Abstract
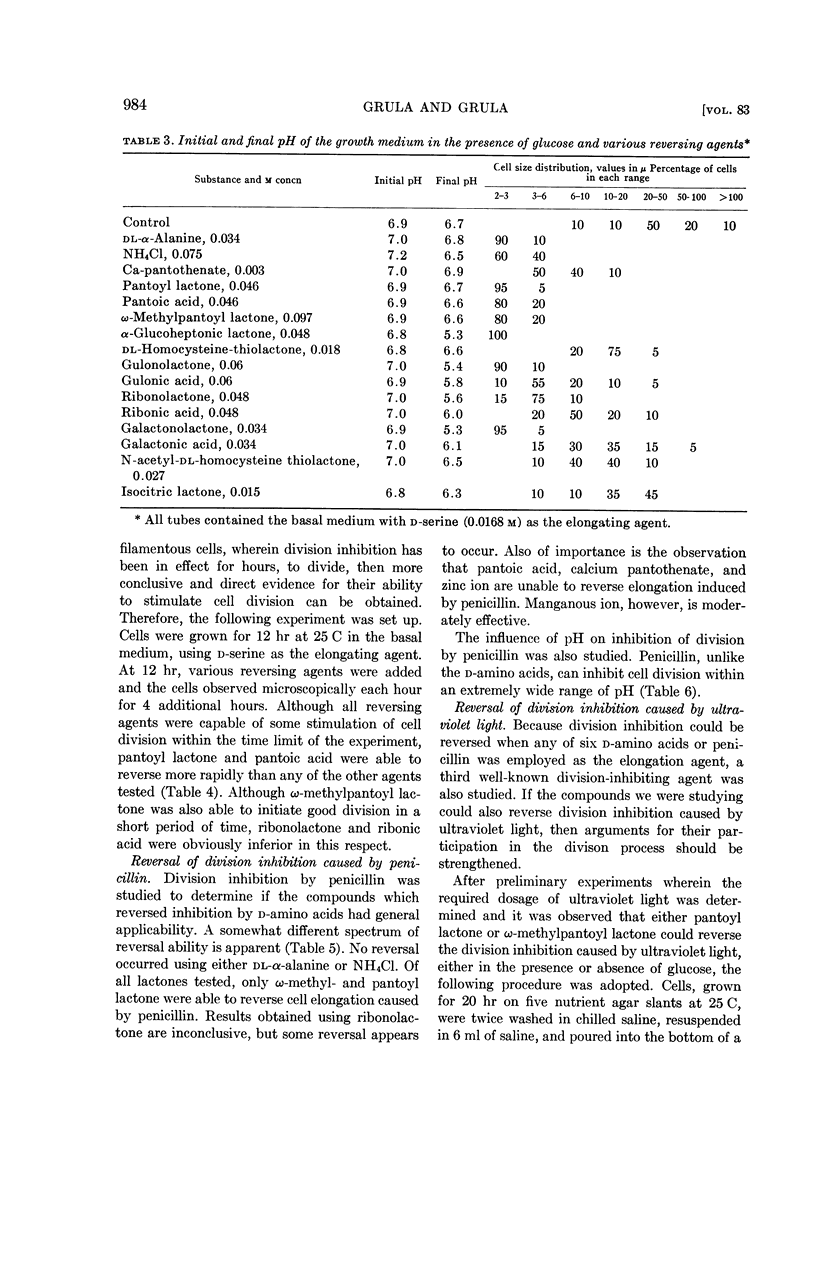
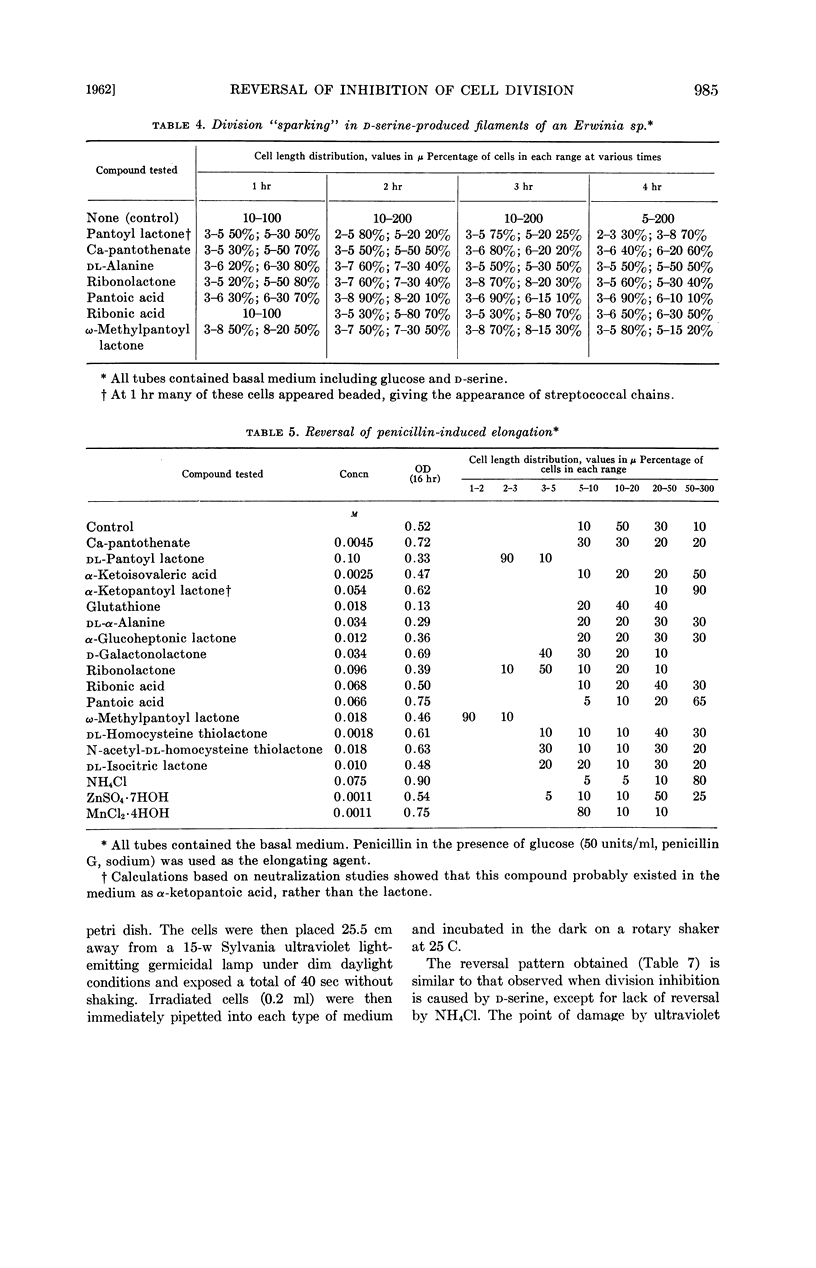
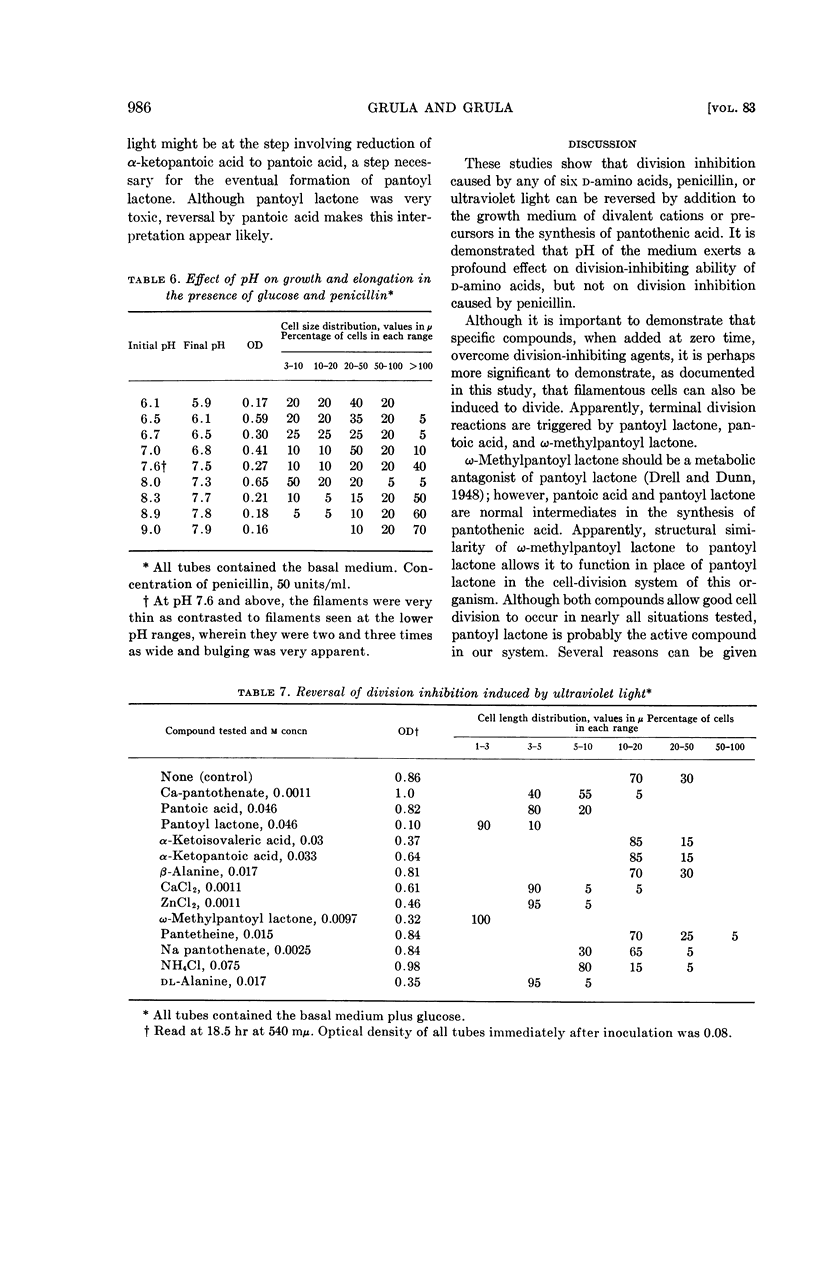
Grula, E. A. (Oklahoma State University, Stillwater) and Mary M. Grula. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. III. Reversal of inhibition of cell division caused by d-amino acids, penicillin, and ultraviolet light. J. Bacteriol. 83:981–988. 1962.—Inhibition of cell division in an Erwinia sp. occurs in the presence of any of six d-amino acids, penicillin, or ultraviolet light. Cell-division inhibition caused by d-amino acids is pH-dependent; however, elongation caused by penicillin occurs over a wide range of pH. Bulging and spheroplast formation in the presence of penicillin occurs only at pH values below 7.6; however, division continues to be inhibited at higher pH levels. Reversal of cell-division inhibition caused by two d-amino acids (phenylalanine and histidine) can be partially overcome by their respective l-isomers. Divalent cations (Zn, Ca, Mn) cause varying amounts of reversal of division inhibition in all systems studied; each system appears to have an individual requirement. All induced division inhibitions, including that caused by penicillin, can be reversed by pantoyl lactone or ω-methylpantoyl