Abstract
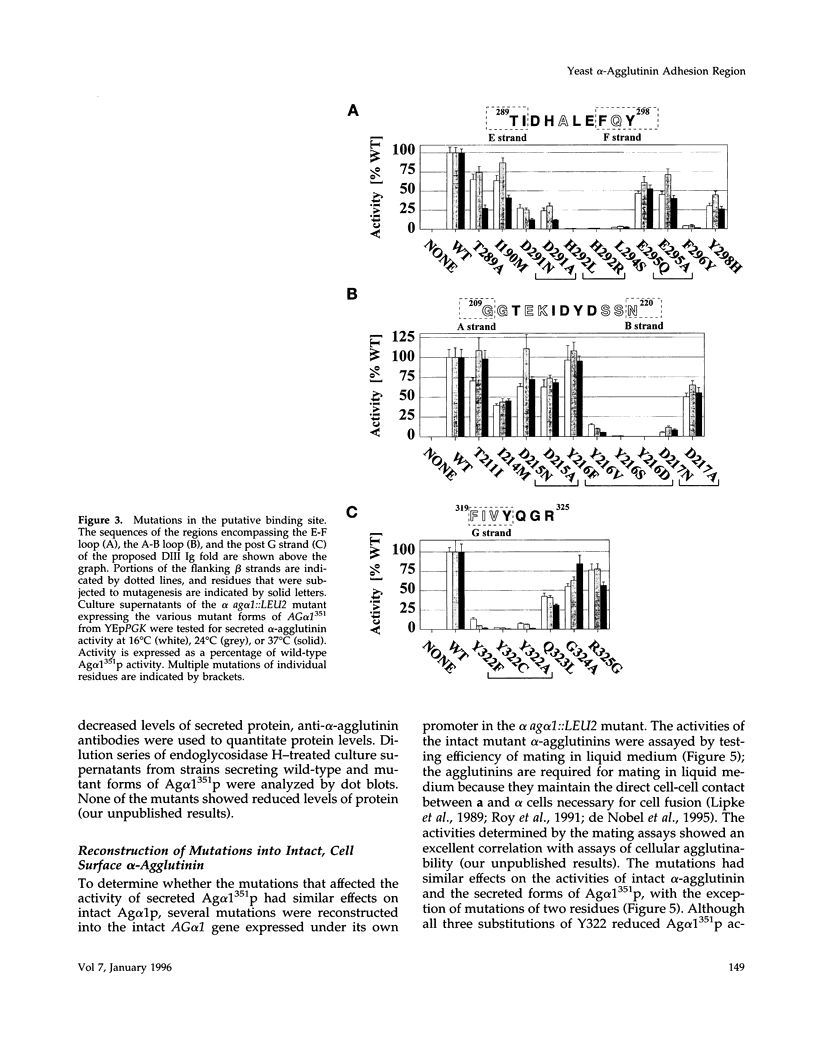
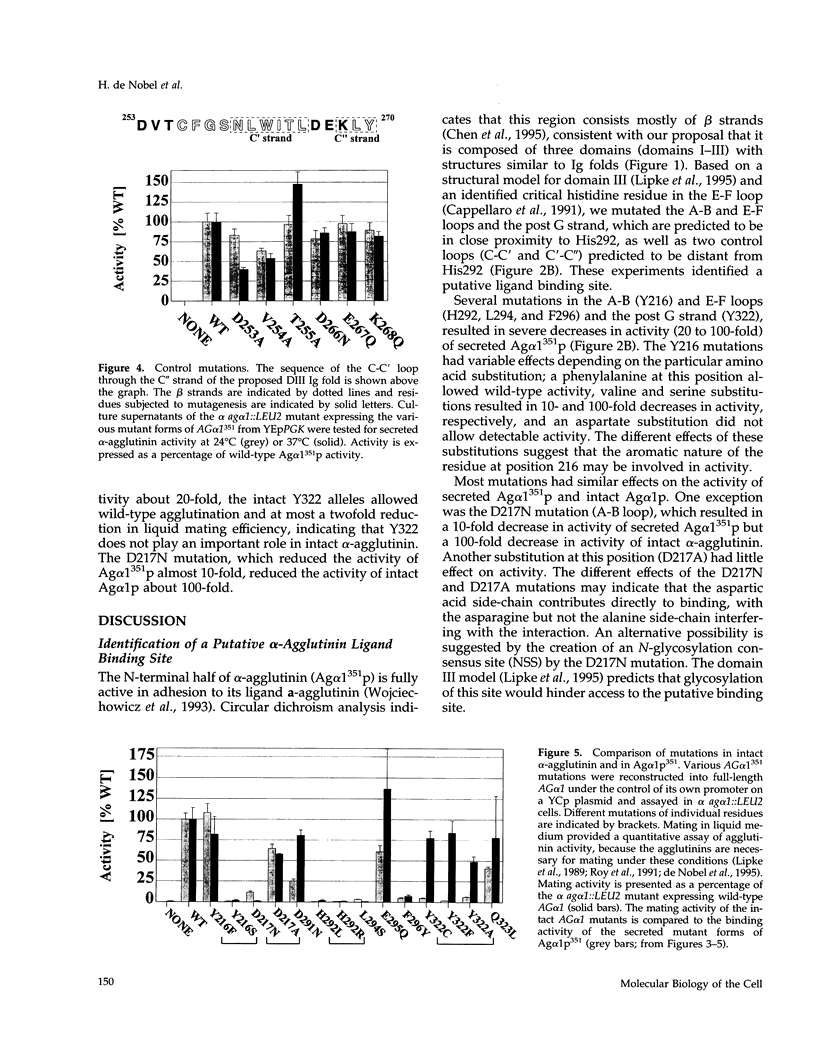
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae adhesion protein alpha-agglutinin (Ag alpha 1p) is expressed by alpha cells and binds to the complementary a-agglutinin expressed by a cells. The N-terminal half of alpha-agglutinin is sufficient for ligand binding and has been proposed to contain an immunoglobulin (Ig) fold domain. Based on a structural homology model for this domain and a previously identified critical residue (His292), we made Ag alpha 1p mutations in three discontinuous patches of the domain that are predicted to be in close proximity to His292 in the model. Residues in each of the three patches were identified that are important for activity and therefore define a putative ligand binding site, whereas mutations in distant loops had no effect on activity. This putative binding site is on a different surface of the Ig fold than the defined binding sites of immunoglobulins and other members of the Ig superfamily. Comparison of protein interaction sites by structural and mutational analysis has indicated that the area of surface contact is larger than the functional binding site identified by mutagenesis. The putative alpha-agglutinin binding site is therefore likely to identify residues that contribute to the functional binding site within a larger area that contacts a-agglutinin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alzari P. M., Lascombe M. B., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of antibodies. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:555–580. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arulanandam A. R., Withka J. M., Wyss D. F., Wagner G., Kister A., Pallai P., Recny M. A., Reinherz E. L. The CD58 (LFA-3) binding site is a localized and highly charged surface area on the AGFCC'C" face of the human CD2 adhesion domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11613–11617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Presta L. G., Marsters S. A., Camerato T. R., Rosenthal K. A., Fendly B. M., Capon D. J. Mapping the CD4 binding site for human immunodeficiency virus by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7150–7154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass S. H., Mulkerrin M. G., Wells J. A. A systematic mutational analysis of hormone-binding determinants in the human growth hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappellaro C., Hauser K., Mrśa V., Watzele M., Watzele G., Gruber C., Tanner W. Saccharomyces cerevisiae a- and alpha-agglutinin: characterization of their molecular interaction. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4081–4088. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
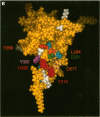
