Abstract
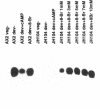
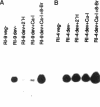
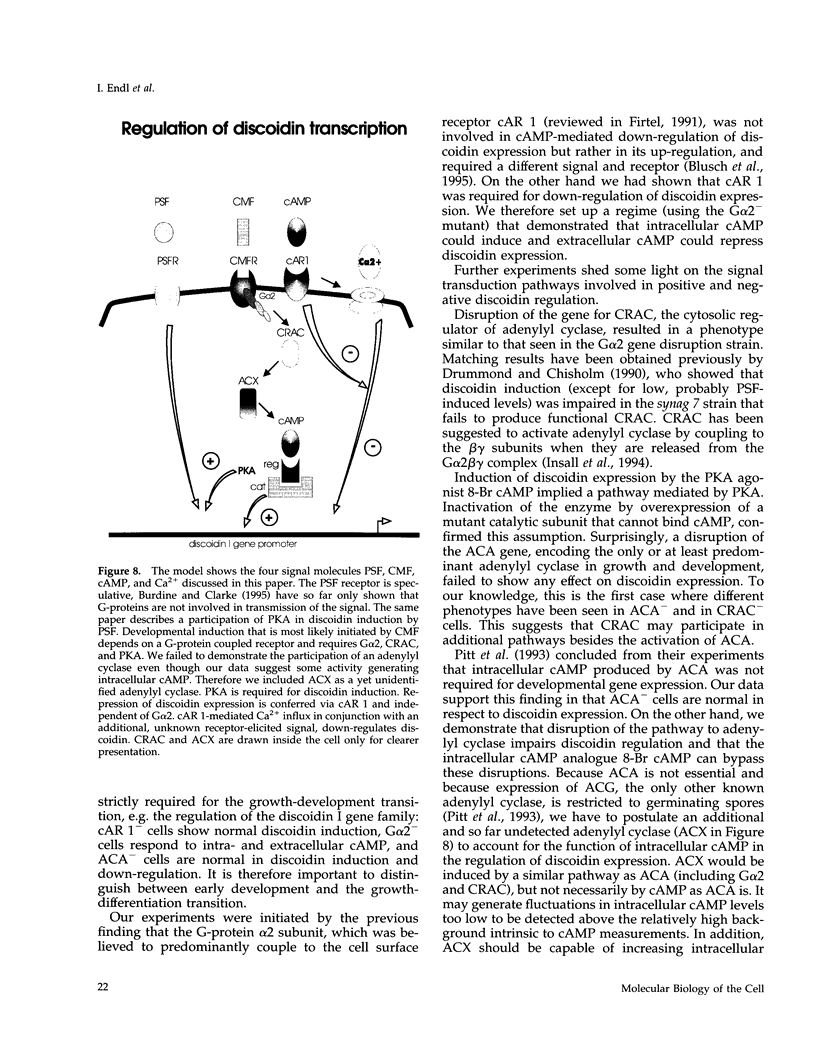
In Dictyostelium, cAMP plays a role as an intracellular second messenger and in addition, as an extracellular first messenger. Both functions are thought to be tightly linked because adenylyl cyclase is coupled via G-proteins to the cell surface cAMP receptor cAR 1. Using the discoidin I gene family as a molecular marker for the first stages of development, we show here that induction of transcription requires the G-protein subunit alpha 2 and thus an as yet unidentified surface receptor, CRAC (cytosolic regulator of adenylyl cyclase), and PKA. Induction can be conferred by an increase in intracellular cAMP. In contrast, transcriptional down-regulation occurs by stimulation of cAR 1 with extracellular cAMP and a subsequent, G-protein-independent Ca2+ influx. In a G alpha 2 gene disruption mutant, discoidin I expression can be efficiently modulated by analogues simulating intracellular cAMP (discoidin induction) and extracellular cAMP (discoidin down-regulation). We thus demonstrate possible antagonistic functions of intra- and extracellular cAMP.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S., Cibulsky A. M., Cuneo S. D. Multiple regulatory genes control expression of a gene family during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A. Mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum blocked in expression of all members of the developmentally regulated discoidin multigene family. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S., Sydow L. M., Wessels D., Soll D. R. Discoidin proteins of Dictyostelium are necessary for normal cytoskeletal organization and cellular morphology during aggregation. Differentiation. 1992 Nov;51(3):149–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1992.tb00691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusch J. H., Nellen W. Folate responsiveness during growth and development of Dictyostelium: separate but related pathways control chemotaxis and gene regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusch J., Alexander S., Nellen W. Multiple signal transduction pathways regulate discoidin I gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1995 Apr;58(4):253–260. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1995.5840253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusch J., Morandini P., Nellen W. Transcriptional regulation by folate: inducible gene expression in Dictyostelium transformants during growth and early development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6235–6238. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdine V., Clarke M. Genetic and physiologic modulation of the prestarvation response in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Mar;6(3):311–325. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Dominguez N., Yuen I. S., Gomer R. H. Growing and starving Dictyostelium cells produce distinct density-sensing factors. Dev Biol. 1992 Aug;152(2):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Kayman S. C., Riley K. Density-dependent induction of discoidin-I synthesis in exponentially growing cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1987;34(2):79–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Nellen W., Gomer R. H., Firtel R. A. Phenocopy of discoidin I-minus mutants by antisense transformation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine J. M., Tsang A. S., Williams J. G. Differential expression of the members of the discoidin I multigene family during growth and development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Chisholm R. L. A pleiotropic defect in cAMP-regulated gene expression in the Dictyostelium agg- mutant synag 7. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90071-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Signal transduction pathways controlling multicellular development in Dictyostelium. