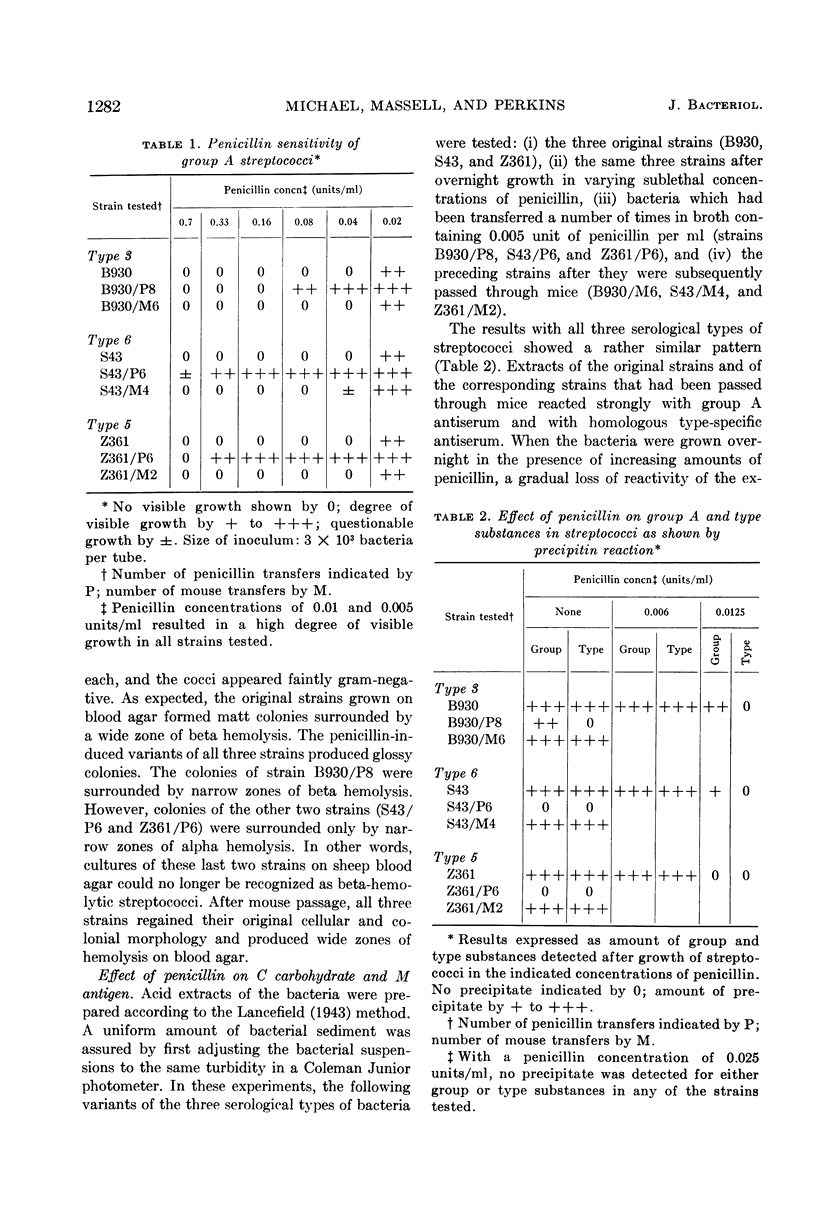
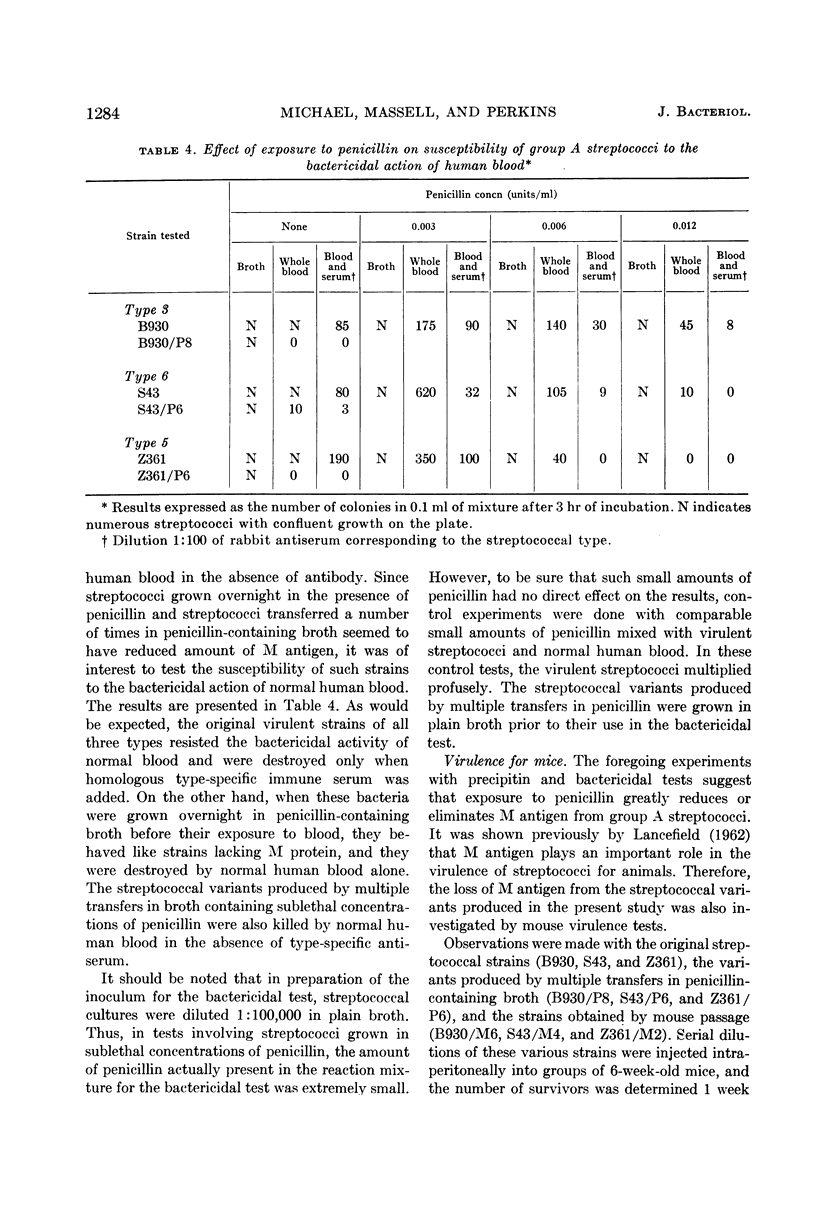
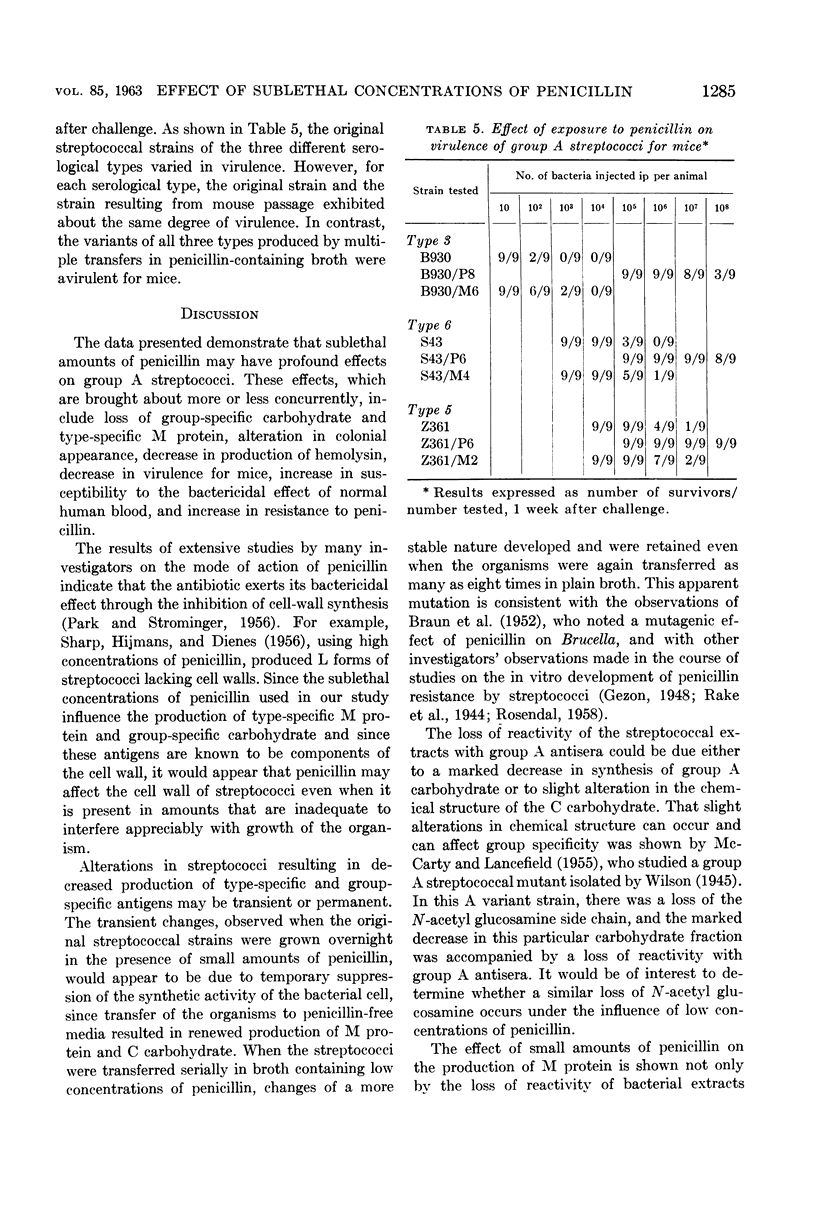
Abstract
Michael, J. Gabriel (House of the Good Samaritan, Children's Hospital Medical Center, Boston, Mass.), Benedict F. Massell, and Robert E. Perkins. Effect of sublethal concentrations of penicillin on the virulence and antigenic composition of group A streptococci. J. Bacteriol. 85:1280–1287. 1963.—Virulent strains of group A streptococci were grown in sublethal concentrations of penicillin and tested for possible changes in colonial morphology, virulence, and antigenic composition. After overnight growth in broth containing penicillin, there was a marked reduction in precipitable group A and M protein content of the bacteria. Upon transfer to broth without antibiotic, the streptococci regained their ability to produce these substances. After multiple transfers in broth containing non-bactericidal levels of penicillin, variants developed which lacked group and type substances and which were also relatively resistant to penicillin. These variants were avirulent for mice and susceptible to the bactericidal action of normal human blood. Two of three strains tested, when grown on blood agar, failed to produce beta hemolysis. The mutants produced by multiple transfers in broth containing small amounts of penicillin, when passed through mice, regained all of their original properties.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUN W., KRAFT M., MEAD D. D., GOODLOW R. J. The effect of penicillin on genetic changes and temporary modifications in populations of brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.1.41-47.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIAK J., HAHN F. E. Concurrent morphological and chemical events in Staphylococcus aureus exposed to penicillin. Science. 1962 Sep 21;137(3534):982–983. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3534.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Mechanism of action of penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):144–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.144-144.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., BRAUN W. Relationships between bacterial resistance to serum and penicillin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jan;97(1):104–107. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., STROMINGER J. L. Mode of action of penicillin. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):99–101. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENDAL K. Investigations of penicillin-resistant streptococci belonging to group A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;42(2):181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP J. T., HIJMANS W., DIENES L. Examination of the L forms of group A streptococci for the group-specific polysaccharide and M protein. J Exp Med. 1957 Feb 1;105(2):153–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