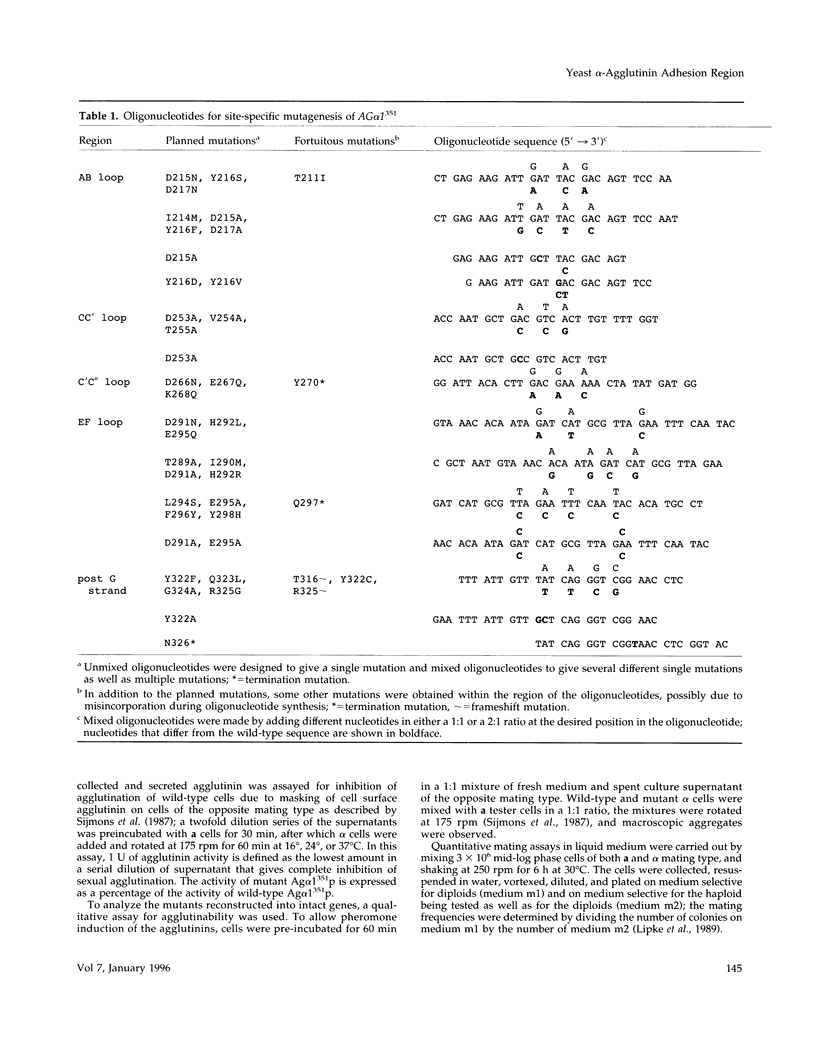
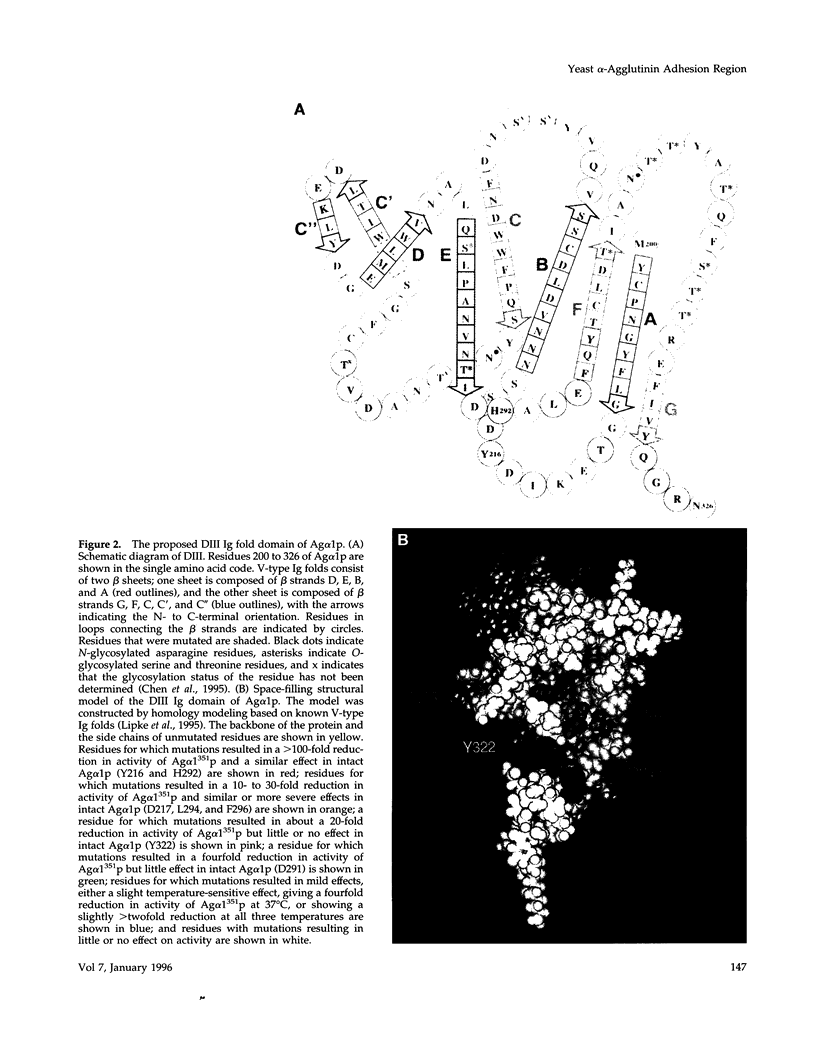
- Chen M. H., Shen Z. M., Bobin S., Kahn P. C., Lipke P. N. Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae alpha-agglutinin. Evidence for a yeast cell wall protein with multiple immunoglobulin-like domains with atypical disulfides. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 3;270(44):26168–26177. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.44.26168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Novotný J., Bruccoleri R., Karplus M. Domain association in immunoglobulin molecules. The packing of variable domains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clackson T., Wells J. A. A hot spot of binding energy in a hormone-receptor interface. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):383–386. doi: 10.1126/science.7529940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., Hussey R. E., Steinbrich R., Ramachandran H., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L. Substitution of murine for human CD4 residues identifies amino acids critical for HIV-gp120 binding. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):363–366. doi: 10.1038/335363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., Sieh M., Pious D. A., Reinherz E. L. Identification of human CD4 residues affecting class II MHC versus HIV-1 gp120 binding. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):548–551. doi: 10.1038/339548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Laver W. G., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., Tulloch P. A., Air G. M., Webster R. G. Three-dimensional structure of a complex of antibody with influenza virus neuraminidase. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):358–363. doi: 10.1038/326358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M. Structure of antibody-antigen complexes: implications for immune recognition. Adv Immunol. 1988;43:99–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. Comparison of a structural and a functional epitope. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):554–563. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll P. C., Cyster J. G., Campbell I. D., Williams A. F. Structure of domain 1 of rat T lymphocyte CD2 antigen. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):762–765. doi: 10.1038/353762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleury S., Lamarre D., Meloche S., Ryu S. E., Cantin C., Hendrickson W. A., Sekaly R. P. Mutational analysis of the interaction between CD4 and class II MHC: class II antigens contact CD4 on a surface opposite the gp120-binding site. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1037–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser K., Tanner W. Purification of the inducible alpha-agglutinin of S. cerevisiae and molecular cloning of the gene. