Abstract
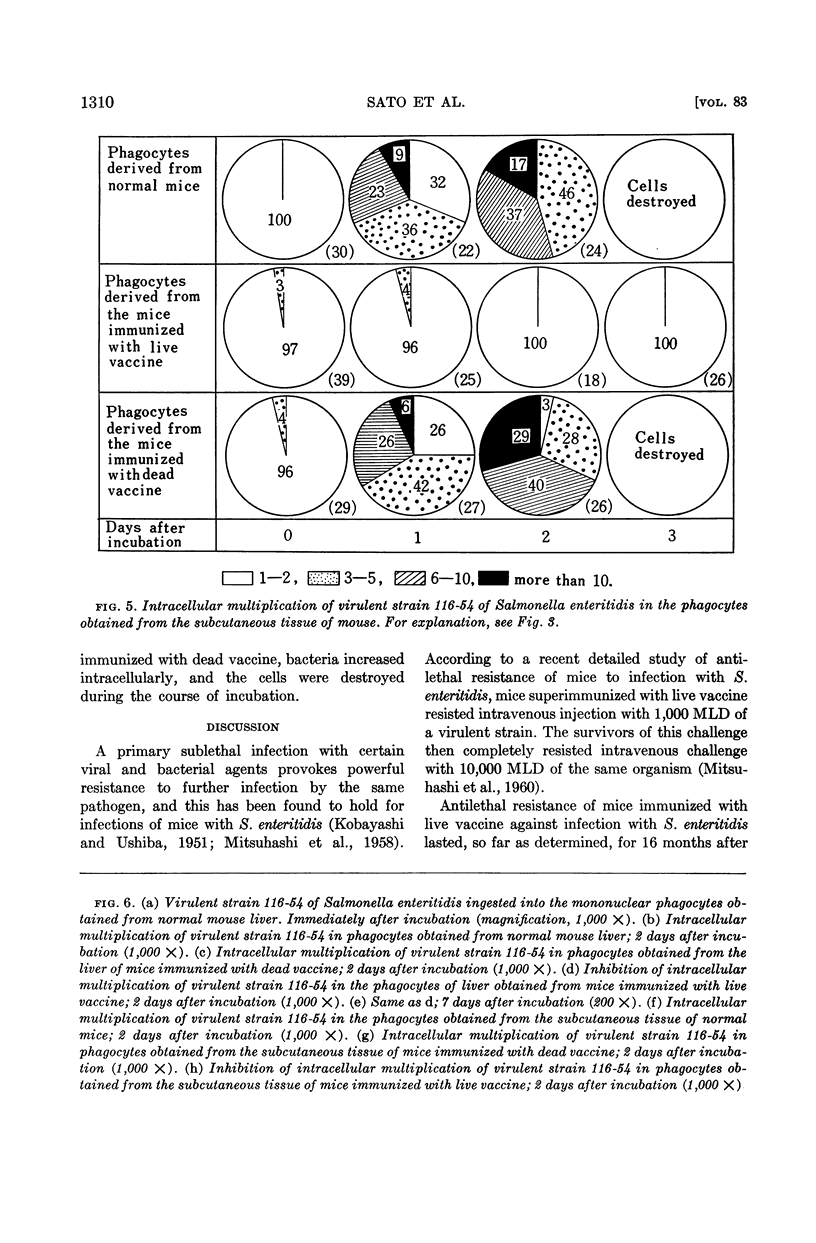
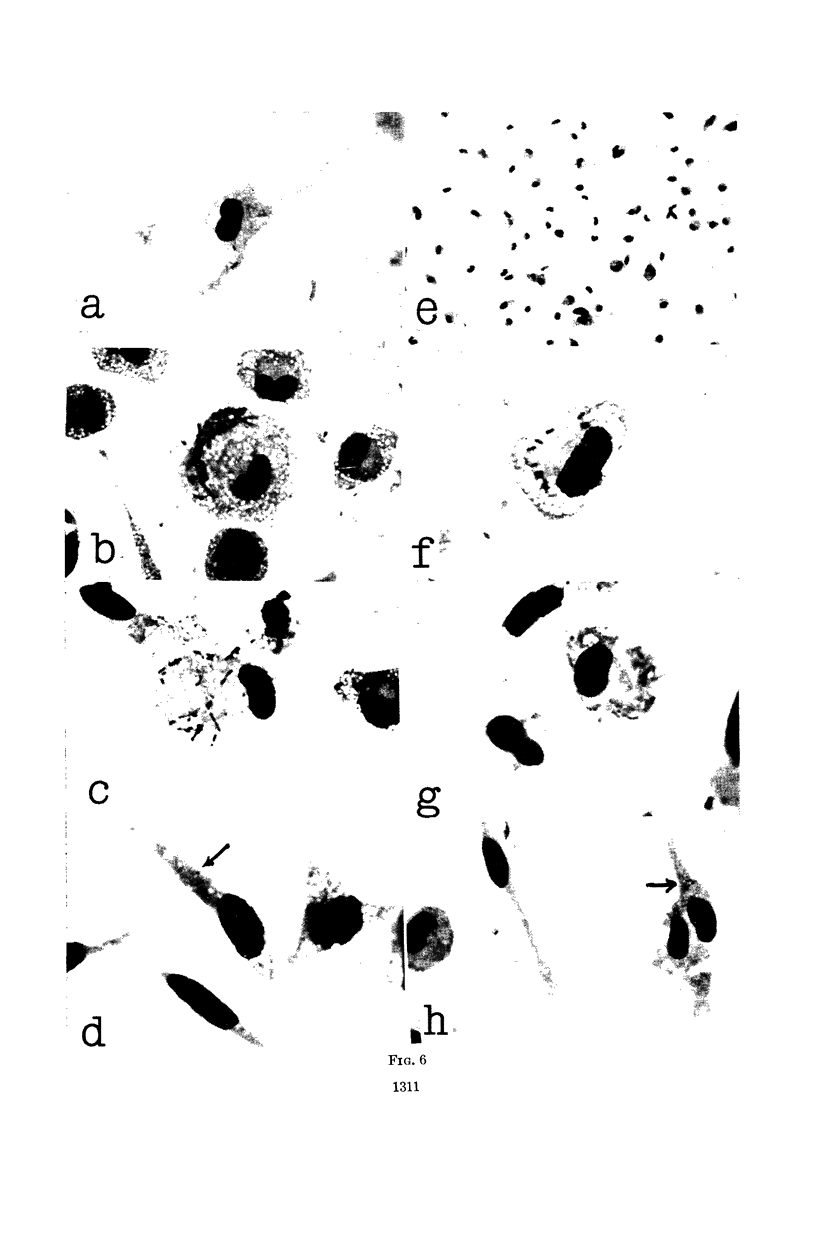
Sato, Ichiei (School of Medicine, Gunma University, Maebashi, Japan), Tokumitsu Tanaka, Kazuko Saito, and Susumu Mitsuhashi. Inhibition of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes from liver and subcutaneous tissue of mice immunized with live vaccine. J. Bacteriol. 83:1306–1312. 1962.—In our earlier studies it was shown that mice hyperimmunized with live vaccine of Salmonella enteritidis resisted intravenous challenge with 1,000 MLD of virulent strain 116–54 of S. enteritidis. Survivors of this challenge completely resisted additional intravenous challenge with 10,000 MLD of the same organism. Mononuclear phagocytes obtained from the abdominal cavity of mice immunized with live vaccine of S. enteritidis inhibited intracellular multiplication of virulent strain 116–54, regardless of the presence of antibody in the cell-culture medium. In the present study, mononuclear phagocytes were obtained in a nearly pure state from liver or subcutaneous tissue of mice and were maintained in vitro in good condition. These cells also resisted cellular degeneration caused by intracellular existence of virulent strain 116–54, regardless of the presence of antibody in the cell-culture medium. In contrast, cells obtained from normal mice or mice immunized with dead vaccine were subject to degeneration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELBERG S. S., SCHNEIDER P., FONG J. Cross-immunity between Brucella melitensis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis; intracellular behavior of Brucella melitensis in monocytes from vaccinated animals. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):545–554. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FONG J., CHIN D., AKIYAMA H. J., ELBERG S. S. Studies on tubercle bacillus-monocyte relationship. III. Conditions affecting the action of serum and cells; modification of bacilli in an immune system. J Exp Med. 1959 Jun 1;109(6):523–543. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.6.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO H., HONDA T., KAWAKAMI M., MITSUHASHI S. Studies on the experimental salmonellosis. VI. Longlasting immunity of mouse immunized with live vaccine of Salmonella enteritidis. Jpn J Exp Med. 1961 Jun;31:187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., HASHIMOTO H., KAWAKAMI M. Antilethal resistance of mice immunized with liver vaccine against infection with Salmonella enteritidis. Jpn J Exp Med. 1960 Oct;30:375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., SATO I., TANAKA T. Experimental salmonellosis. Intracellular growth of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes of mice, and cellular basis of immunity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:863–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.863-868.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]