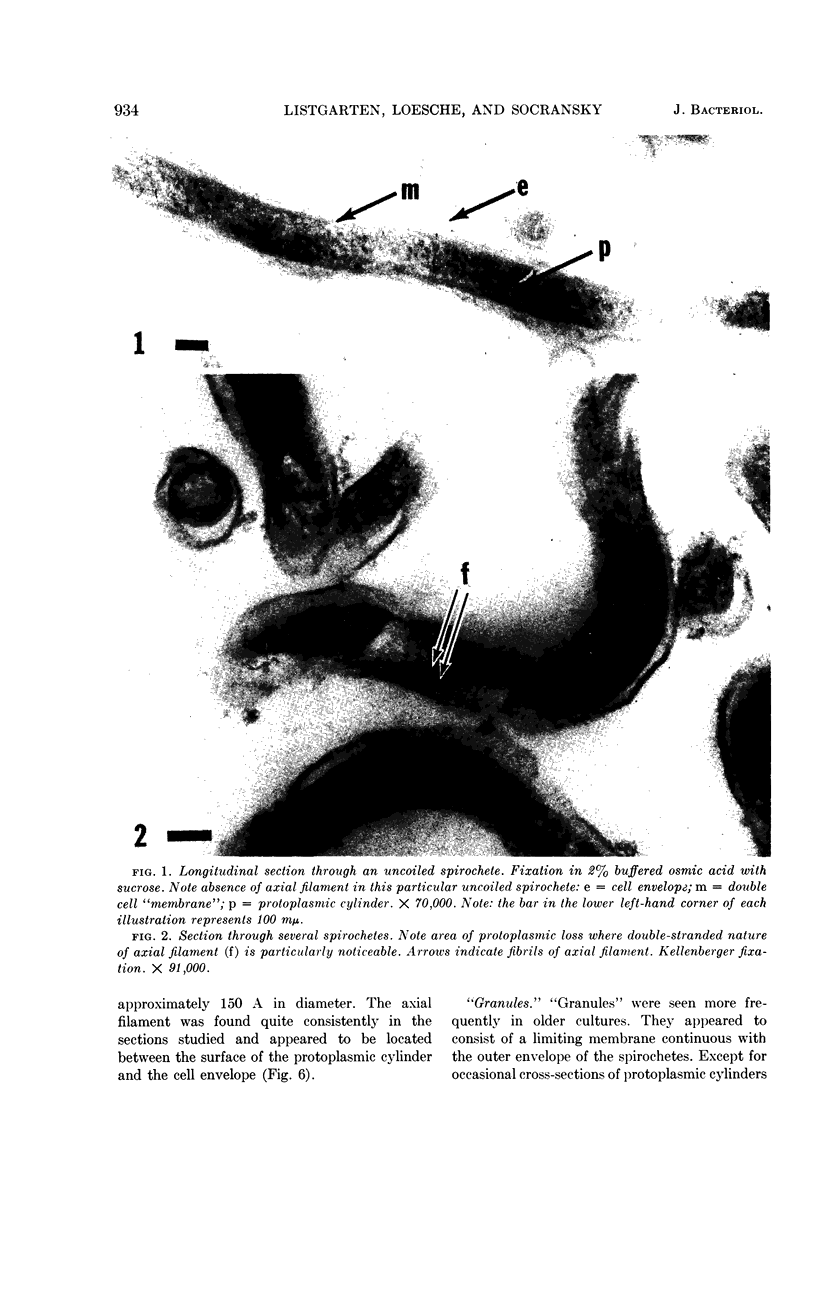
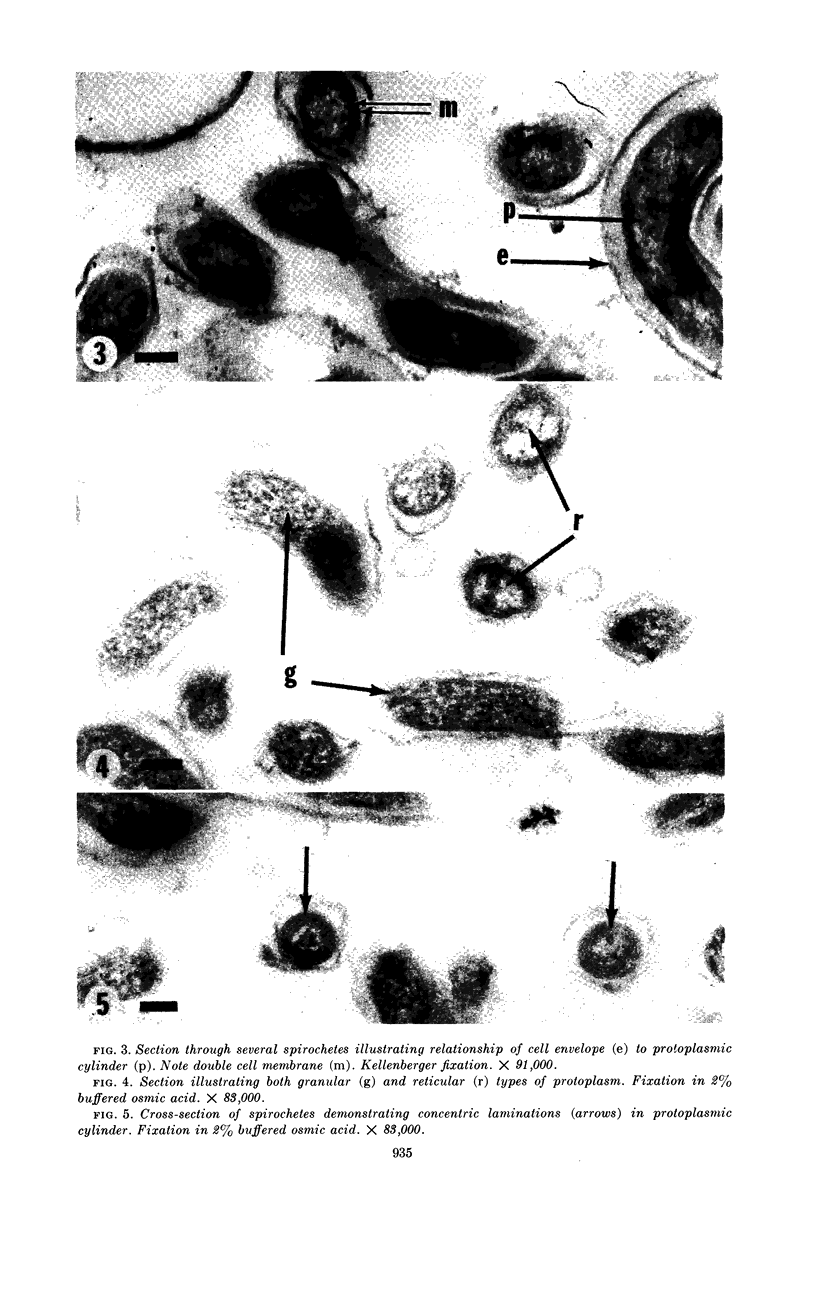
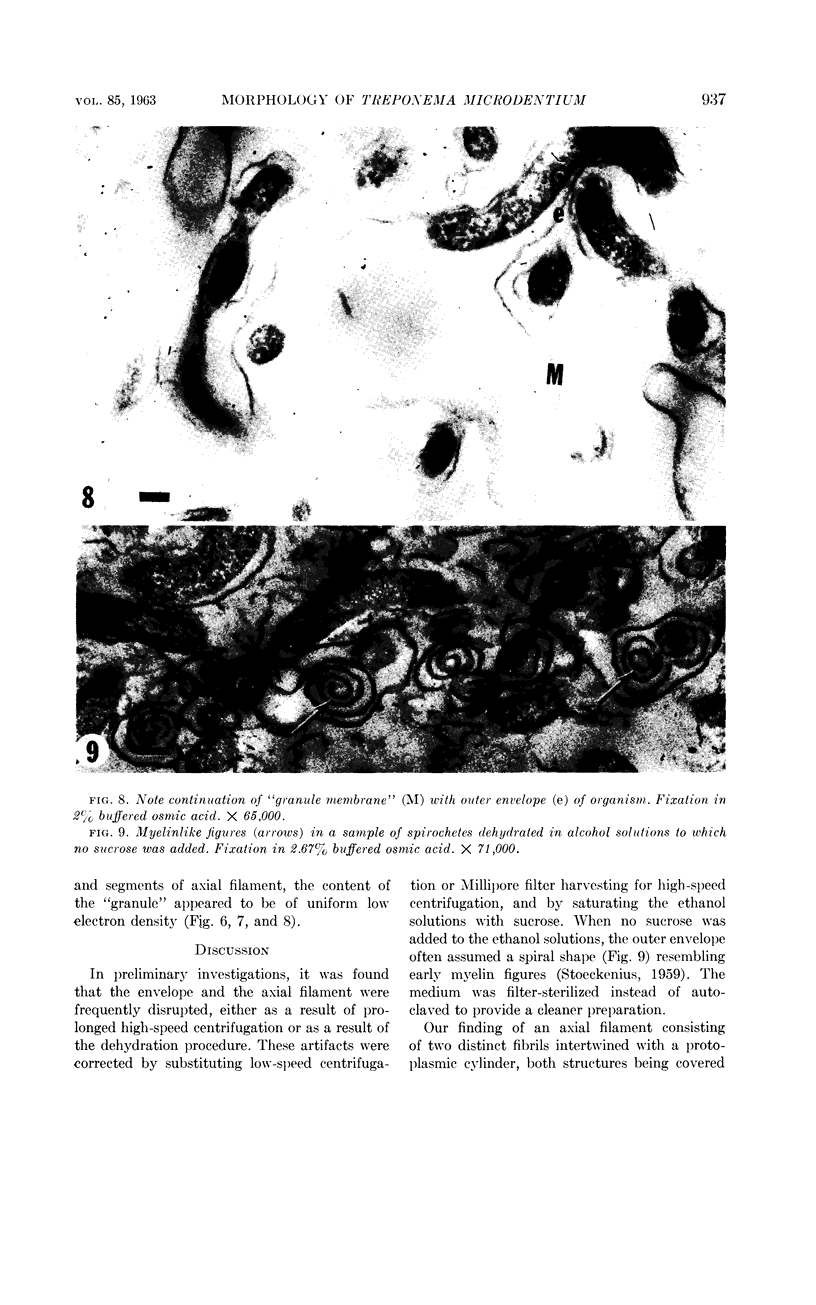
Abstract
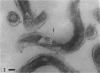
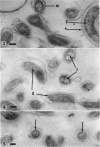
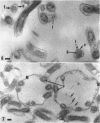
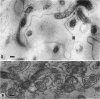
Listgarten, M. A. (Harvard School of Dental Medicine and Forsyth Dental Infirmary, Boston, Mass.), W. J. Loesche, and S. S. Socransky. Morphology of Treponema microdentium as revealed by electron microscopy of ultrathin sections. J. Bacteriol. 85:932–939. 1963.—Broth cultures of a strain of Treponema microdentium were harvested on Millipore filters, fixed in osmic acid, and sectioned for electron microscopy. The sections revealed that the spirochetes had an axial filament, made up of two fibrils approximately 150 A in diameter, which was situated between an external envelope approximately 140 A in thickness and a protoplasmic cylinder. The protoplasmic cylinder had a cross-sectional diameter of 100 to 200 mμ, and was surrounded by a double “membrane” consisting of two 40-A electron-dense structures separated by a 45-A space. Cross-sections of spirochetal “granules” revealed that the limiting membrane was continuous with the outer envelope of the spirochetes, and surrounded the protoplasmic cylinder and axial filament.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABUDIERI B. [The cell structure and serology of Leptospira]. