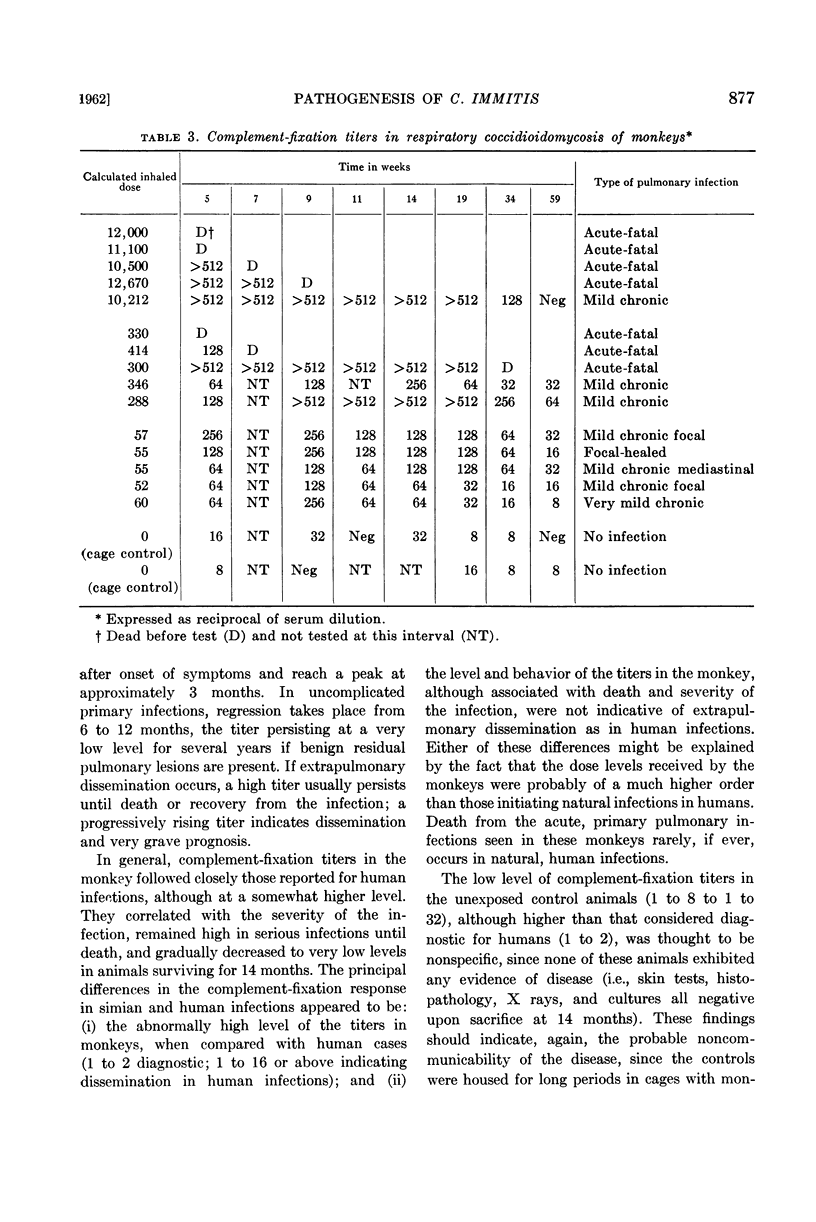
Abstract
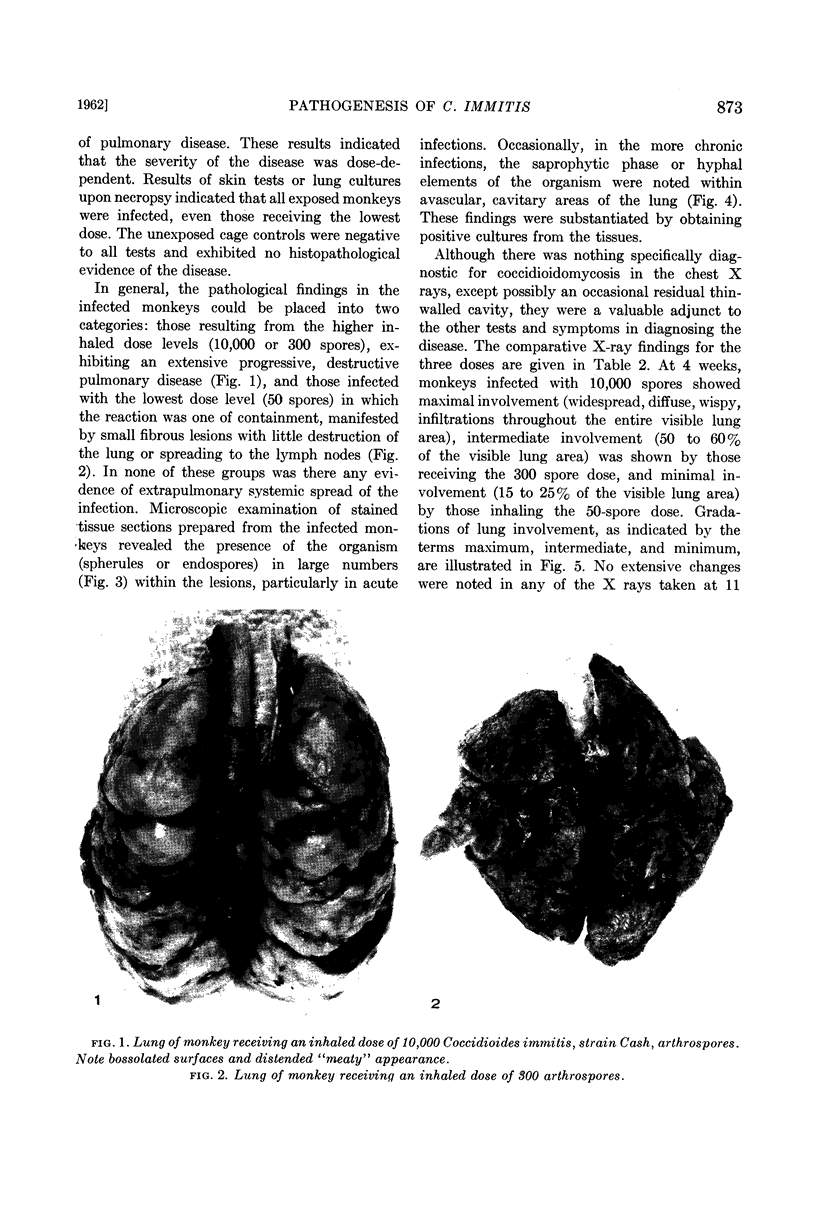
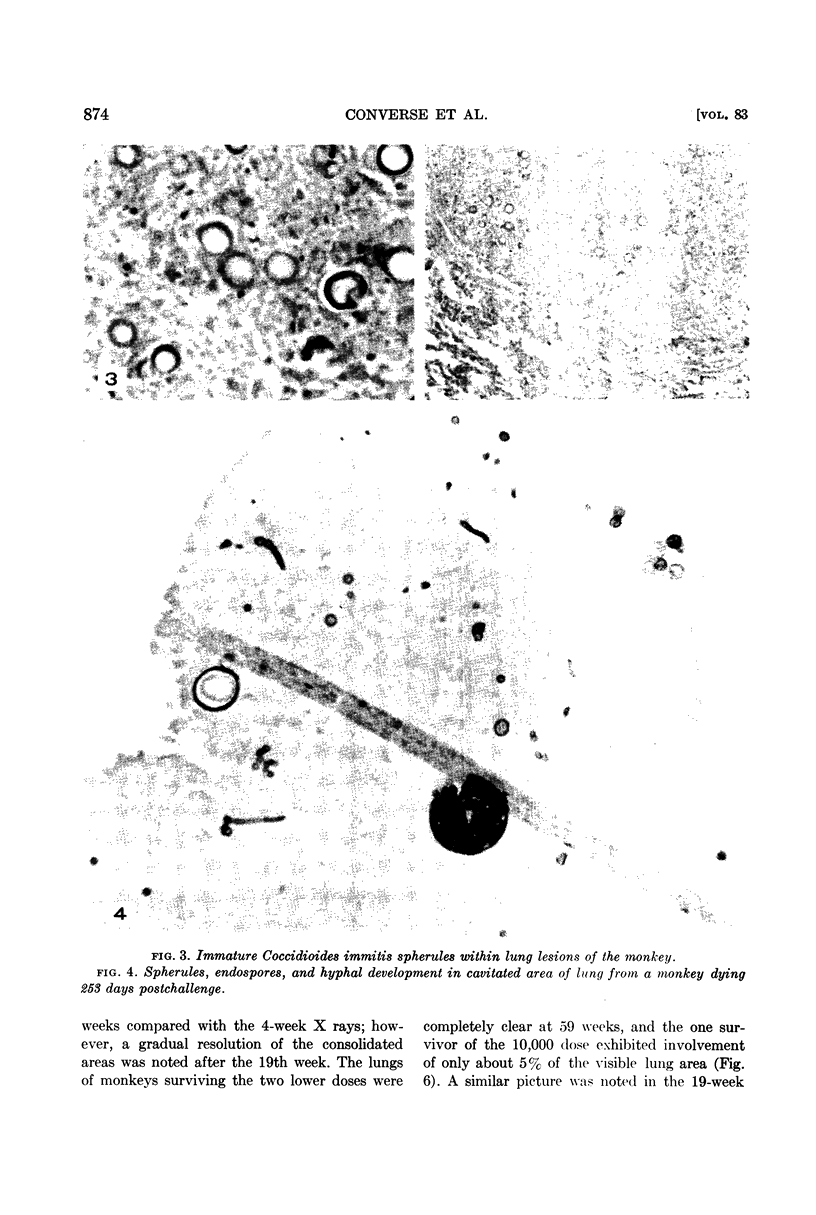
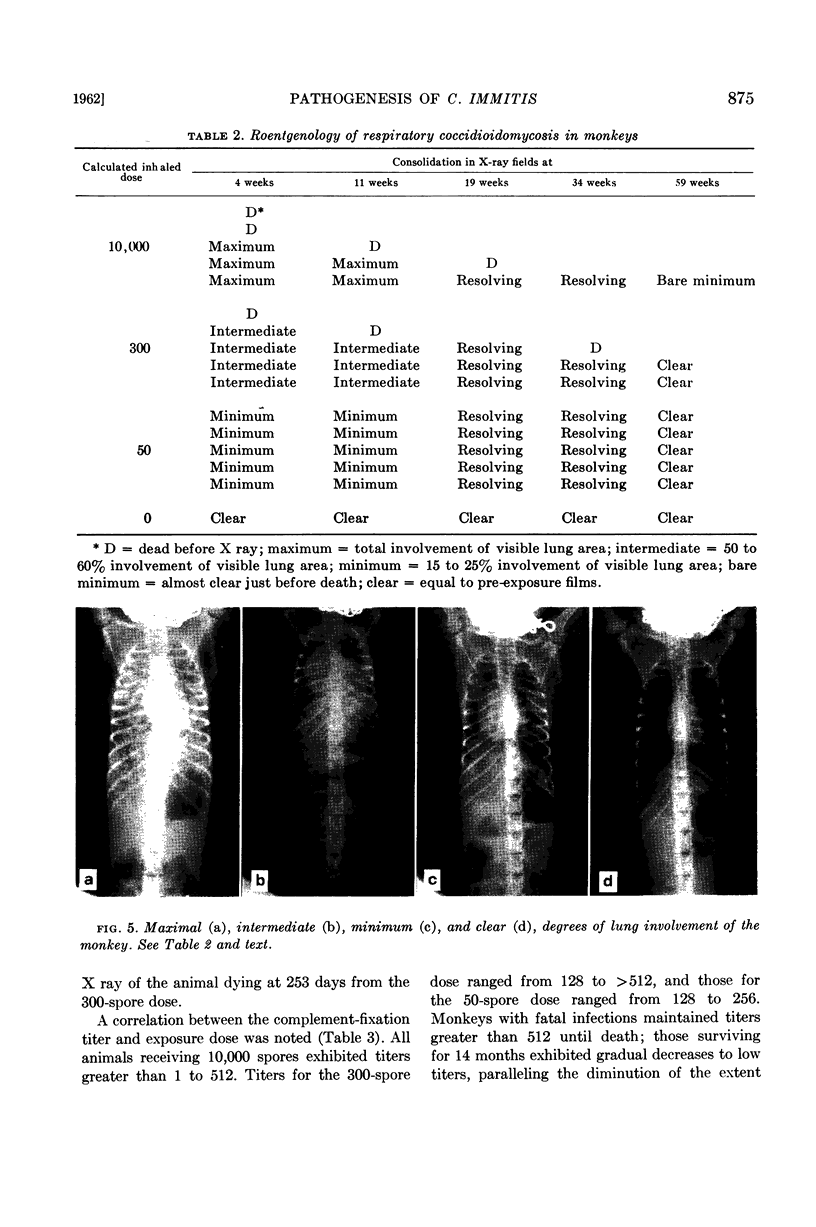
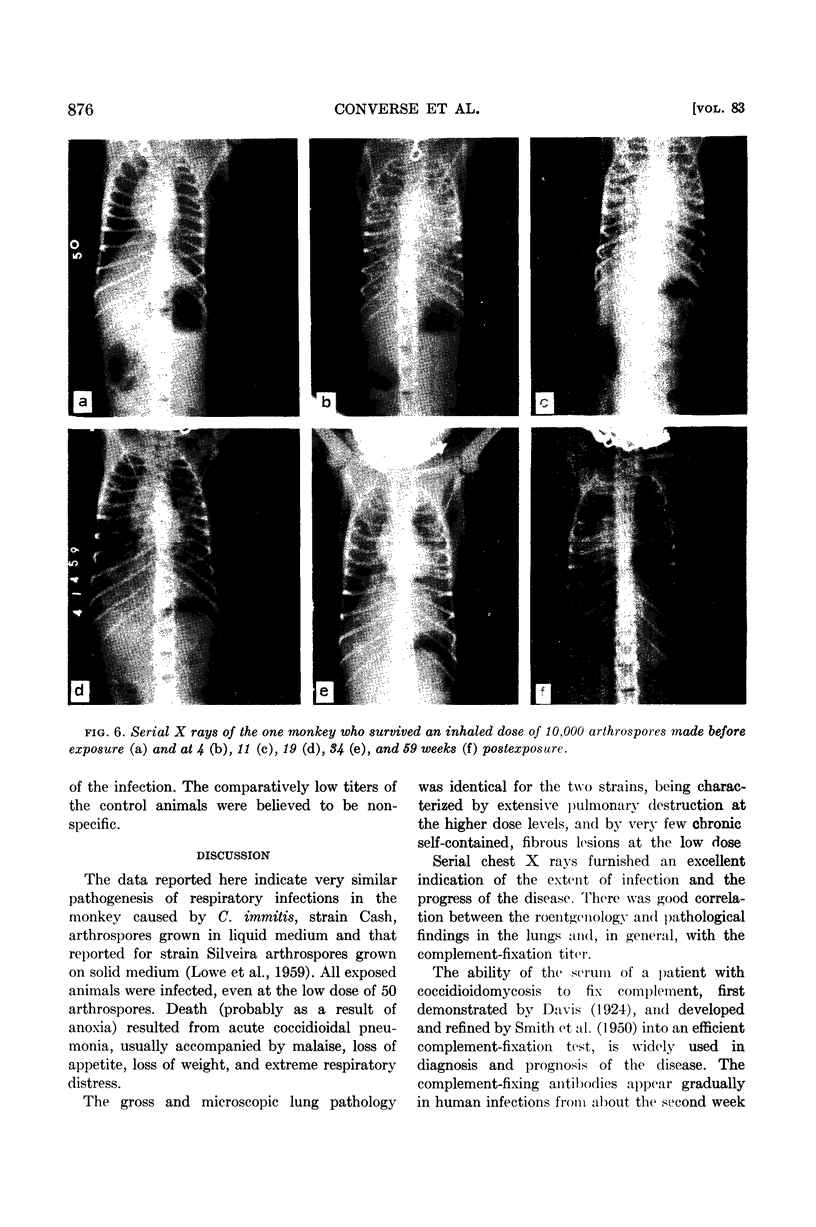
Converse, J. L. (U. S. Army Chemical Corps, Fort Detrick, Frederick, Md.), E. P. Lowe, M. W. Castleberry, G. P. Blundell, and A. R. Besemer. Pathogenesis of Coccidioides immitis in monkeys. J. Bacteriol. 83:871–878. 1962.—Respiratory exposure to arthrospores from the submerged growth of Coccidioides immitis, strain Cash, in liquid medium resulted in similar pathogenesis in monkeys to that of strain Silveira arthrospores harvested from solid medium. Infectivity of 100% was noted with