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):290–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. E., Russell S. J., Baier M., Winter G. The contribution of contact and non-contact residues of antibody in the affinity of binding to antigen. The interaction of mutant D1.3 antibodies with lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):958–964. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness C. L., Bates P. A., Little A. J., Buckley C. D., McDowall A., Bossy D., Hogg N., Simmons D. L. Analysis of the binding site on intercellular adhesion molecule 3 for the leukocyte integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):877–884. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16027–16030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Davis S. J., Williams A. F., Harlos K., Stuart D. I. Crystal structure at 2.8 A resolution of a soluble form of the cell adhesion molecule CD2. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):232–239. doi: 10.1038/360232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. S., Kane J., Kurjan J., Stadel J. M., Tipper D. J. Effects of expression of mammalian G alpha and hybrid mammalian-yeast G alpha proteins on the yeast pheromone response signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2582–2590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Axel R., Hendrickson W. A. Crystal structure of a soluble form of the human T cell coreceptor CD8 at 2.6 A resolution. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1145–1162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90085-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipke P. N., Chen M. H., de Nobel H., Kurjan J., Kahn P. C. Homology modeling of an immunoglobulin-like domain in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae adhesion protein alpha-agglutinin. Protein Sci. 1995 Oct;4(10):2168–2178. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipke P. N., Kurjan J. Sexual agglutination in budding yeasts: structure, function, and regulation of adhesion glycoproteins. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):180–194. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.180-194.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipke P. N., Wojciechowicz D., Kurjan J. AG alpha 1 is the structural gene for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae alpha-agglutinin, a cell surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions during mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3155–3165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. F., Kurjan J., Lipke P. N. A pathway for cell wall anchorage of Saccharomyces cerevisiae alpha-agglutinin. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4825–4833. