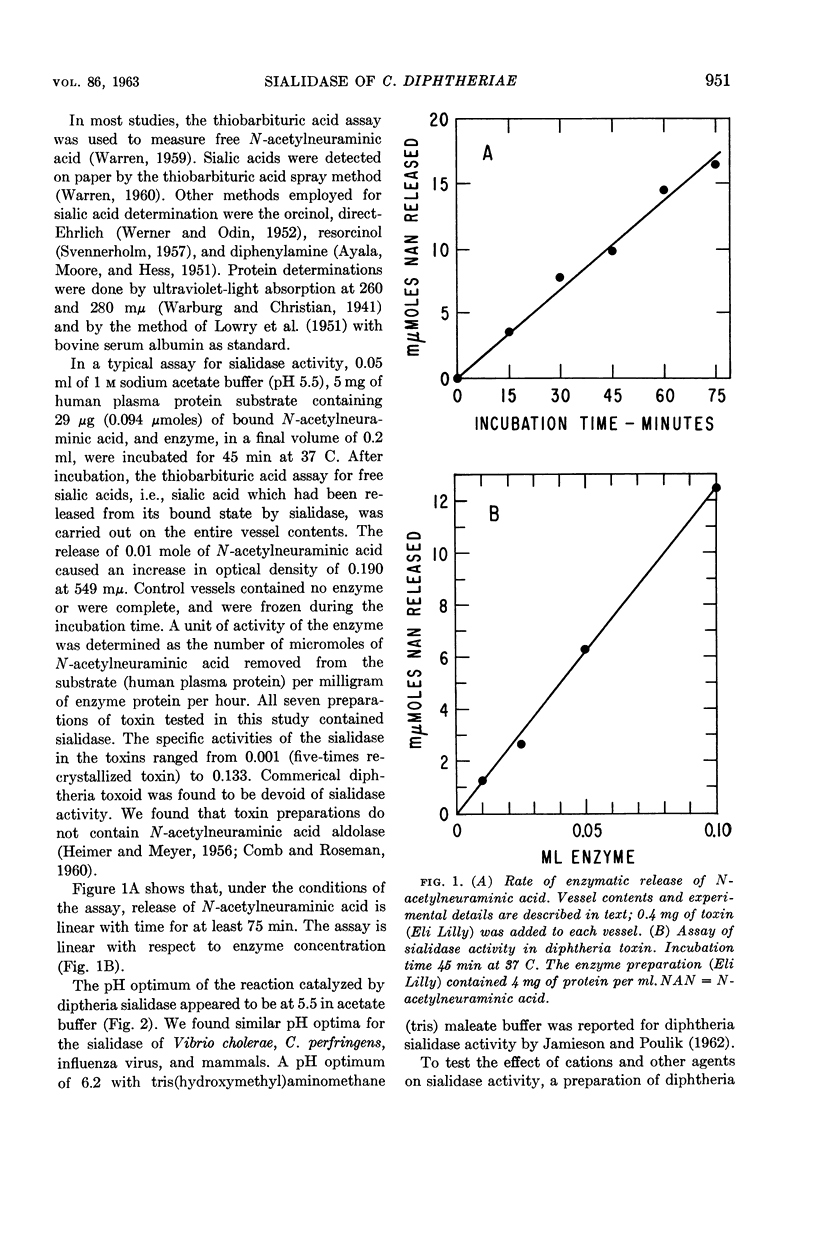
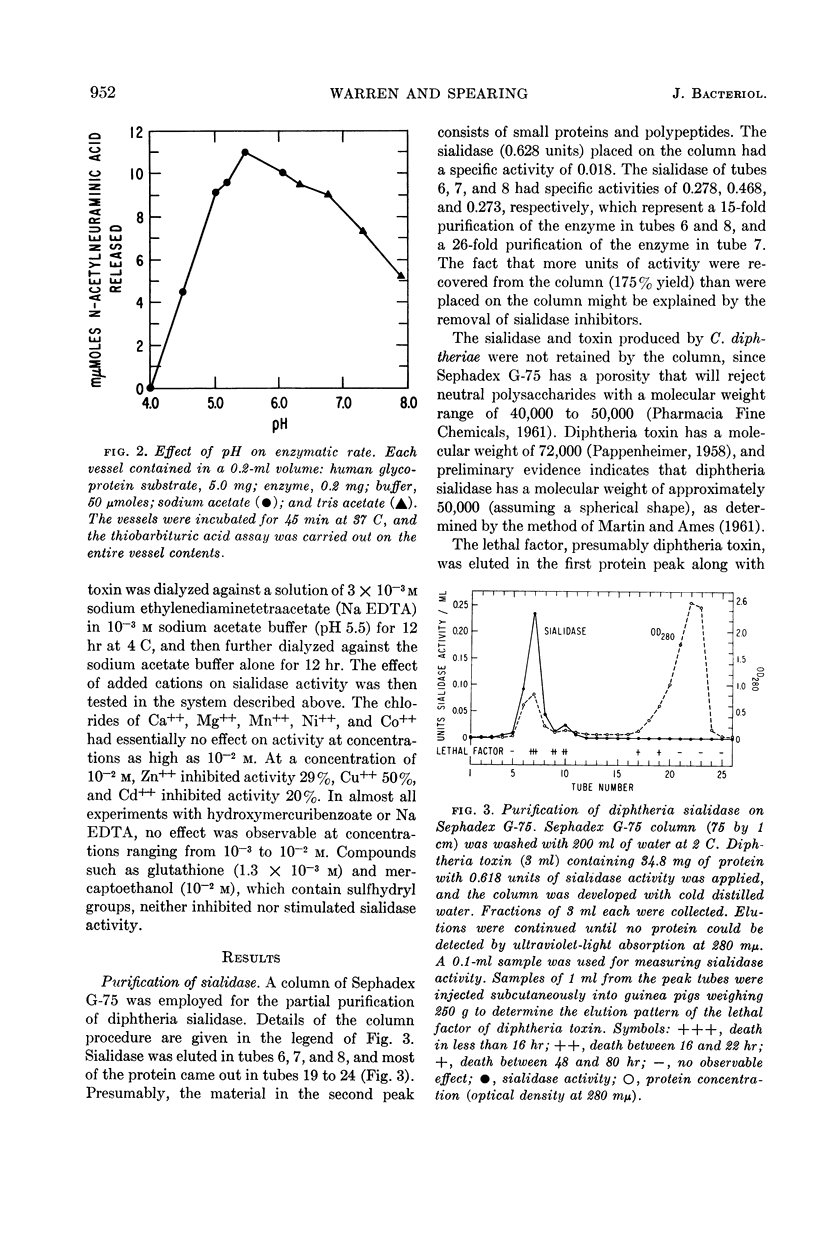
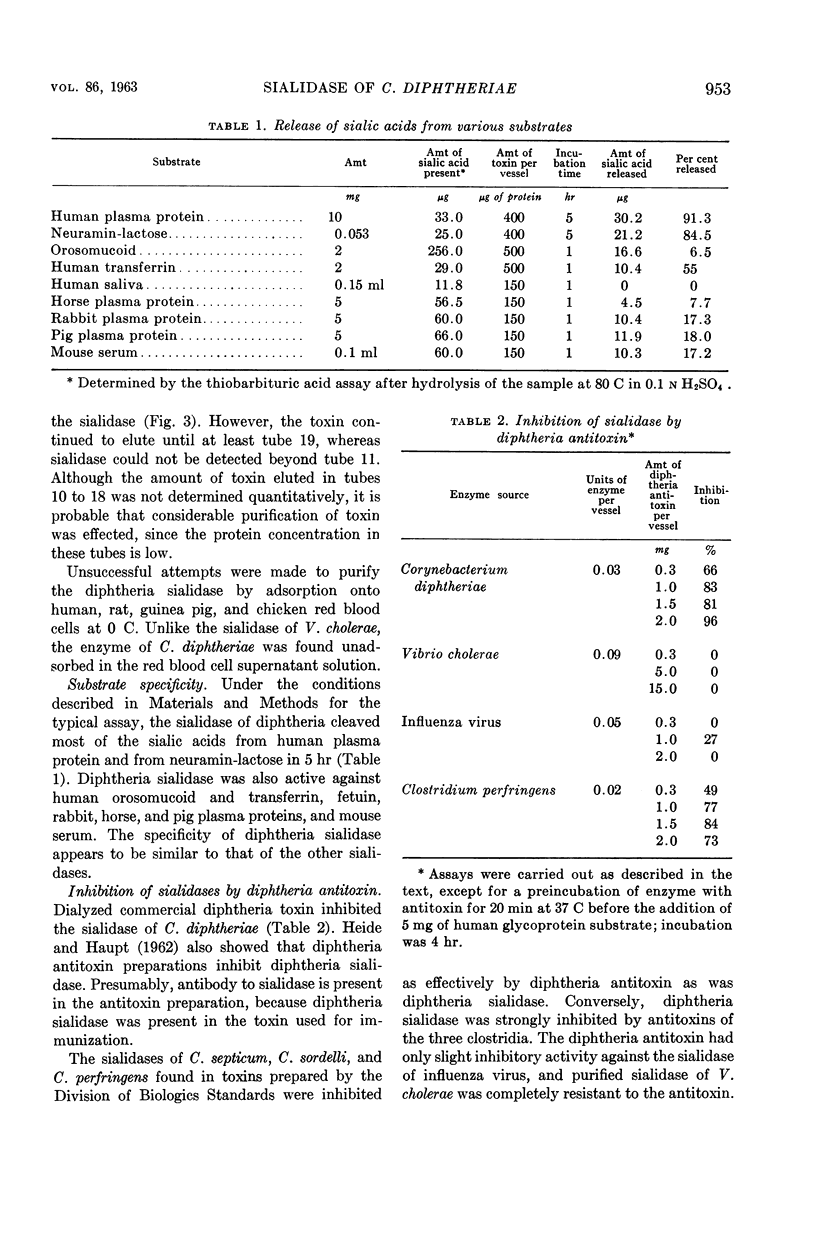
Abstract
Warren, Leonard (National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases, Bethesda, Md.) and C. W. Spearing. Sialidase (neuraminidase) of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Bacteriol. 86:950–955. 1963.—The characteristics of a sialidase produced by Corynebacterium diphtheriae were studied. The enzyme was partially purified from preparations of diphtheria toxin on a column of Sephadex G-75. By this means the lethal factor of diphtheria toxin was separated, in part, from the sialidase activity. There appeared to be a close immunological relationship between the sialidases of C. diphtheriae and clostridia, since a preparation of diphtheria antitoxin was as effective an inhibitor of diphtheria sialidase as of the sialidase of three species of clostridia. Conversely, antitoxin to clostridia inhibited diphtheria sialidase. Diphtheria antitoxin was essentially inactive toward influenza virus sialidase, and was completely inactive against purified sialidase of Vibrio cholerae. Removal of sialic acid from the proteins in a preparation of diphtheria antitoxin did not alter the inhibitory activity of the antitoxin against diphtheria sialidase. The enzyme operated optimally at pH 5.5 and did not require calcium ions for activity. The substrate specificity of