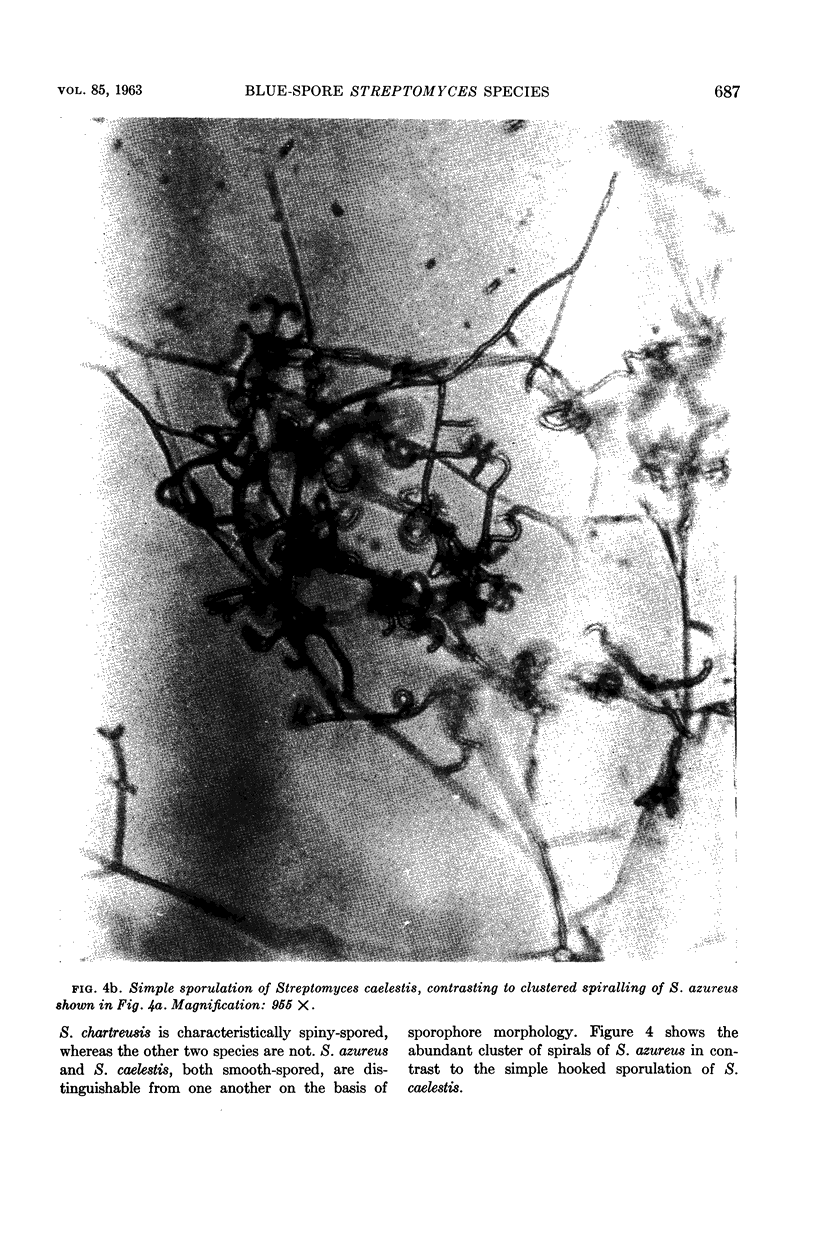
Trejo, W. H. (Squibb Institute for Medical Research, New Brunswick, N.J.) and R. E. Bennett. Streptomyces species comprising the blue-spore series. J. Bacteriol. 85:676–690. 1963.—The objective of this study was to define and delimit the streptomycetes of the blue-spored (Viridochromogenes) series. The series, as defined in this study, includes 11 blue and blue-green species. The green-spored species were excluded on the basis of morphology as well as color. It was proposed that NRRL B-1511 be designated as the neotype strain of Streptomyces viridochromogenes (Krainsky) Waksman and Henrici, and that IMRU 3761 be designated as the neotype for Streptomyces cyaneus (Krassilnikov) Waksman. Evidence was presented to show that physiological criteria cannot be used to differentiate these organisms below the series level. The major characteristics of the Viridochromogenes series are blue to blue-green spores borne in spirals, and chromogenicity (melanin-positive). Reverse color and spore morphology provide a basis for separation below the series level.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DONOVICK R., PAGANO J. F., STOUT H. A., WEINSTEIN M. J. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. I. In vitro studies. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:554–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUNK A., DIVEKAR P. V. Caerulomycin, a new antibiotic from Streptomyces caeruleus Baldacci. I. Production, isolation, assay, and biological properties. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Aug;5:317–321. doi: 10.1139/m59-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. E., MIHM J. M. A comparative study of some strains received as nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):15–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.15-27.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. E., SMITH M. M. Proposed group of characters for the separation of Streptomyces and Nocardia. J Bacteriol. 1955 Feb;69(2):147–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.2.147-150.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUETTER R. [On the systematology of actinomycetes. 5. The genus Streptomyces albus (Rossi-Doria emend. Krainsky) Waksman et Henrici 1943]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:367–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUETTER R. [On the systematology of actinomycetes. 7. Streptomycetes with blue, blue-green and green aerial mycelia]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:23–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY J., KUTSCHER A. H., TUOT I. F. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic: tube dilution sensitivity studies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1959 Nov;12:1334–1339. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(59)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIDHAM T. G., HESSELTINE C. W., BENEDICT R. G. A guide for the classification of streptomycetes according to selected groups; placement of strains in morphological sections. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Jan;6(1):52–79. doi: 10.1128/am.6.1.52-79.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridham T. G., Gottlieb D. The Utilization of Carbon Compounds by Some Actinomycetales as an Aid for Species Determination. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.1.107-114.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANCHEZ-MARROQUIN A. Constancy of characteristics in the streptomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1183–1192. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1183-1192.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABER W. A. Identification of an alkaline-dependent Streptomyces as Streptomyces caeruleus Baldacci and characterization of the species under controlled conditions. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Aug;5:335–344. doi: 10.1139/m59-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRESNER H. D., DANGA F. Hydrogen sulfide production by Streptomyces as a criterion for species differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.239-244.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]