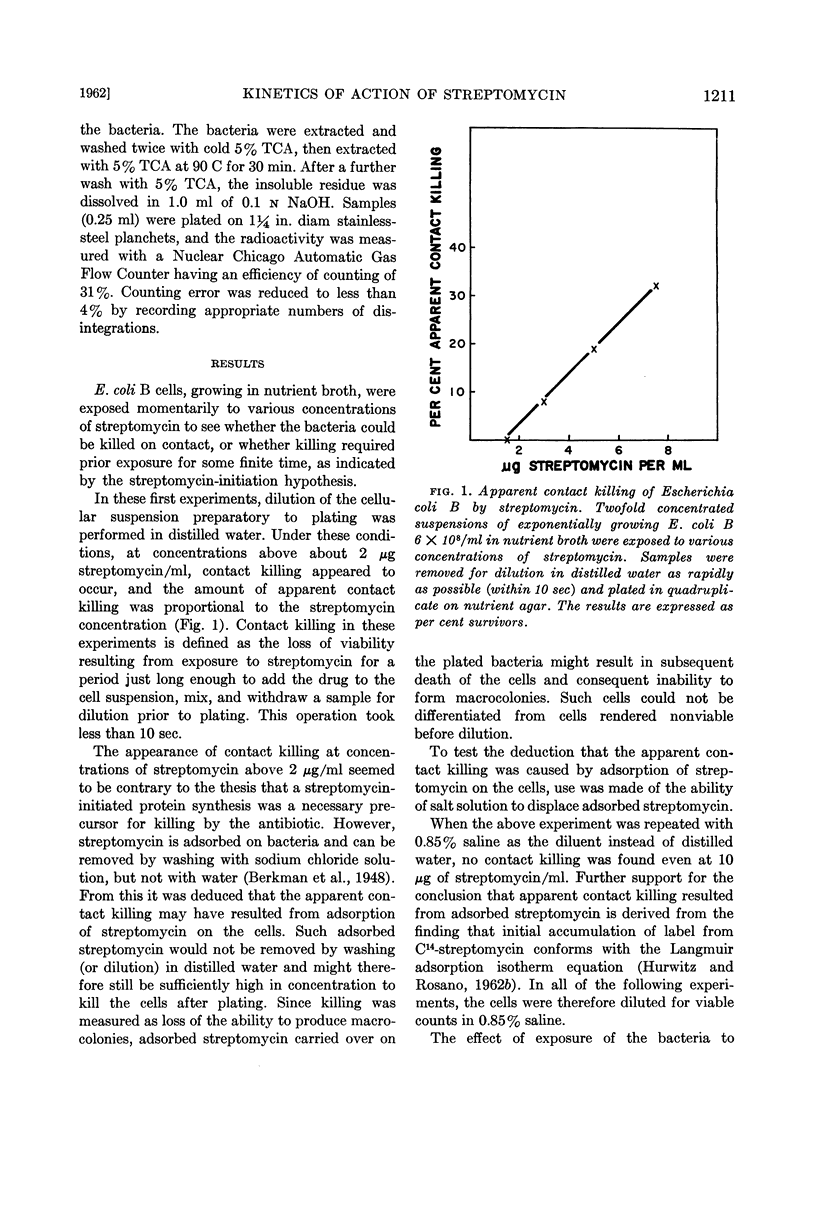
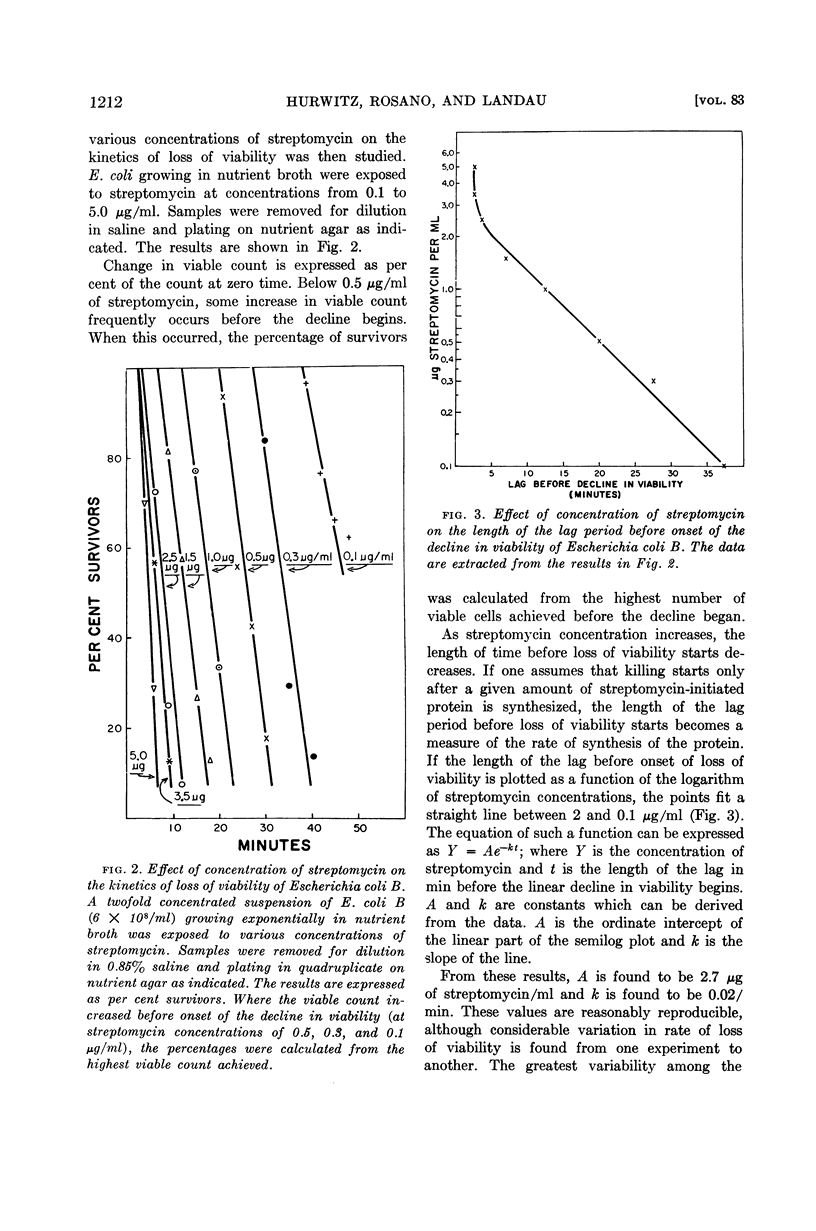
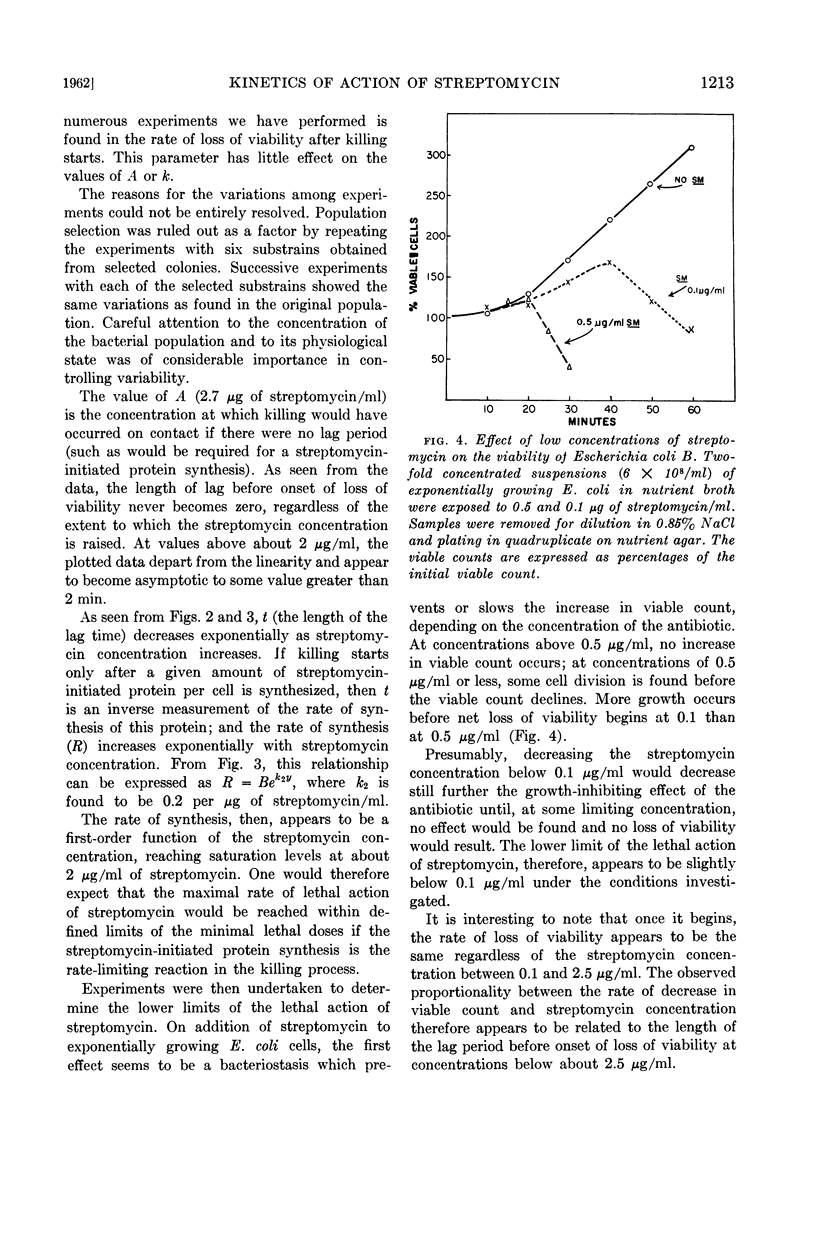
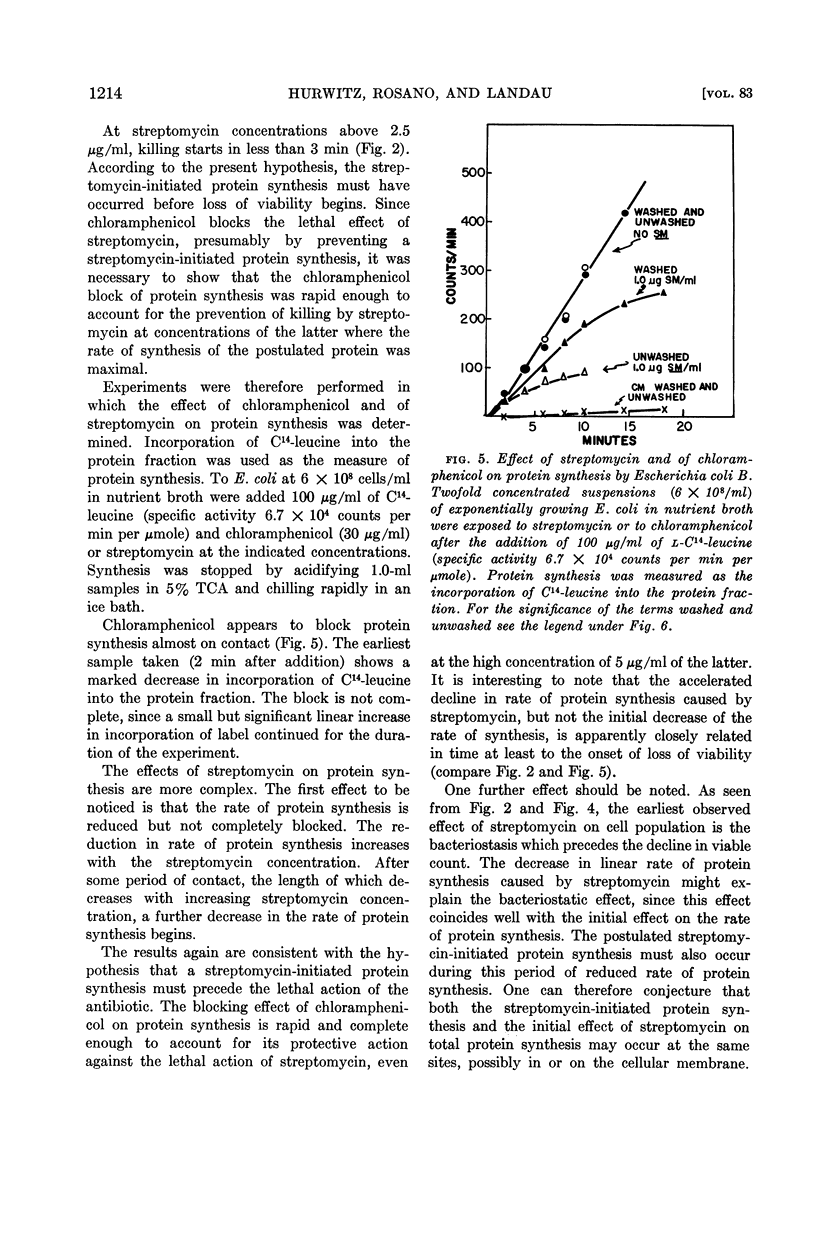
Abstract
Hurwitz, C. (Veterans Administration Hospital, Albany, N.Y.), C. L. Rosano, and J. V. Landau. Kinetics of loss of viability of Escherichia coli exposed to streptomycin. J. Bacteriol. 83:1210–1216. 1962.—The first effect of streptomycin on Escherichia coli B cells growing in nutrient broth is a decrease or cessation (depending on the concentration of antibiotic) of the rate of increase of viable cells. After this apparent bacteriostasis, a rapid decline in viable count begins. The length of time before onset of decline of viability is a first order function of the concentration of streptomycin between 0.1 and 2.0 μg/ml. Above 2.0 μg/ml, the lag in onset of loss of viability approaches asymptotically a value greater than 2 min. The length of the lag in onset of loss of viability is interpreted to be a measure of the rate of synthesis of the postulated streptomycin-initiated protein required for the later lethal action of the drug. Measurements of the effect of streptomycin on the rate of synthesis of protein by E. coli B cells show an immediate effect on the rate of protein synthesis, corresponding to the apparent bacteriostasis; this is followed by a later decrease in the rate of synthesis, which corresponds in time with the decline in viability. Washing exponentially growing E. coli B cells by centrifugation and resuspension in fresh nutrient broth makes the cells more resistant to streptomycin. The lag before the onset of decline in viability is prolonged, and the inhibition of protein synthesis is likewise affected. The washing procedure has no effect on total protein synthesis (as measured by incorporation of C14-leucine). Since synthesis of β-galactosidase is also delayed by the washing procedure, this effect is interpreted to mean that washing delays induced protein synthesis, but has no effect on the rate of total protein synthesis.