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Fromm H., Huesgen A., Wick U. Control of cell-contact sites by cyclic AMP pulses in differentiating Dictyostelium cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):547–549. doi: 10.1038/255547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood A. J., Hopper N. A., Simon M. N., Bouzid S., Veron M., Williams J. G. Multiple roles for cAMP-dependent protein kinase during Dictyostelium development. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90266-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insall R., Kuspa A., Lilly P. J., Shaulsky G., Levin L. R., Loomis W. F., Devreotes P. CRAC, a cytosolic protein containing a pleckstrin homology domain, is required for receptor and G protein-mediated activation of adenylyl cyclase in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1537–1545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R., Gomer R. H. A developmentally regulated cell surface receptor for a density-sensing factor in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9128–9136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniak M., Saur U., Nellen W. A colony-blot technique for the detection of specific transcripts in eukaryotes. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):78–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Firtel R. A. cAMP-dependent protein kinase differentially regulates prestalk and prespore differentiation during Dictyostelium development. Development. 1993 Sep;119(1):135–146. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne J. L., Devreotes P. N. The surface cyclic AMP receptors, cAR1, cAR2, and cAR3, promote Ca2+ influx in Dictyostelium discoideum by a G alpha 2-independent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):283–292. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt G. S., Brandt R., Lin K. C., Devreotes P. N., Schaap P. Extracellular cAMP is sufficient to restore developmental gene expression and morphogenesis in Dictyostelium cells lacking the aggregation adenylyl cyclase (ACA). Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2172–2180. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt G. S., Milona N., Borleis J., Lin K. C., Reed R. R., Devreotes P. N. Structurally distinct and stage-specific adenylyl cyclase genes play different roles in Dictyostelium development. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90411-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley B. B., Jensen B. R., Barclay S. L. Conditions that elevate intracellular cyclic AMP levels promote spore formation in Dictyostelium. Differentiation. 1989 Jul;41(1):5–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlatterer C., Gollnick F., Schmidt E., Meyer R., Knoll G. Challenge with high concentrations of cyclic AMP induces transient changes in the cytosolic free calcium concentration in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Sci. 1994 Aug;107(Pt 8):2107–2115. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.8.2107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza G. M., Klein C., Maia J. C., Da Silva A. M. Calcium uptake and gp80 messenger RNA destabilization follows cAMP receptor down regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Signal. 1994 Nov;6(8):883–895. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauti F., Morandini P., Blusch J., Sachse A., Nellen W. Regulation of the Discoidin I gamma gene in Dictyostelium discoideum: identification of individual promoter elements mediating induction of transcription and repression by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4080–4088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterauer B., Jacobsen G., Morandini P., MacWilliams H. Mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum with defects in the regulation of discoidin I expression. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):184–195. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen I. S., Jain R., Bishop J. D., Lindsey D. F., Deery W. J., Van Haastert P. J., Gomer R. H. A density-sensing factor regulates signal transduction in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1251–1262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]