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. F., Montijn R. C., Brown J. L., Klis F., Kurjan J., Bussey H., Lipke P. N. Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-dependent cross-linking of alpha-agglutinin and beta 1,6-glucan in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):333–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overduin M., Harvey T. S., Bagby S., Tong K. I., Yau P., Takeichi M., Ikura M. Solution structure of the epithelial cadherin domain responsible for selective cell adhesion. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):386–389. doi: 10.1126/science.7824937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Lu C. F., Marykwas D. L., Lipke P. N., Kurjan J. The AGA1 product is involved in cell surface attachment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell adhesion glycoprotein a-agglutinin. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4196–4206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Silverton E. W., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Smith-Gill S. J., Finzel B. C., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of an antibody-antigen complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijmons P. C., Nederbragt A. J., Klis F. M., Van den Ende H. Isolation and composition of the constitutive agglutinins from haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Sep;148(3):208–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00414813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Erickson H. P., Springer T. A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90805-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrance K., Heller P., Wu Y. S., Lipke P. N. Identification of glycoprotein components of alpha-agglutinin, a cell adhesion protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.475-482.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrance K., Lipke P. N. Sexual agglutination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):889–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.889-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. E-cadherin: a distant member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):342–342. doi: 10.1126/science.7824932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowicz D., Lu C. F., Kurjan J., Lipke P. N. Cell surface anchorage and ligand-binding domains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell adhesion protein alpha-agglutinin, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2554–2563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nobel H., Pike J., Lipke P. N., Kurjan J. Genetics of a-agglutunin function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 May 20;247(4):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00293141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]