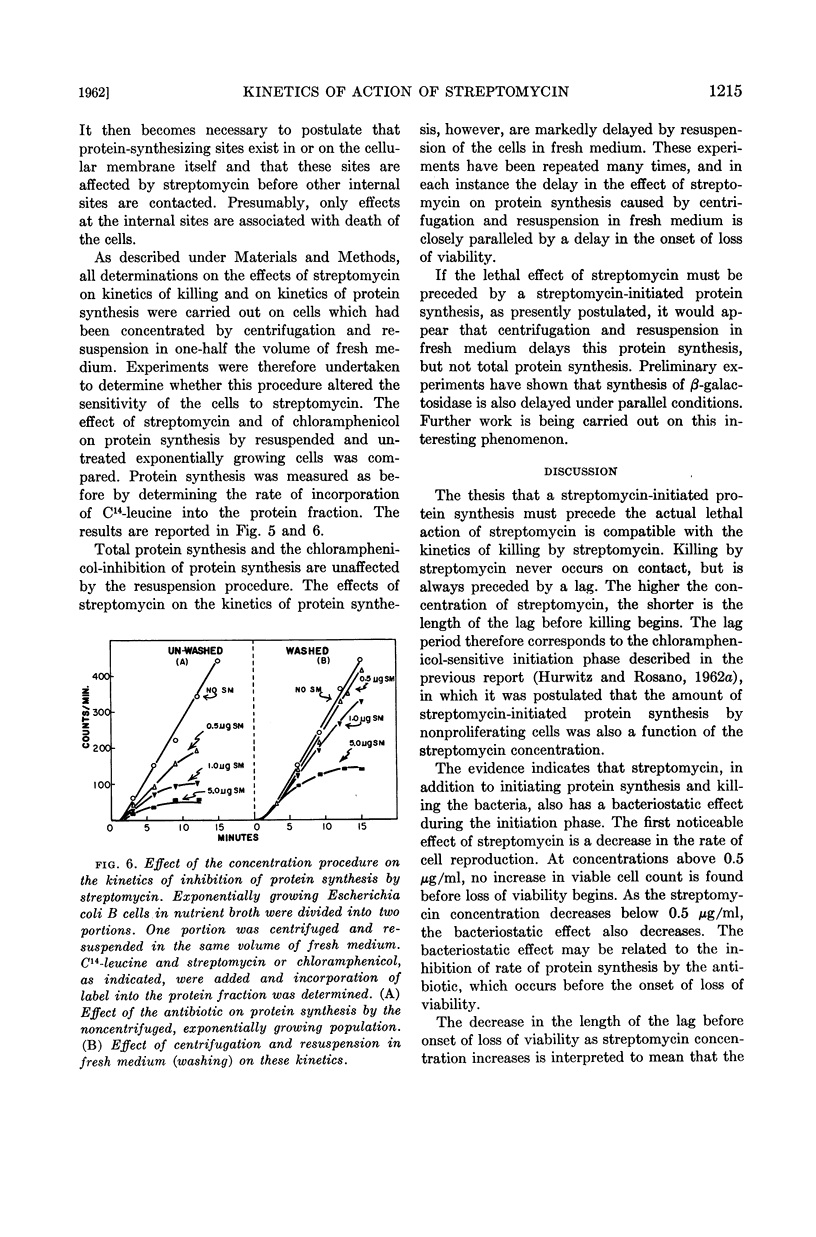
In an accompanying communication (Hurwitz and Rosano, 1962a), evidence was presented in support of the thesis that a chloramphenicol-sensitive, streptomycin-initiated protein synthesis is a necessary precursor for the lethal action of streptomycin. If a streptomycin-initiated protein synthesis is a necessary precursor of the lethal action of streptomycin, the kinetics of loss of viability of growing cells should show delineated phases corresponding to both the initiation and killing phases described in the preceding report. Studies of the kinetics of loss of viability and of the kinetics of inhibition of protein synthesis resulting from exposure of Escherichia coli to streptomycin were therefore undertaken to examine further the validity of the above thesis. In another accompanying report, the kinetics of accumulation of radioisotopic label from C14-streptomycin will be discussed in a similar context (Hurwitz and Rosano, 1962b).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edwards J., Panos C. STREPTOCOCCAL L FORMS V. : Acid-Soluble Nucleotides of a Group A Streptococcus and Derived L Form. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1202–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1202-1208.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1193–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1193-1201.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. The initial kinetics of enzyme induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:77–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90871-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN A. E., LESSNER J. M., WEST M. K. Reversal of the streptomycin injury of Escherichia coli. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):213–223. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


