Abstract
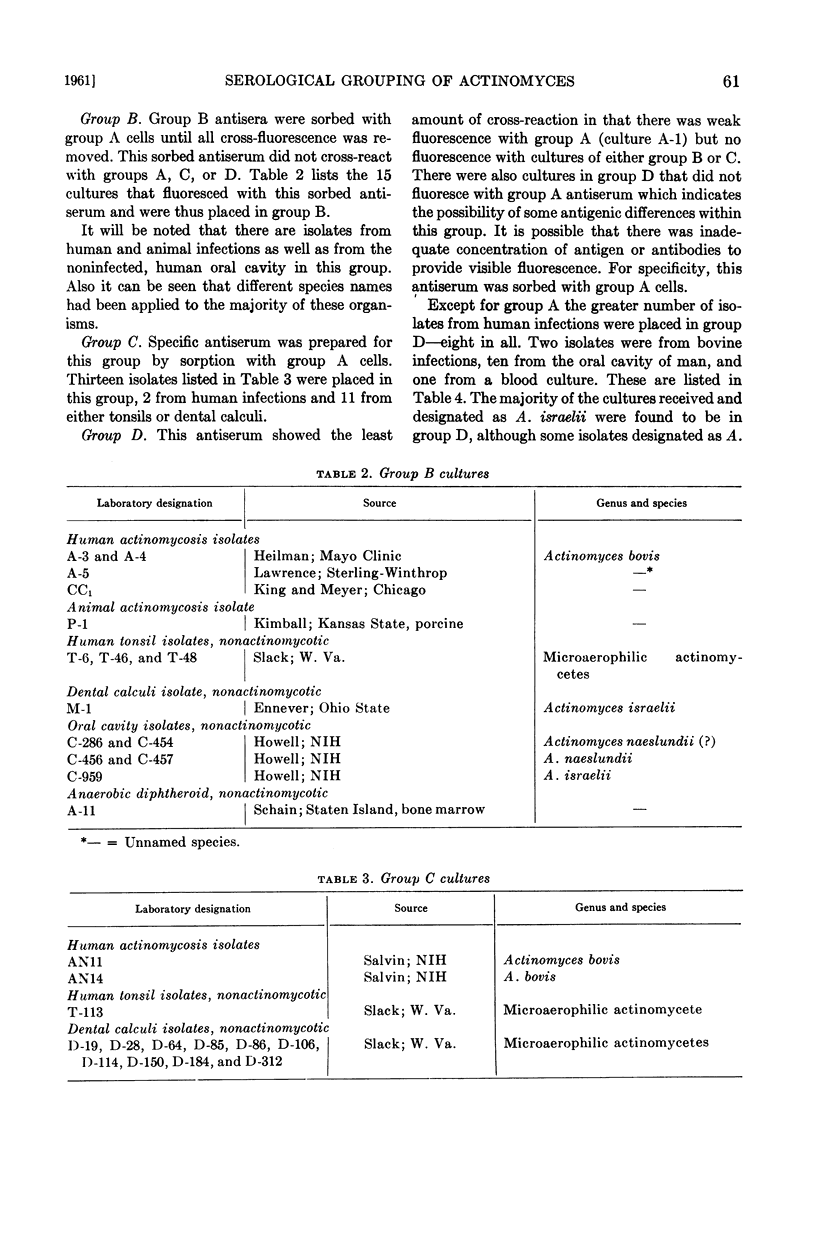
Slack, John M. (West Virginia University, Morgantown), Ann Winger, and Dane W. Moore, Jr. Serological grouping of actinomyces by means of fluorescent antibodies. J. Bacteriol. 82:54–65. 1961.—Serological groups A, B, C and D of actinomyces were established using fluorescent antibody techniques. One hundred and thirty-eight cultures were included in the study. Eighty-nine were classed in group A, 15 in B, 13 in C, and 21 in D.
The isolates were from patients and animals with actinomycosis and from healthy human beings. There was no correlation between source of the isolate and serological group. Furthermore, no one species could be placed exclusively in one group although the majority of those designated as Actinomyces bovis were in group A.
Seventeen anaerobic diphtheroids and seven Corynebacterium acnes isolates were placed in group A. One diphtheroid was in each of groups B and D. On this basis it is suggested that these organisms be included in the genus Actinomyces.
Additional species of Corynebacterium as well as Lactobacillus Propionibacterium, Streptomyces, and Nocardia did not fluoresce with any of the group antisera.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERENS H. Etude comparative de six souches de bactéries anaérobies non sporulées: Actinomyces bovis A.T.C.C 8373 (bovine), A. bovis A.T.C.C. 8374 (humaine), A. israeli var. liquefaciens, Corynebacterium acnes, Corynebacterium avidum, Corynebacterium liquefaciens. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jun;84(6):1026–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEACON W. E., PEACOCK W. L., Jr, FREEMAN E. M., HARRIS A. Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by means of fluorescent antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):322–325. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., LABREC E. H. Rapid identification of cholera vibrios with fluorescent antibody. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:886–891. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.886-891.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, MURPHY W. C., 3rd, PAUL F., STEPHAN R. M. Oral strains of Actinomyces. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):82–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.82-95.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING S., MEYER E. Metabolic and serologic differentiation of Actinomyces bovis and anaerobic diphtheroids. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):234–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.234-238.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABREC E. H., FORMAL S. B., SCHNEIDER H. Serological identification of Shigella flexneri by means of fluorescent antibody. J Bacteriol. 1959 Sep;78:384–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.3.384-391.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., ELLIS E. C., UPDYKE E. L. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. IV. Grouping streptococci with fluorescent antibody. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):553–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.553-560.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., SEIWALD R. J., BURCKHALTER J. H., DOWNS C. M., METCALF T. G. Isothiocyanate compounds as fluorescent labeling agents for immune serum. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1081–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPE M. E. A serological classification of lactobacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLACK J. M., LUDWIG E. H., BIRD H. H., CANBY C. M. Studies with microaerophilic actinomycetes. I. The agglutination reaction. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):721–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.721-735.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLACK J. M., SPEARS R. G., SNODGRASS W. G., KUCHLER R. J. Studies with microaerophilic actinomycetes. II. Serological groups as determined by the reciprocal agglutinin adsorption technique. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.400-404.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMASON B. M., CHERRY W. B., EDWARDS P. R. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. VI. Identification of Salmonellae in fecal specimens. J Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(4):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.4.478-486.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMASON B. M., CHERRY W. B., MOODY M. D. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. III. Antigenic analysis of Salmonella typhosa by means of fluorescent antibody and agglutination reactions. J Bacteriol. 1957 Oct;74(4):525–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.4.525-532.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]