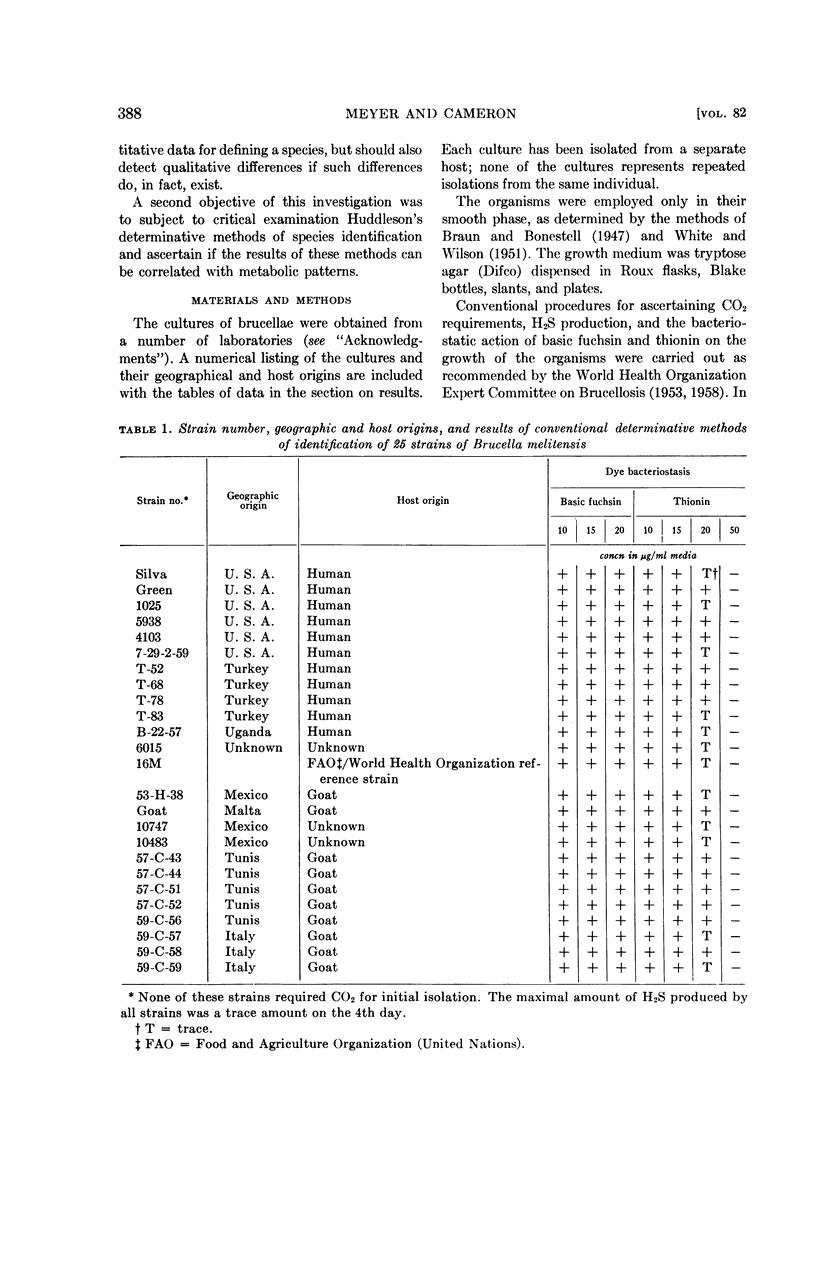
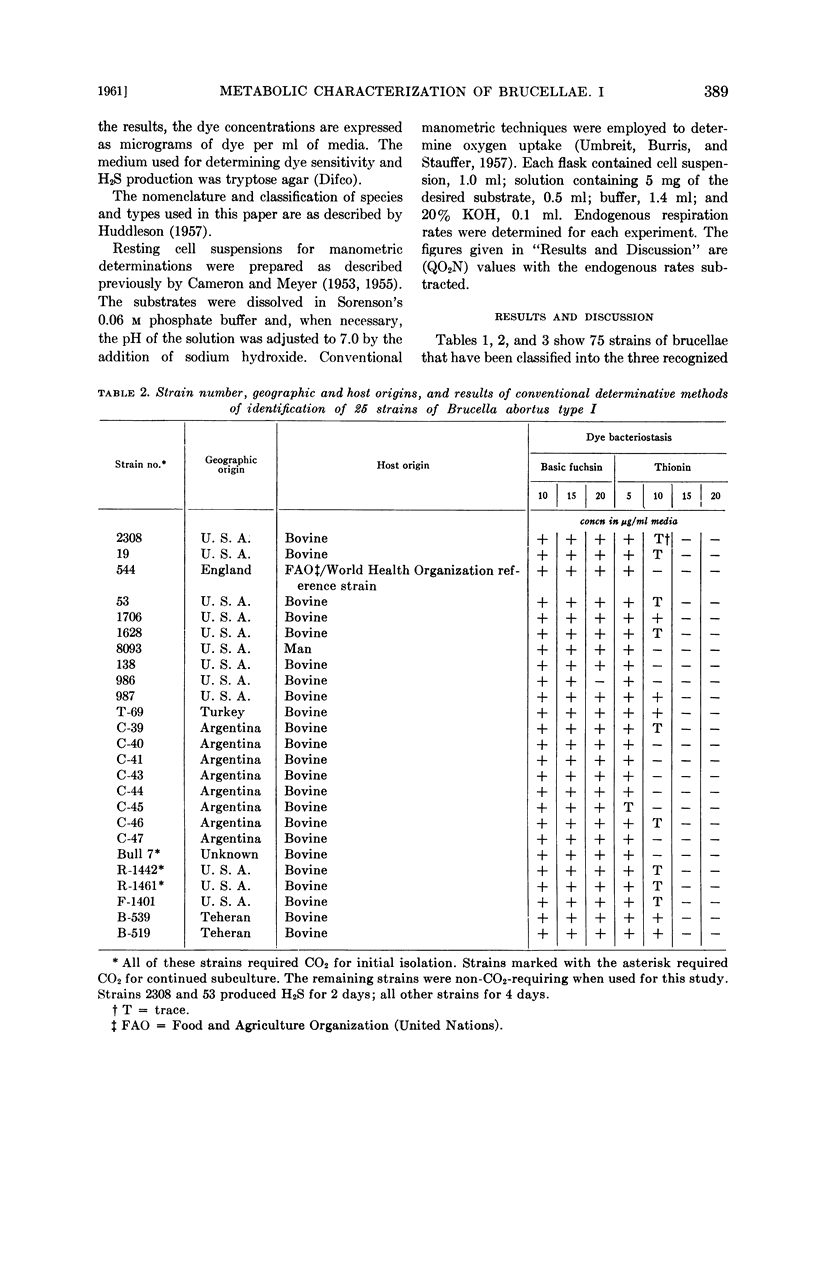
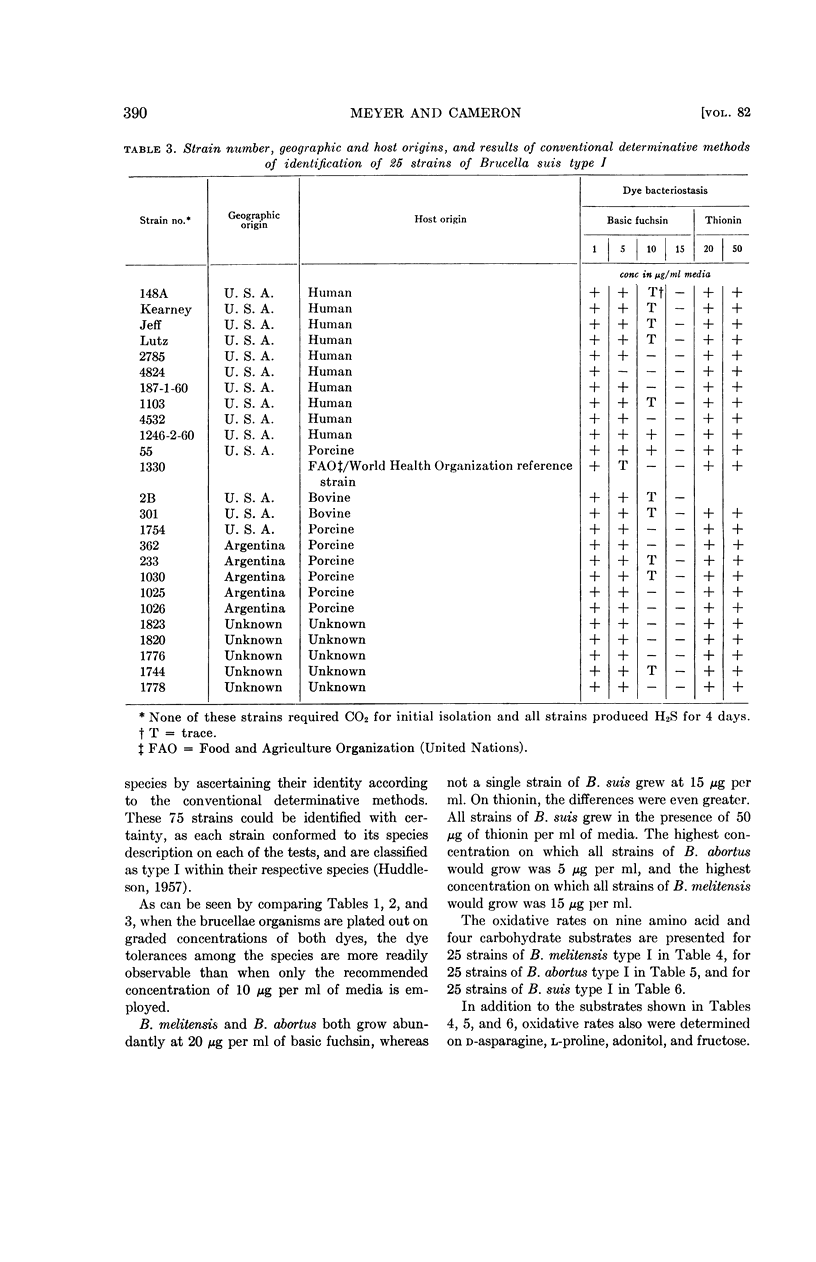
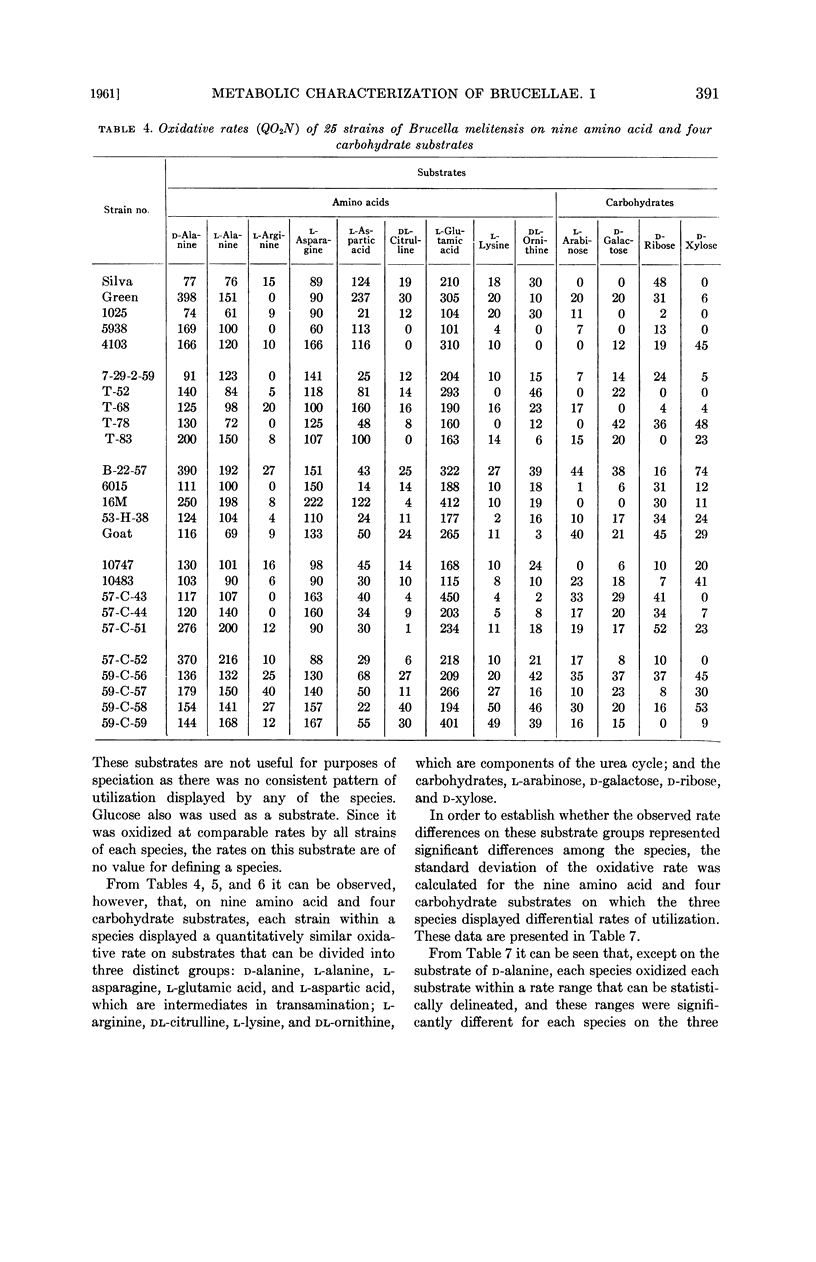
Abstract
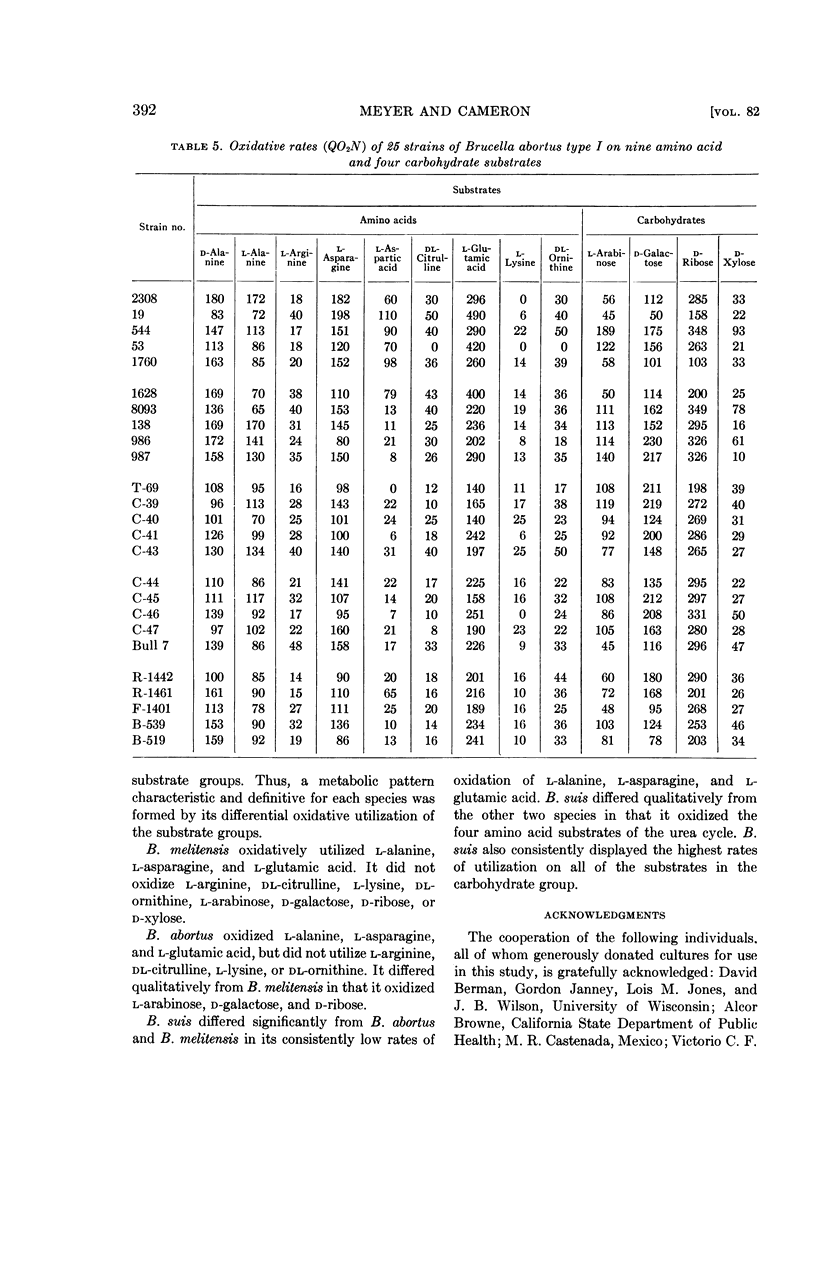
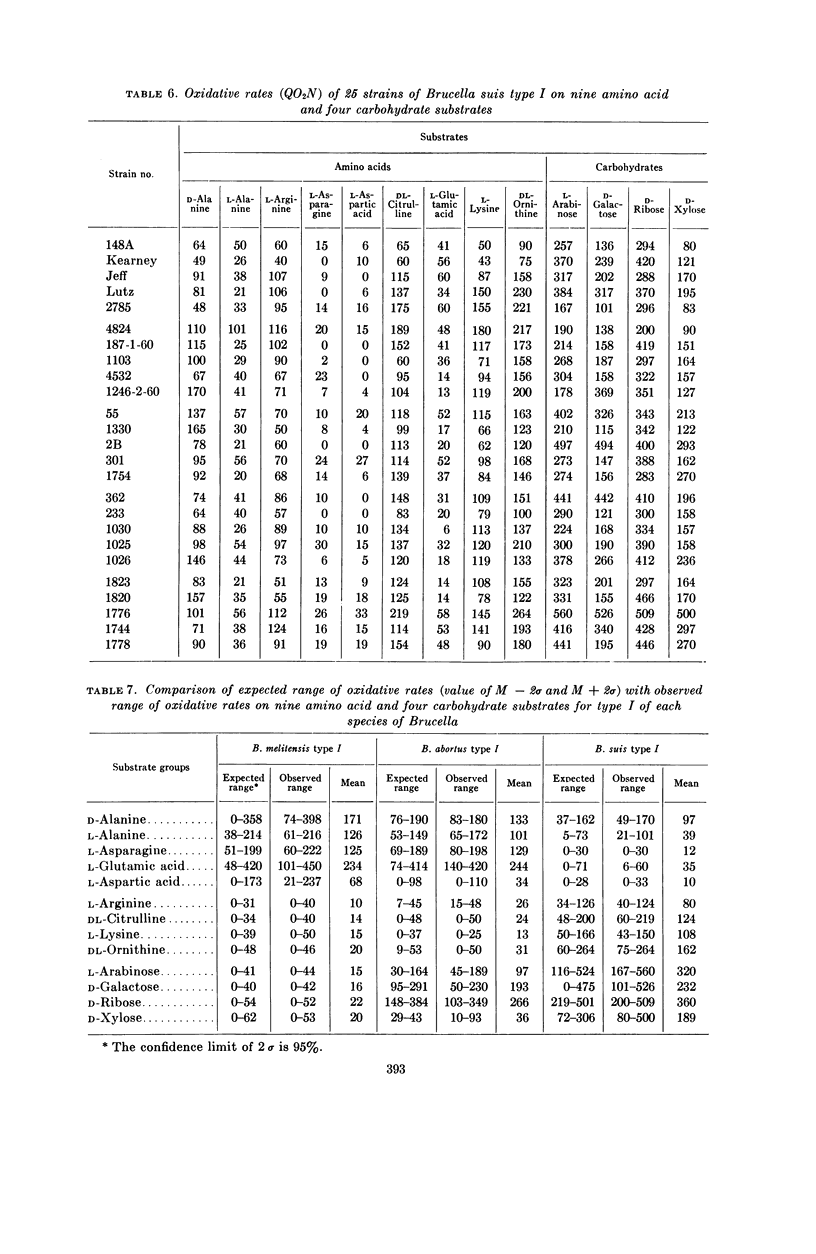
Meyer, Margaret E. (University of California, Davis), and H. S. Cameron. Metabolic characterization of the genus Brucella. I. Statistical evaluation of the oxidative rates by which type I of each species can be identified. J. Bacteriol. 82:387–395. 1961.—The oxidative uptake rates on 11 amino acid and seven carbohydrate substrates were determined for 75 strains of brucellae that had been identified by the conventional determinative methods as Brucella melitensis type I, Brucella abortus type I, or Brucella suis type I. By calculating the standard deviation of the oxidative rates, it was demonstrated that a