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1960;33:259–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADFIELD J. R. G., CATER D. B. Electron-microscopic evidence on the structure of spirochaetes. Nature. 1952 Jun 7;169(4310):944–946. doi: 10.1038/169944a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN G. B. Electron microscopy of ultrathin sections of bacteria. III. Cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, and nuclear material. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.96-104.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZEKALOWSKI J. W., EAVES G. The structure of leptospirae as revealed by electron microscopy. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):129–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampp E. G., Scott D. B., Wyckoff R. W. Morphologic Characteristics of Certain Cultured Strains of Oral Spirochetes and Treponema pallidum as Revealed by the Electron Microscope. J Bacteriol. 1948 Dec;56(6):755–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.6.755-769.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. E., RAKE G., ROSE N. R. Electron microscope studies of treponemes. III. Flagella. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1951 Nov;35(6):503–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUREAU M., GIUNTINI J. Etude au microscope électronique de quatre espèces de tréponèmes anaérobies d'origine génitale. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Jun;90(6):728–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. G., Wilson R. B. IN VIVO AND IN VITRO OBSERVATIONS OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84(3):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.569-576.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S., Polevitzky K., Anderson T. F. Bacterial Morphology as shown by the Electron Microscope: V. Treponema pallidum, T. macrodentium and T. microdentium. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):15–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.15-24.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON C. F., WHITE F. H. Electron microscope studies and staining reactions of leptospires. J Infect Dis. 1961 Nov-Dec;109:243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S., MACDONALD J. B., SAWYER S. The cultivation of Treponema microdentium as surface colonies. Arch Oral Biol. 1959 Oct;1:171–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(59)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAIN R. H. Electron microscopic studies of the morphology of pathogenic spirochaetes. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):117–128. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARPHOLOMEEVA A. A., STANISLAVSKY E. S. Recherches sur la morphologie des Leptospires à l'aide du microscope électronique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Mar;94(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]