Abstract
Landy, Maurice (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md.), J. Gabriel Michael, and James L. Whitby. Bactericidal method for the measurement in normal serum of antibody to gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 83:631–640. 1962.—The bactericidal effect of normal serum on gram-negative bacteria was investigated with the objective of determining whether this antibody-complement reaction could be used for the measurement of antibody. The major variables affecting the outcome of this complement-dependent reaction were explored systematically to establish the test conditions in which specific antibody was the limiting factor. Among these were the use of an excess of absorbed human serum as a complement source, inoculum, reaction conditions, and precise enumeration of surviving bacteria. It was demonstrated that the test conditions could be controlled so as to provide a sensitive and objective assay for antibody to representative strains of various gram-negative genera.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FISCHER J. [On modification of the bacterial properties of the serum. A contribution to the problem of nonspecific resistance]. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1959;22:827–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAINES S., LANDY M. Prevalence of antibody to Pseudomonas in normal human sera. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):628–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.628-633.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., LAMB E. Estimation of Vi antibody employing erythrocytes treated with purified Vi antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Apr;82(4):593–598. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
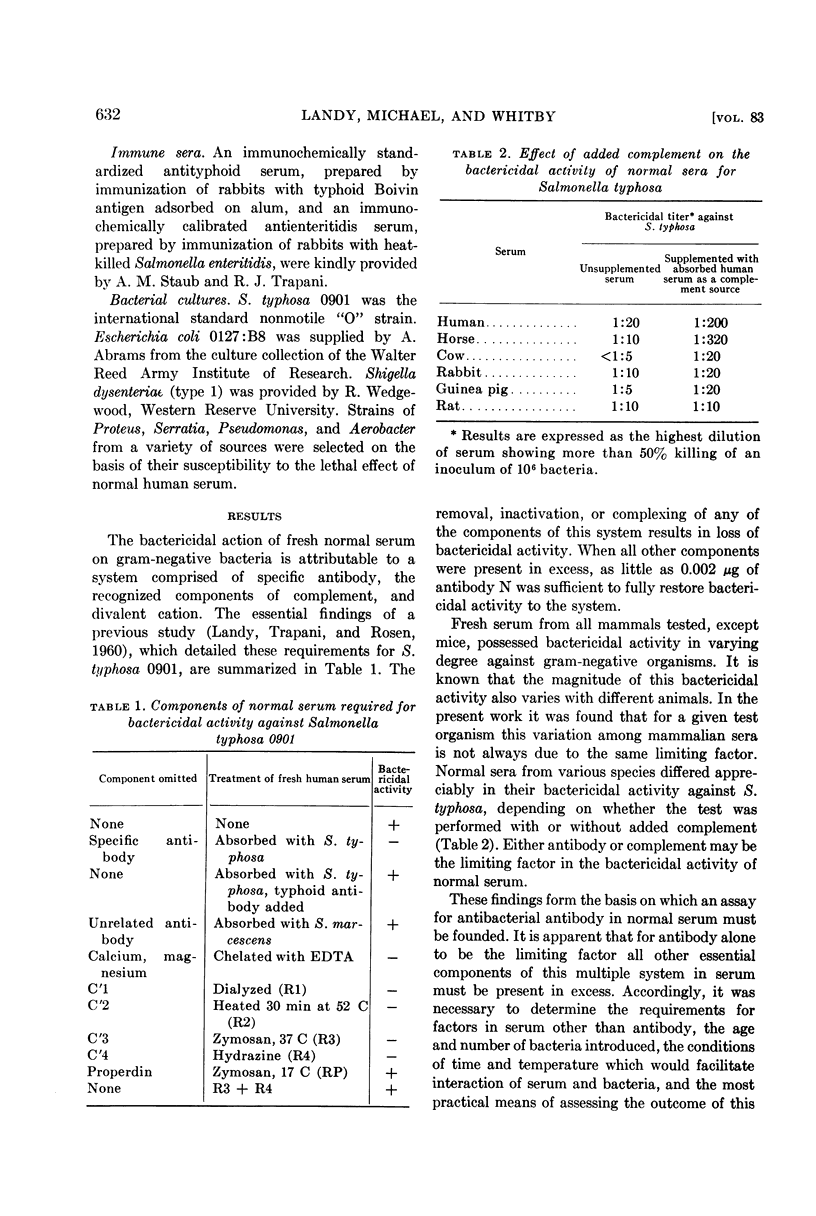
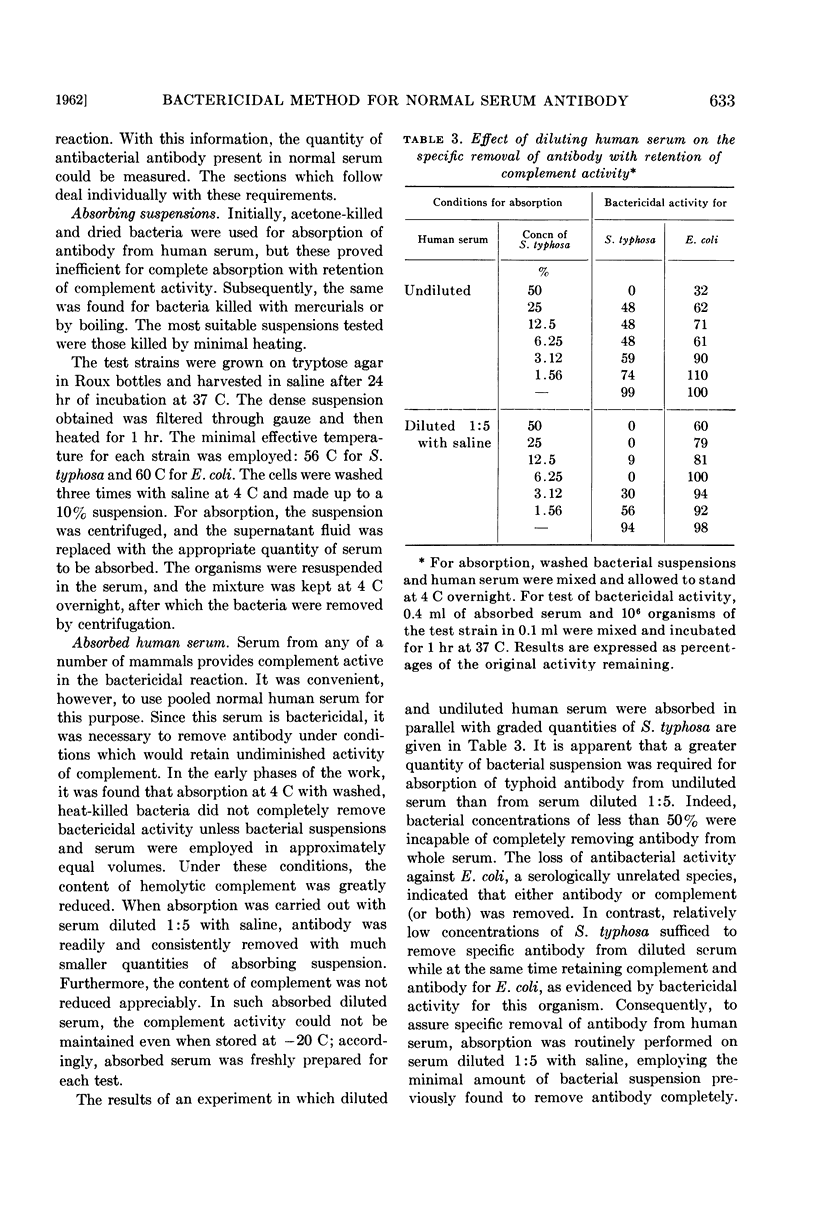
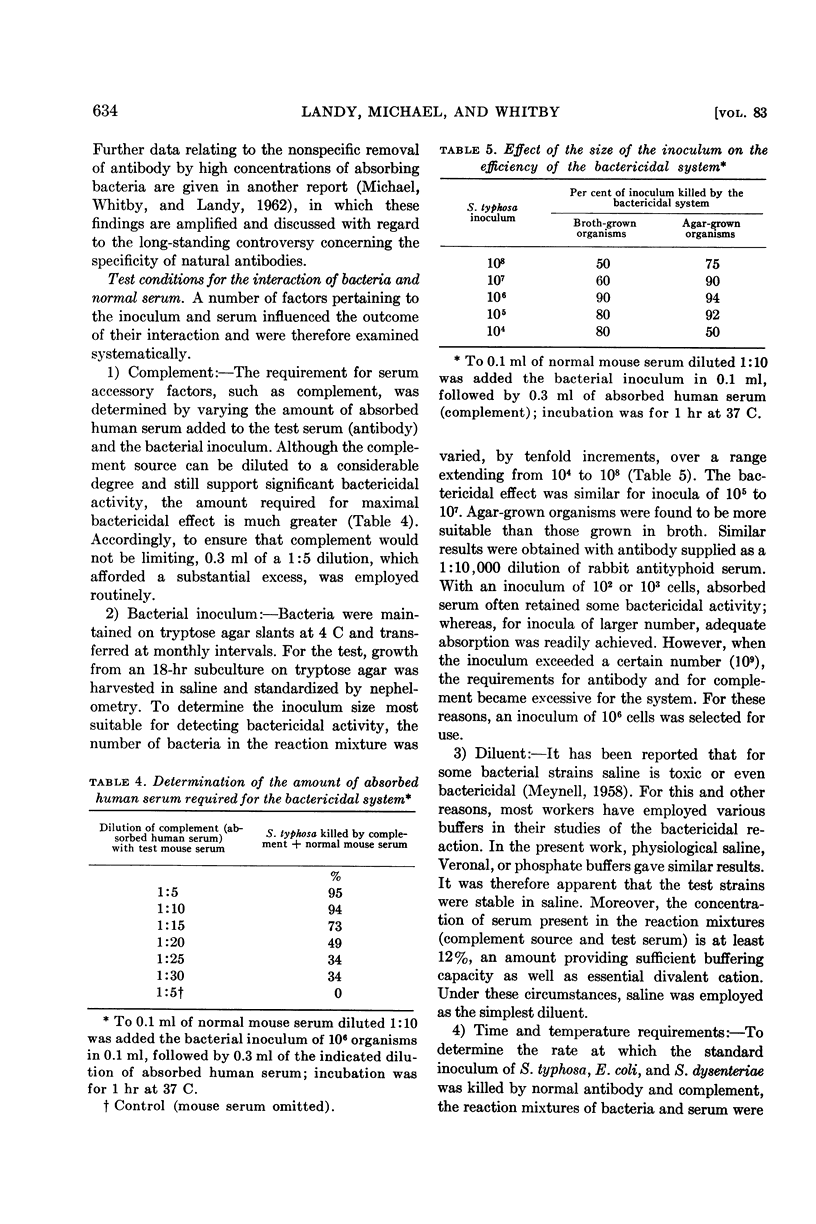
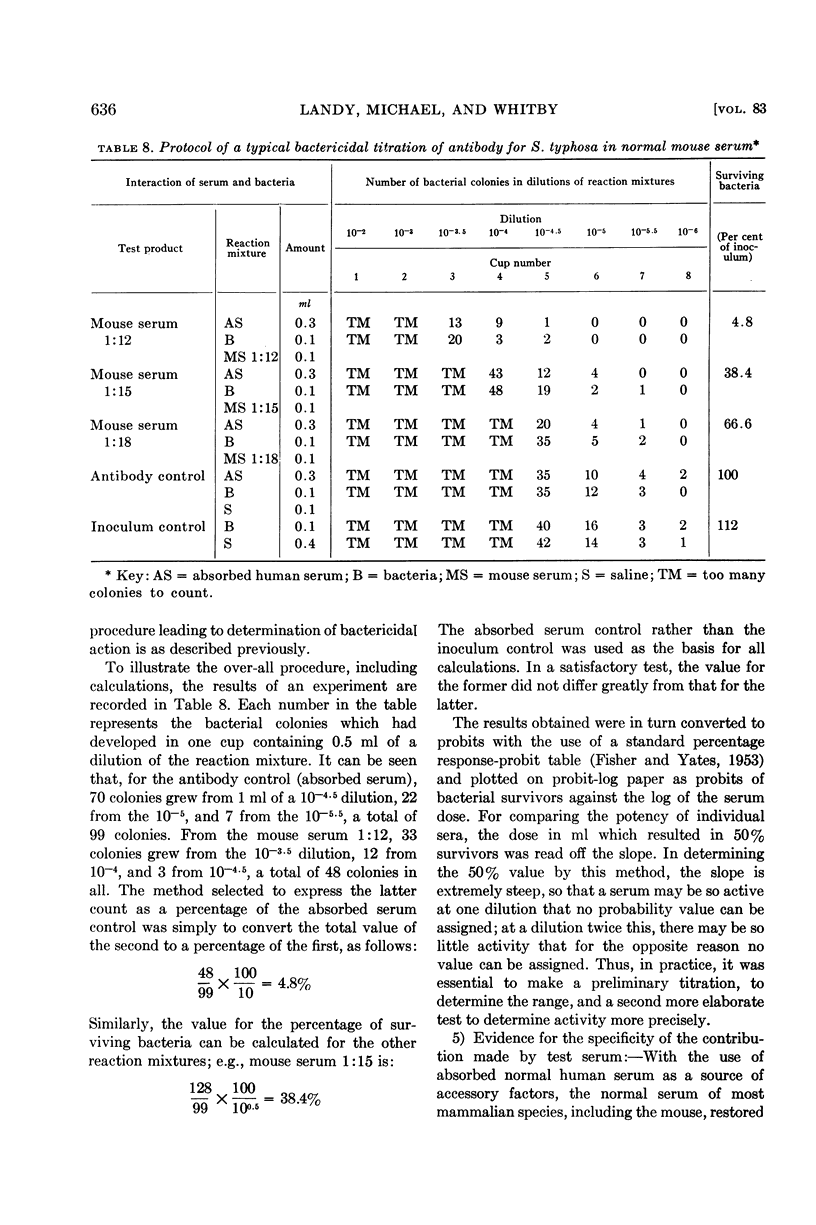
- LANDY M., TRAPANI R. J., ROSEN F. S. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. VI. Two separate systems required for viable and killed Salmonella typhosa. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:352–363. doi: 10.1172/JCI104046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS S., ESPLIN D. W., DONALDSON D. M. Lack of bactericidal effect of mouse serum on a number of common microorganisms. Science. 1954 Jun 18;119(3103):877–877. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3103.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. The effect of sudden chilling on Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):380–389. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Studies on natural antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:131–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., CHAMBERLIN R. H., OSAWA E. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. I. Activity against Salmonella typhi strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):376–382. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Serum bactericidal actions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1265–1272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., TREFFERS H. P. Quantitative studies on the bactericidal actions of serum and complement. I. A rapid photometric growth assay for bactericidal activity. J Immunol. 1956 Jan;76(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGINGTON J. The bactericidal action of typhoid antibody. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Aug;37(4):385–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GINO R. M., GORZYNSKI E. A. Demonstration of antibodies against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in sera of children of various ages. Pediatrics. 1955 Dec;16(6):801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. Rapidly induced changes in the level of non-specific immunity in laboratory animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):223–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKARNES R. C., WATSON D. W. Antimicrobial factors of normal tissues and fluids. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):273–294. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.273-294.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITBY J. L., MICHAEL J. G., WOODS M. W., LANDY M. Symposium on bacterial endotoxins. II. Possible mechanisms whereby endotoxins evoke increased nonspecific resistance to infection. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Dec;25:437–446. doi: 10.1128/br.25.4.437-446.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