metabolic pattern that is characteristic and definitive for each of the species was formed by their differential oxidative utilization of substrate groups, and that qualitative as well as quantitative metabolic differences exist among the Brucella species. B. melitensis oxidized l-alanine, l-asparagine, and l-glutamic acid, but not l-arginine, dl-citrulline, l-lysine, dl-ornithine, l-arabinose, d-galactose, d-ribose, or d-xylose. B. abortus differed qualitatively from B. melitensis in that it oxidized the carbohydrate substrates. B. suis differed quantitatively from both of these species in its consistently low oxidative rates of l-alanine, l-asparagine, and l-glutamic acid, and its high rates of utilization of the carbohydrate substrates. It differed qualitatively in that it oxidized the four amino acid substrates that are components of the urea cycle.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUNI A., DE FELIP G. Sulla differenziazione delle specie del genere Brucella con la prova di Renoux. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1954 Jul;30(7):793–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMERON H. S., MEYER M. E. Comparative metabolic studies on the genus Brucella. II. Metabolism of amino acids that occur in the urea cycle. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jan;67(1):34–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.1.34-37.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMERON H. S., MEYER M. E. Synthesis of amino acids from urea by the genus Brucella. Am J Vet Res. 1955 Jan;16(58):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huddleson I. F. Differentiation of the Species of the Genus Brucella. