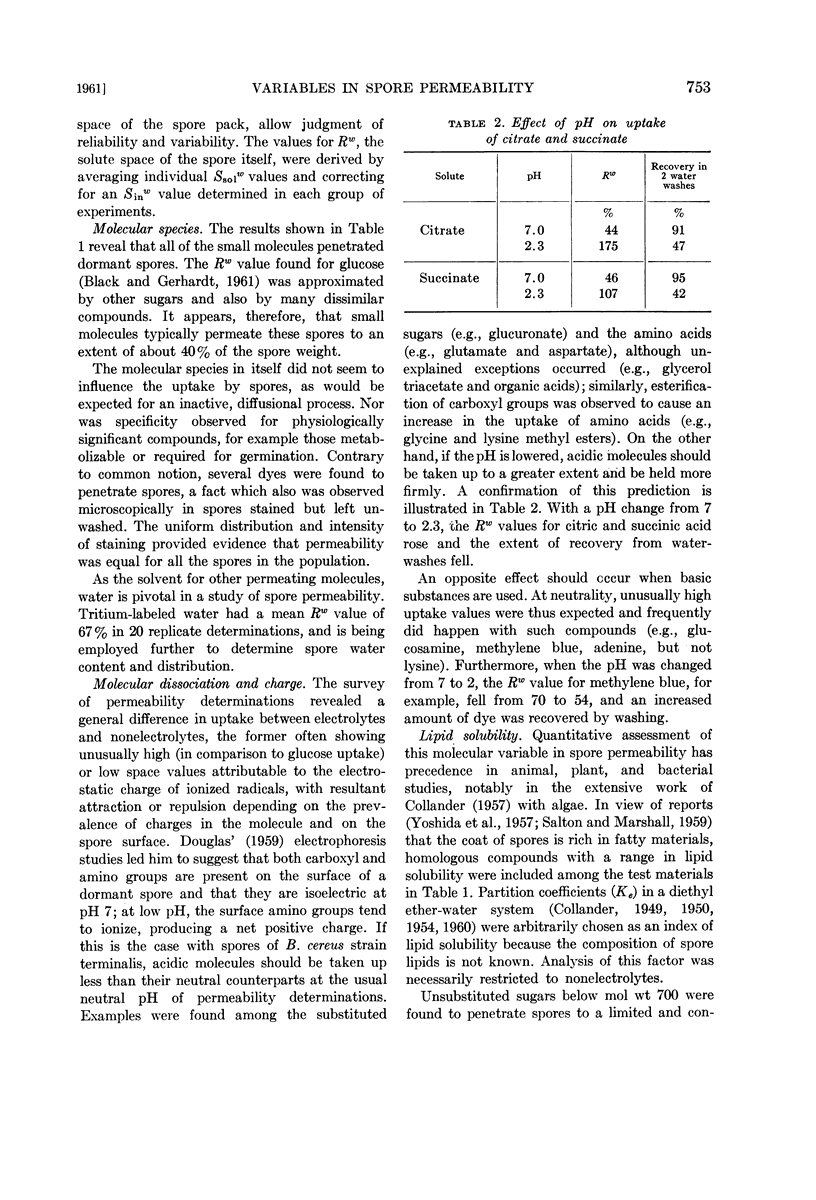
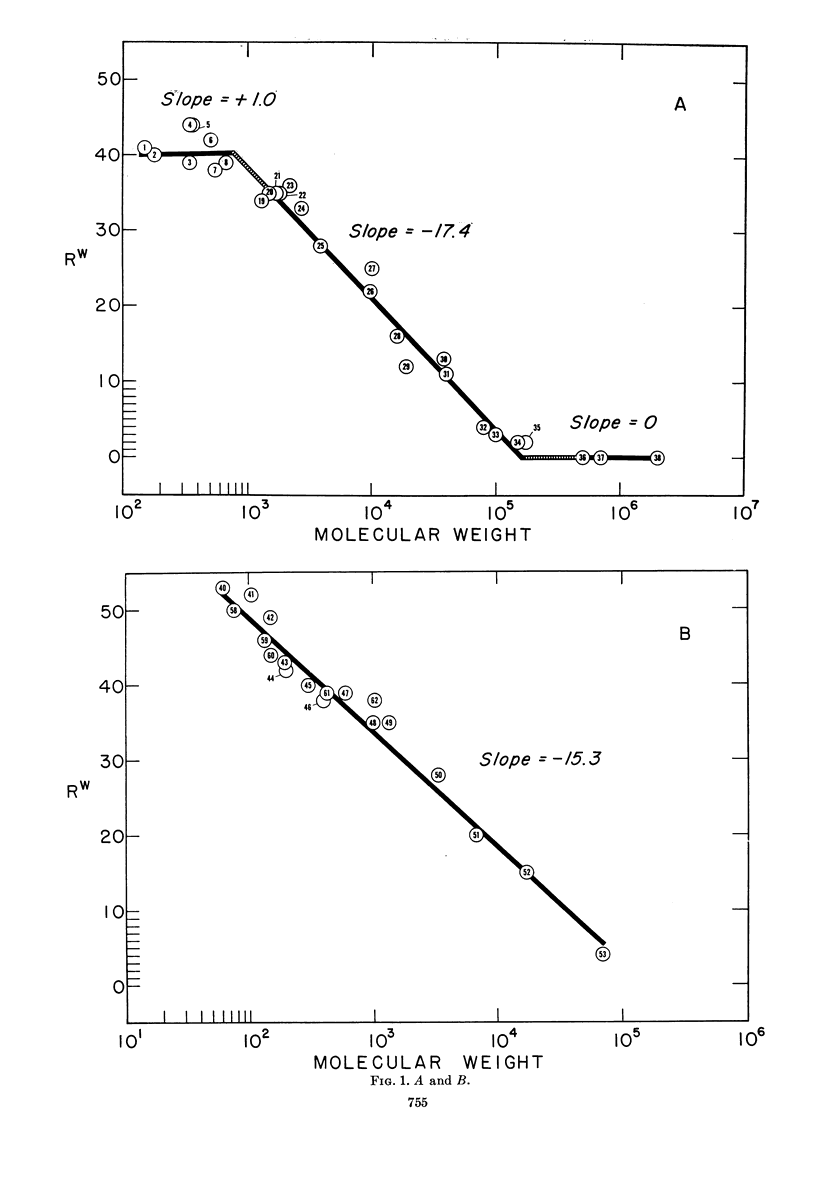
Abstract
Gerhardt, Philipp (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor) and S. H. Black. Permeability of bacterial spores. II. Molecular variables affecting solute permeation. J. Bacteriol. 82:750–760. 1961.—More than 100 compounds were tested for their uptake by dormant spores of a bacillus. The extent of penetration was found to be dependent on at least three molecular properties: (i) The dissociation of electrolytes usually resulted in high or low uptake predictable from their charge. (ii) Lipid insolubility restricted permeation of small molecules. (iii) The molecular weight of unsubstituted glycol and sugar polymers exponentially limited penetration to eventual exclusion at mol wt above 160,000. The results were plotted as a generalized curve, calculations from which permitted an interpretation that the effective spore surface contains pores varying in diameter from 10 to 200 A.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK S. H., GERHARDT P. Permeability of bacterial spores. I. Characterization of glucose uptake. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:743–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.743-749.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITT E. M., GERHARDT P. Bacterial permeability; total uptake of lysine by intact cells, protoplasts, and cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):288–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.288-293.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROTTE G. Passage of dextran molecules across the blood-lymph barrier. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1956;211:1–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. O. A study of the relationship between the surface charge and the adsorption of acid dyes by bacterial cells. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.649-652.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSDEN N. V., OSTLING S. G. Accumulation of dextran in human red cells after haemolysis. Nature. 1959 Aug 29;184(Suppl 10):723–724. doi: 10.1038/184723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCalla T. M. Cation Adsorption by Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1940 Jul;40(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.1.23-32.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., RENKIN E. M., BORRERO L. M. Filtration, diffusion and molecular sieving through peripheral capillary membranes; a contribution to the pore theory of capillary permeability. Am J Physiol. 1951 Oct;167(1):13–46. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. S., Böventer-Heidenhain B. V., Lowry R. J. Physiology of the Cell Surface of Neurospora Ascospores. IV. The Functions of Surface Binding Sites. Plant Physiol. 1957 Nov;32(6):586–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.6.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLENIUS G. [Renal clearance of dextran as a measure of glomerular permeability]. Acta Soc Med Ups Suppl. 1954 Apr 8;59(4):1–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA N., IZUMI Y., TANI I., TANAKA S., TAKAISHI K., HASHIMOTO T., FUKUI K. Studies on the bacterial cell wall. XIII. Studies on the chemical composition of bacterial cell walls and spore membranes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jul;74(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.1.94-100.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