doses of 50 to 10,000 arthrospores. The disease was characterized by loss of appetite and weight, malaise, and extreme respiratory distress accompanied by coughing, with the immediate cause of death being acute coccidioidal pneumonia. The pathological picture was one of extensive, progressive, destructive pulmonary disease in the higher dose levels and few, small, self-contained, fibrous lesions, with little destruction of lung tissue, in the low doses. This was correlated in general with the findings of serial X rays and serological tests. The presence of the parasitic phase (spherule and endospore) of the organism was noted in large numbers within the pulmonary lesions and bronchial exudates and was substantiated by cultural methods. Occasionally, hyphal elements of the saprophytic growth phase were noted around the periphery of residual cavitated areas of the lungs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER O., BRAUDE A. I. A study of stimuli leading to the production of spherules in coccidioidomycosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Feb;47(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUNDELL G. P., CASTLEBERRY M. W., LOWE E. P., CONVERSE J. L. The pathology of Coccidioides immitis in the Macaca mulatta. Am J Pathol. 1961 Nov;39:613–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCKETT T. F. Hyphae of Coccidioides immitis in tissues of the human host. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Aug;70(2):320–327. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., BEARD R. R., KEPP R. M., CLARK R. W., EDDIE B. U. Serological tests in the diagnosis and prognosis of coccidioidomycosis. Am J Hyg. 1950 Jul;52(1):1–21. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL R. A., FETTER B. F., CONANT N. F., LOWE E. P. Preliminary studies on artificial active immunization of guinea pigs against respiratory challenge with Coccidioides immitis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Sep;70(3):498–503. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.3.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]