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1931 May;21(5):491–498. doi: 10.2105/ajph.21.5.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER M. E., CAMERON H. S. Comparative metabolism of species and types of organisms within the genus Brucella. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):130–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.130-136.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCULLOUGH N. B., BEAL G. A. Growth and manometric studies on carbohydrate utilization of Brucella. J Infect Dis. 1951 Nov-Dec;89(3):266–271. doi: 10.1093/infdis/89.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACHECO G., de MELLO M. T. A urease test for the differentiation of Brucella suis. J Bacteriol. 1950 May;59(5):689–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.5.689-691.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKETT M. J., NELSON E. L., LIBERMAN J. D. Speciation within the genus Brucella. II. Evaluation of differential dye, biochemical, and serological tests. J Bacteriol. 1953 Aug;66(2):210–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.2.210-219.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKETT M. J., NELSON E. L. Speciation within the genus Brucella. IV. Fermentation of carbohydrates. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):333–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.333-336.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITAL A., COOPER R. E., LEISE J. M. Rapid method for determining carbohydrate utilization by Brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):422–425. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.422-425.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENOUX G., QUATREFAGES H. L'identification des Brucella par leur activité ureasique comparaison avec les autres méthodes de différenciation. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1951 Feb;80(2):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENOUX G. Une nouvelle méthode de différenciation des variétés de Brucella; action du diéthyldithiocarbamate de soude. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 May;82(5):556–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERS E., WARNER J. Urease and catalase activities of Brucella melitensis from different geographical regions. Am J Vet Res. 1953 Jul;14(52):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. G., WILSON J. B. Differentiation of smooth and nonsmooth colonies of Brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):239–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.239-240.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


