Abstract
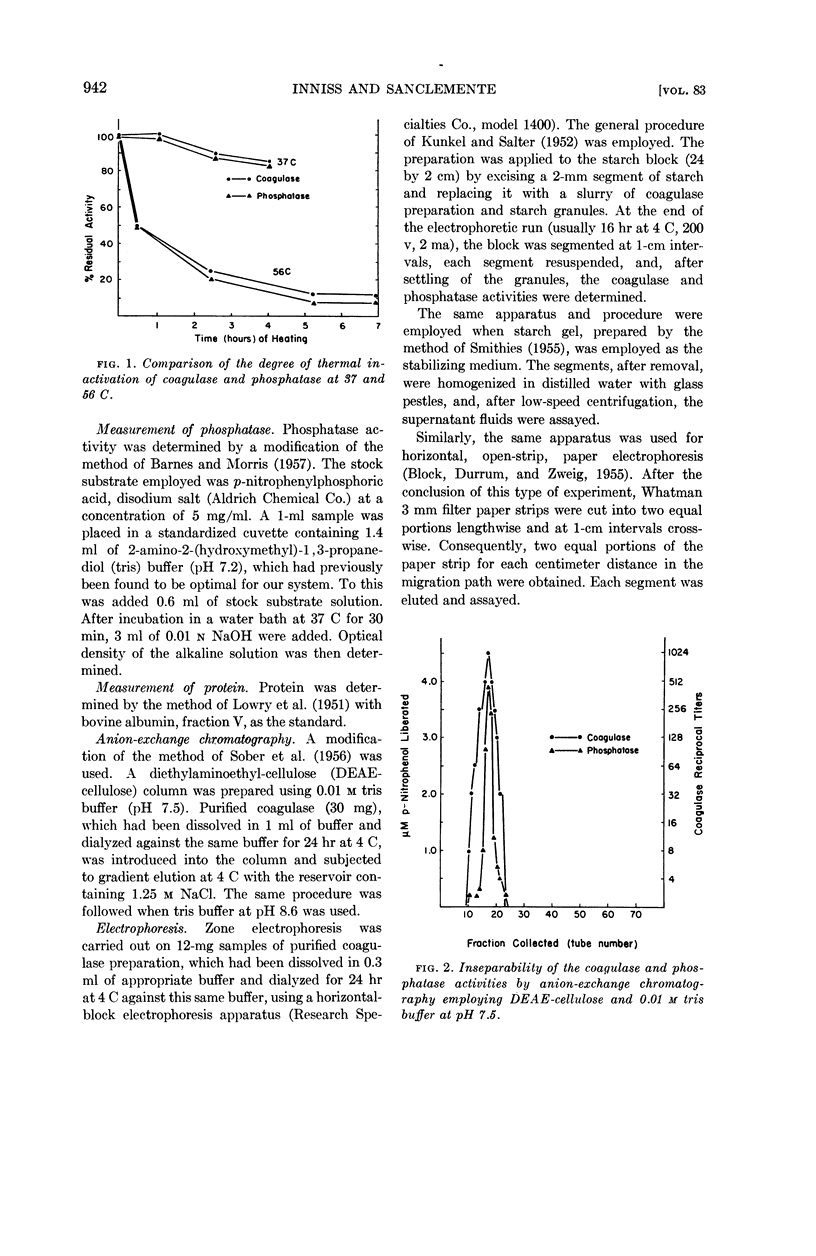
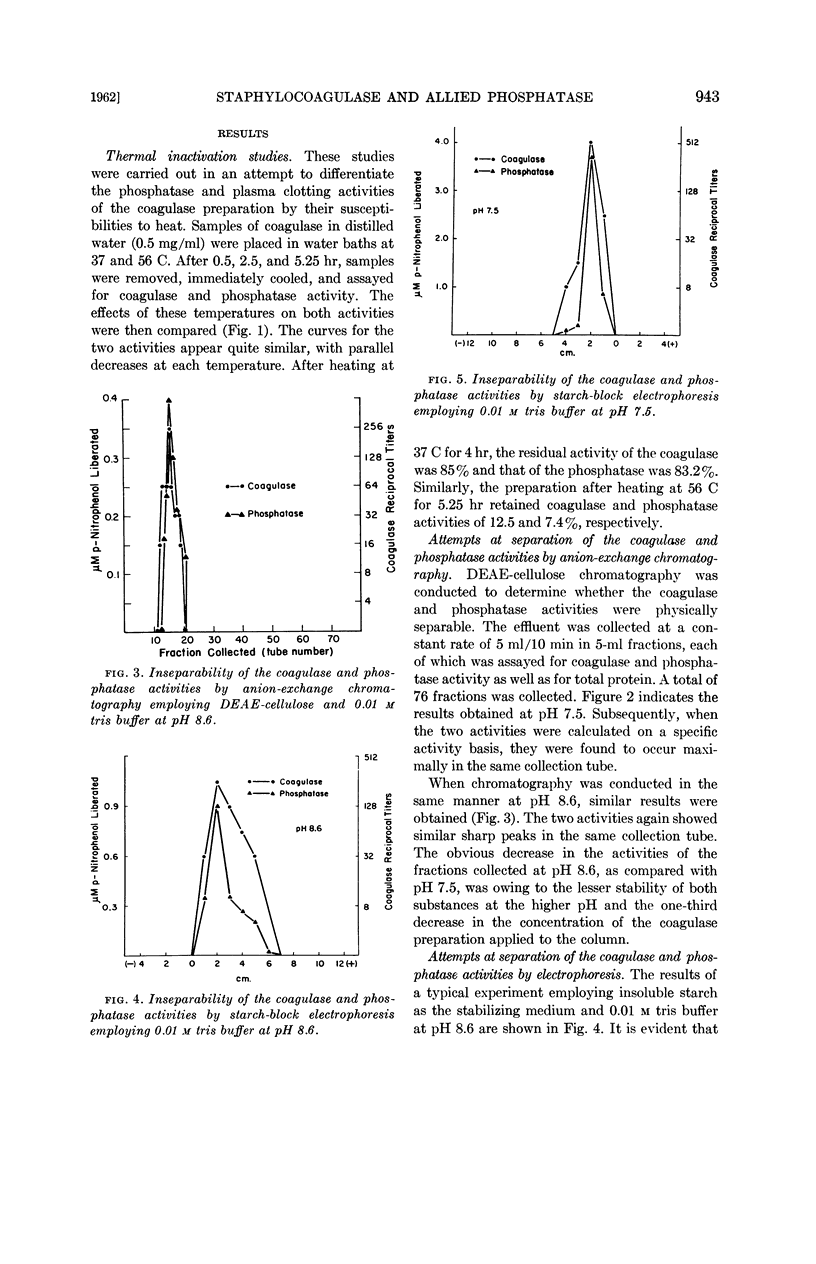
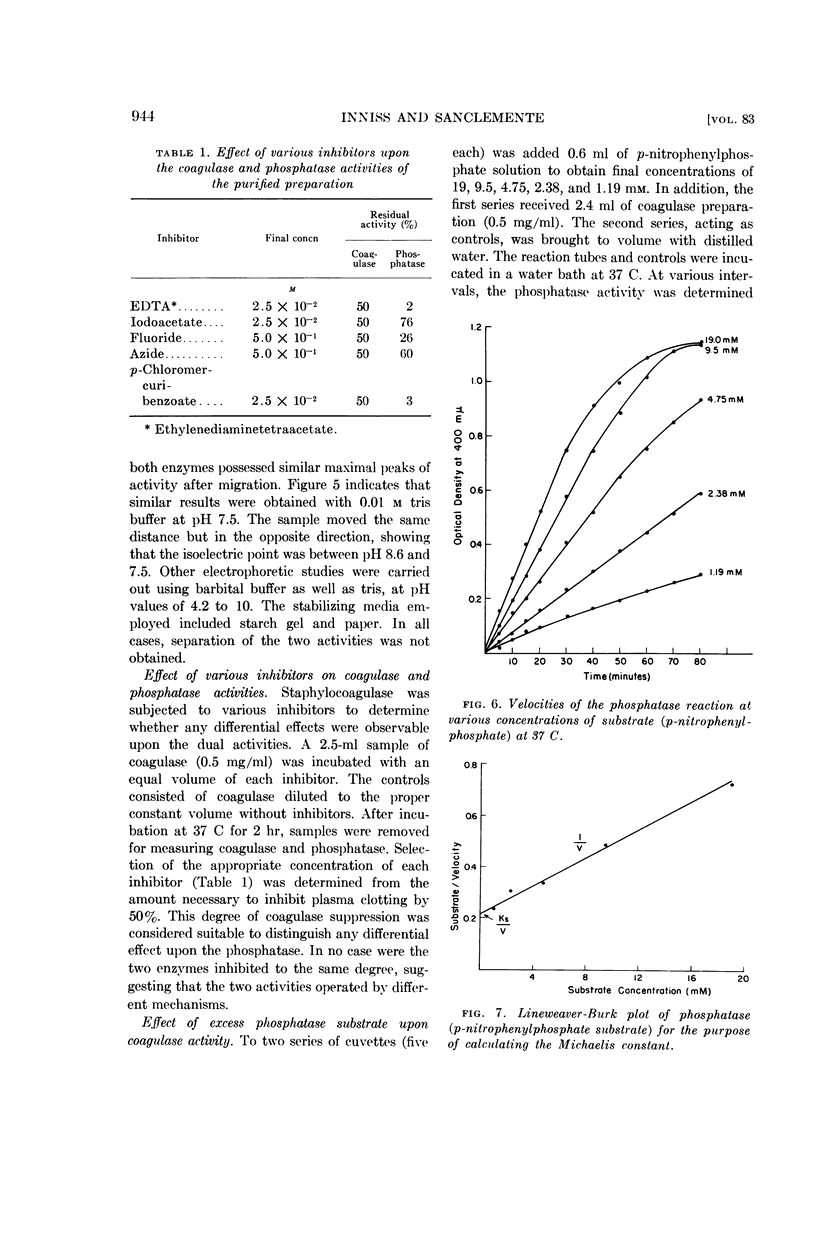
Inniss, William E. (Michigan State University, East Lansing) and Charles L. SanClemente. Biochemical studies on staphylocoagulase and an allied phosphatase activity. J. Bacteriol. 83:941–947. 1962.—The present investigation was undertaken to determine whether the reported correlation between the coagulase and phosphatase activity of the staphylococci was functional. Staphylococcus aureus, phage-propagating strain 70, grown in brain heart infusion was the source of the purified coagulase. The concomitant phosphatase activity, measured spectrophotometrically at 400 mμ using p-nitrophenylphosphate as substrate, showed a parallel decrease during thermal inactivation at 37 and 56 C. Anion-exchange chromatography and electrophoresis using starch, starch gel, and paper as stabilizing media failed to separate the two activities. Since iodoacetate, ethylenediamine-tetraacetate, fluoride, azide, and p-chloromercuribenzoate always exerted different degrees of inactivation, apparently