Abstract
Cohen, Jay O. (Communicable Disease Center, Atlanta, Ga.), Glenda S. Cowart, and William B. Cherry. Antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in nonimmunized rabbits. J. Bacteriol. 82:110–114. 1961.—Antibody against staphylococci was demonstrated in the serum of each of 36 nonimmunized specific-pathogen-free rabbits that were tested. Evidence obtained is in agreement with the proposition that two distinct staphylococcal antibodies are present in the sera from these nonimmunized rabbits. One is responsible for agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus Cowan serotype I, and the other for the formation of a reaction line observed in Ouchterlony plates with soluble antigens of both Cowan serotype I and Cowan serotype III.
Fluorescent antibody reagent prepared from preimmune rabbit serum stained some strains of coagulase positive staphylococci, including Cowan's types I and III, and failed to stain any of 14 coagulase negative strains.
The sera of rabbits obtained from a commercial source were shown to contain other antibodies for staphylococci in addition to the two found in the sera of specific-pathogen-free rabbits. The data suggested that rabbits from commercial sources have had contact with a great variety of antigens capable of stimulating staphylococcal antibody.
Evidence demonstrated that normal rabbit serum from specific-pathogen-free animals of our colony could be used for differentiation of certain staphylococcal strains.
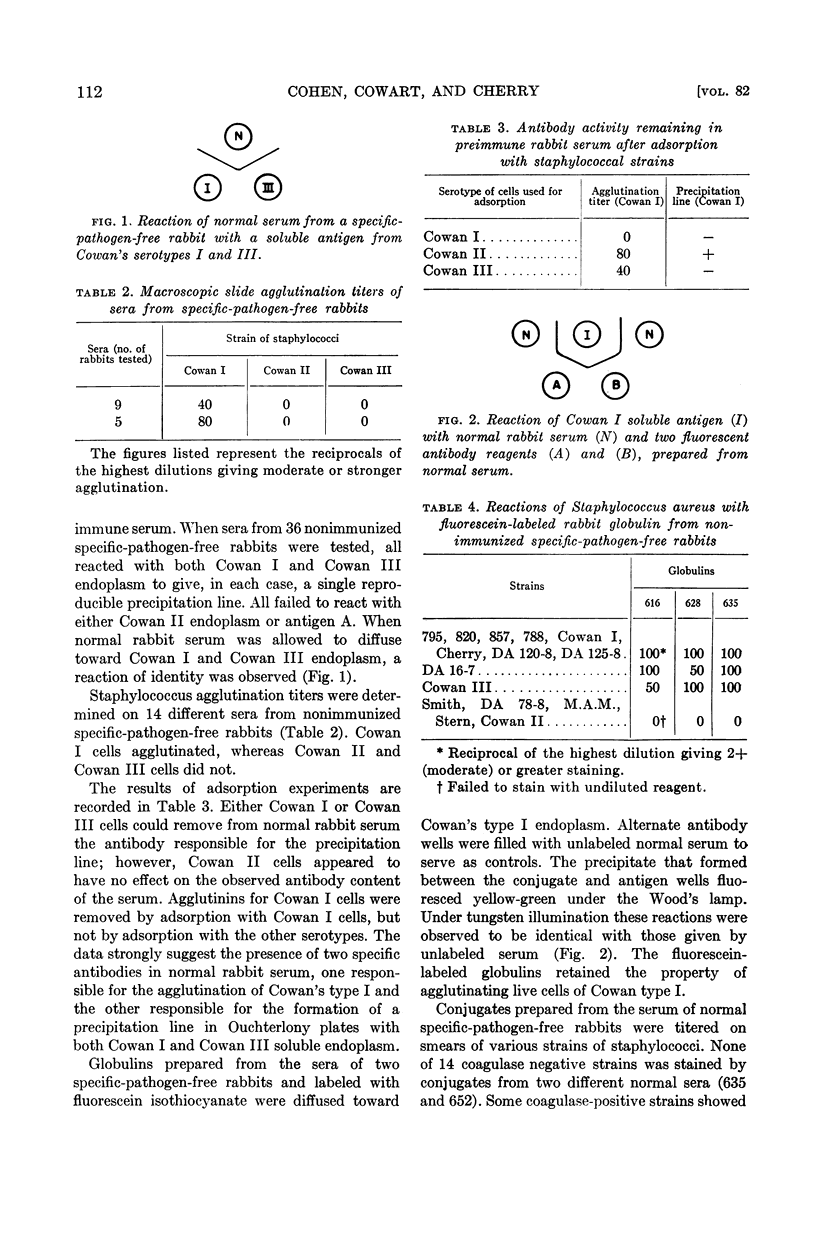