lactone. Evidence is presented and discussed concerning the possible importance of pantoyl lactone and divalent cations in terminal steps of the cell-division process in this organism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAIN R. B. The metabolism of protocatechuic acid by a vibrio. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:298–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0790298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL R. G., SCHULTZE M. O. Inhibition of Escherichia coli by S-(dichlorovinyl)-L-cysteine; its prevention by aromatic amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Apr;93:56–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. I. Inhibition of division by D-amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:375–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.375-385.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. I. Initial observations relating to nutritional dependency. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA M. M., GRULA E. A. Cell division in a species of Erwinia IV. Metabolic blocks in panothenate biosynthesis and their relationship to inhibition of cell division. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:989–997. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.989-997.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K. Pantothenate studies, II. Evidence from Mutants for interference by salicylate with pantoate synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.227-232.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K., VOGEL H. J. alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid, a precursor of pantothenic acid in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(4):388–393. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.4.388-393.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURKO M., NELSON W. O., WOOD W. A. The nutritional equivalence of pantothenate and p-aminobenzoate for the growth of Bacterium linens. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):561–567. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.561-567.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURKO M., NELSON W. O., WOOD W. A. The role of p-aminobenzoate in pantoate synthesis by Bacterium linens. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZE M. O., KLUBES P., PERMAN V., MIZUNO N. S., BATES F. W., SAUTTER J. H. Blood dyscrasia in calves induced by S-(dichlorovinyl)-L-cysteine. Blood. 1959 Sep;14:1015–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