the same mechanism was not involved. This supposition was supported by subsequent saturation of the phosphatase with excess substrate (100-fold Ks value) and the demonstration that under this condition coagulase was not inhibited. During this purification process, comparable increases in specific activity occurred for both coagulase and phosphatase, indicating the presence of a common protein carrier.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., BROOKSBANK B. W. L., KUPER S. W. A. Staphylococcal phosphatase, glucuronidase and sulphatase. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;63(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., KUPER S. W. A. Identification of Staphylococcus pyogenes by the phosphatase reaction. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;63(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES E. H., MORRIS J. F. A quantitative study of the phosphatase activity of Micrococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.100-104.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. The bacteriophage typing of staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOBEL H., BERMAN D. T., SIMON J. Purification of staphylococcal coagulase. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jun;79:807–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.6.807-815.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUMMOND M. C., TAGER M. Enzymatic activity of staphylocoagulase. I. Characterization of an esterase associated with purified preparations. J Bacteriol. 1959 Sep;78:407–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.3.407-412.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGHTON G., DUTHIE E. S. The activation of staphylococcal free coagulase by plasma constituents and the hydrolysis of Nalpha-toluene-p-sulphonyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) by activated coagulase. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):348–355. doi: 10.1042/bj0710348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., SLATER R. J. Zone electrophoresis in a starch supporting medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 May;80(1):42–44. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