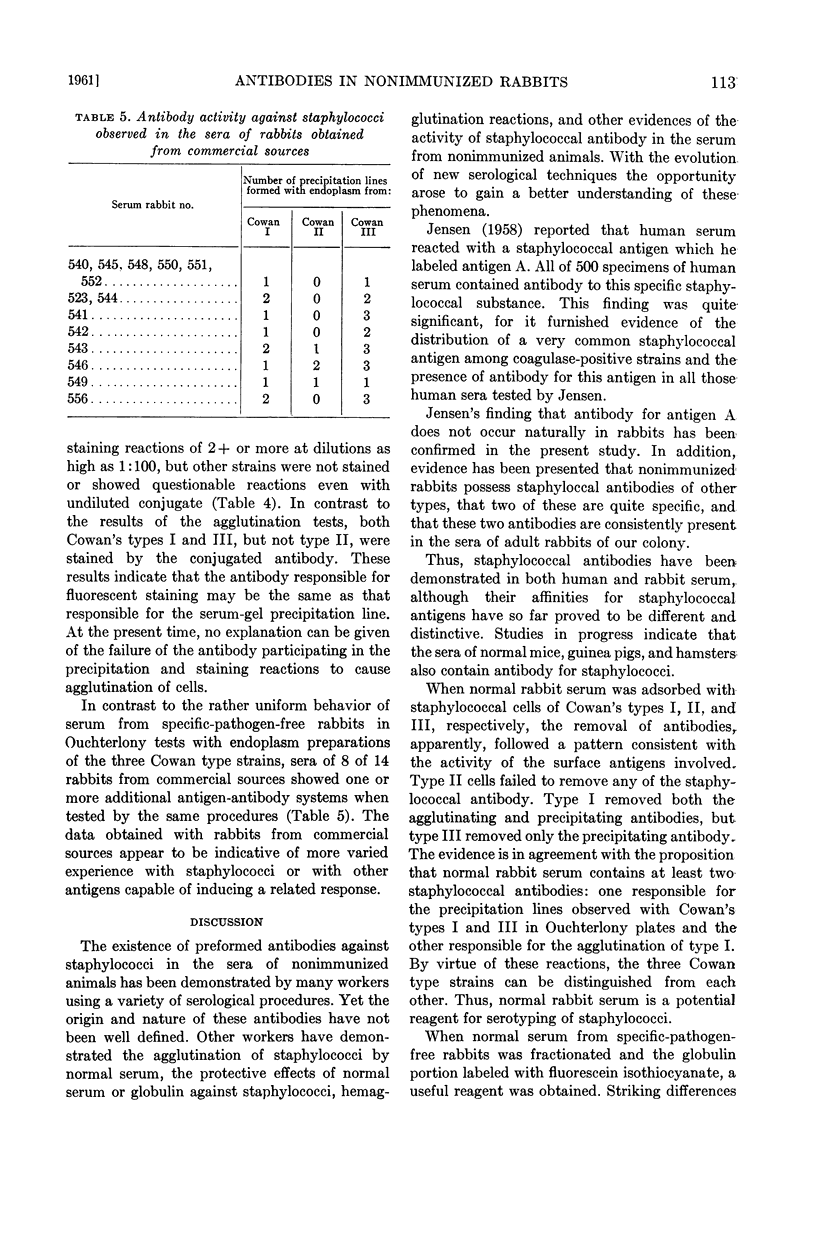
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FISHER M. W. Measurement of a staphylococcal antibody in human serum by a mouse protection test. Nature. 1959 Jun 13;183(4676):1692–1693. doi: 10.1038/1831692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN M., MOODY M. D., THOMASON B. M. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. I. General methods for Malleomyces pseudomallei. J Bacteriol. 1956 Sep;72(3):357–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.3.357-361.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., GORZYNSKI E. A., DRISLANE A. M., HARRIS A. H., RAJNOVICH E. Detection of staphylococcal antibodies in human gamma globulin and serum by hemagglutination tests. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jul;101(3):484–487. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSAWA E., MUSCHEL L. H. The bactericidal action of normal serum and the properdin system. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHOU R., QUINCHON C., PANTALEON J. Recherches sur les agglutinines antistaphylococciques naturelles des sérums humains et animaux. Rev Immunol Ther Antimicrob. 1959 Jan-Mar;23(1-2):39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., SEIWALD R. J., BURCKHALTER J. H., DOWNS C. M., METCALF T. G. Isothiocyanate compounds as fluorescent labeling agents for immune serum. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1081–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