diphtheria sialidase appears to be the same as that of other previously described sialidases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., FRENCH E. L. Purification of bacterial neuraminidase (receptor-destroying enzyme). Nature. 1959 Jun 20;183(4677):1740–1741. doi: 10.1038/1831740b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AYALA W., MOORE L. V., HESS E. L. The purple color reaction given by diphenylamine reagent. I. With normal and rheumatic fever sera. J Clin Invest. 1951 Jul;30(7):781–785. doi: 10.1172/JCI102492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARUBELLI R., TRUCCO R. E., CAPUTTO R. Neuraminidase activity in mammalian organs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 18;60:196–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. The sialic acids. I. The structure and enzymatic synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2529–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNIS S. M. Spermicidal activity of bacterial endotoxin. Nature. 1962 Sep 22;195:1227–1228. doi: 10.1038/1951227b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Meyer K. STUDIES ON SIALIC ACID OF SUBMAXILLARY MUCOID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):728–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER W. C., BEARN A. G. Alterations in sialic acid content of human transferrin. Science. 1961 Mar 31;133(3457):1014–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3457.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Interaction of transferrin, haptoglobin and other serum proteins with neuraminidase of diphtheria toxin. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Jul;6:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Tests of purity of diphtheria toxins by electrophoresis in starch gel. Nature. 1956 May 26;177(4517):982–983. doi: 10.1038/177982a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAFELSON M. E., Jr THE NEURAMINIDASES AND THEIR ACTION ON GLYCOPROTEINS AND OTHER SIALIC ACID-CONTAINING COMPOUNDS. Expos Annu Biochim Med. 1963;24:121–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. On the isolation and characterization of N-acetyl-sialic acid. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1956 Jun 30;61(1-2):74–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L., SPEARING C. W. Mammalian sialidase (neuraminidase). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:489–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. Thiobarbituric acid spray reaction for deoxy sugars and sialic acids. Nature. 1960 Apr 16;186:237–237. doi: 10.1038/186237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER I., ODIN L. On the presence of sialic acid in certain glycoproteins and in gangliosides. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1952;57(3-4):230–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


