Abstract
Pdx-1 (pancreatic-duodenal homeobox-1), a MODY4 homeodomain transcription factor, serves as a master regulator in the pancreas because of its importance during organogenesis and in adult islet insulin-producing β cell activity. Here, we show that KLF11, an SP/Krüppel-like (SP/KLF) transcription factor, mutated in French maturity onset diabetes of the young patients (MODY7), regulates Pdx-1 transcription in β cells through two evolutionarily conserved GC-rich motifs in conserved Area II, a control region essential to islet β cell-enriched expression. These regulatory elements, termed GC1 (human base pair −2061/−2055) and GC2 (−2036/−2027), are also nearly identical to the consensus KLF11 binding sequence defined here by random oligonucleotide binding analysis. KLF11 specifically associates with Area II in chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, while preventing binding to GC1- and/or GC2-compromised Pdx1-driven reporter activity in β cell lines. Mechanistically, we find that KLF11 interacts with the coactivator p300 via its zinc finger domain in vivo to mediate Pdx-1 activation. Together, our data identified a hierarchical regulatory cascade for these two MODY genes, suggesting that gene regulation in MODY is more complex than anticipated previously. Furthermore, because KLF11 like most MODY-associated transcription factors uses p300, these data further support a role for this coactivator as a critical chromatin link in forms of type 2 diabetes.
Introduction
The Pdx-1 transcription factor is critical to pancreatic organogenesis and the maintenance of adult islet β cell function. Homozygous inactivating mutations in Pdx-1 result in pancreatic agenesis in both humans and mice (1–3). In addition, heterozygous mutations cause glucose intolerance in murine models and a juvenile (4, 5) and maturity onset form of type 2 diabetes in humans (MODY4) (4). Initially detected throughout the developing pancreatic epithelium, Pdx-1 expression becomes essentially restricted to insulin-producing cells in adult islets (6), wherein this factor directly regulates insulin transcription as well as genes involved in energy-sensing and insulin release in β cells (7, 8).
The first molecular sign of pancreatic development is the restricted expression of Pdx-1 in both the dorsal and ventral gut epithelium prior to hormone transcription at embryonic day (E)6 8.5 (2, 9). Appropriate Pdx-1 expression in this precursor cell population is essential for the development of the endocrine and exocrine compartments. Islet β cell progenitors appear around E13.5 at the start of a massive wave of β cell differentiation, a population of cells associated with relatively high Pdx-1 levels (2, 9). During this period, the first islet somatostatin (δ) and pancreatic polypeptide-producing cells are detected at E15.5 and E18.5, respectively.
Islet β cell-enriched expression of human Pdx-1 is directed by conserved sequences located between bp −2839/−2521 (termed Area I) and bp −2252/−2023 (Area II) relative to the transcription start site. Thus, a transgene driven by Area I and Area II alone recapitulates the endogenous Pdx-1 expression pattern in developing and adult islet β cells in mice (10). Area II appears to be the functional core of this regulatory region, as indicated by its unique ability to both independently direct islet β cell-enriched expression in vivo and activate with enhancer-like properties in cell-lined based assays (10, 11). Complete deletion of Area I, Area II, and Area III (bp −1879 to −1600) in mice, which together direct transgenic expression to embryonic Pdx1+ endocrine and exocrine cells (12), results in severe pancreatic agenesis similar to that of the global knock-out mouse, while maintaining extra-pancreatic (i.e. stomach and duodenal) Pdx-1 expression (13). Collectively, these data demonstrate that Area I and Area II are critical for directing and controlling Pdx-1 transcription levels in islet β cells.
Detailed analyses of conserved sequences within Area I and Area II have begun to elucidate the transcriptional regulatory milieu enabling Pdx-1 to be transcribed in islet β cells. For example, activation of Areas I and II is controlled by islet-enriched factors that are not only involved in β cell differentiation but also glucose homeostasis, including Nkx2.2, FoxA2, MafB, Pax6, HNF1α (MODY3), and PDX-1 (MODY4) itself (14–17). However, these proteins likely only represent a fraction of the necessary regulatory factors, as there remain many potential cis-acting elements within conserved, uncharacterized sequences of Areas I and II (14, 18).
Here we describe, for the first time, the existence of a hierarchical cascade in which KLF11 (MODY7) transregulates the Pdx-1 (MODY4) gene. We show that KLF11 binding regulates Pdx-1 expression in islet β cells, a transcription factor linked to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (19). Mammalian SP/KLF proteins act as potent activators and/or repressors of gene transcription while regulating a diverse array of physiological processes, including cell growth (20), differentiation (21, 22), and early embryonic development (23). KLF11 binds to GC-rich elements within Area II, termed GC1 and GC2, with each acting independently in activation. Moreover, activation is found to be p300-dependent, suggesting that this coactivator behaves as the central node that integrates these pathways. Previous work suggests that the diabetogenic properties of KLF11 result from effects on insulin production, as this factor weakly stimulates insulin-driven transcription in vitro (19). We now demonstrate that MODY7 disease variants of KLF11 display impaired transactivation of Pdx-1, thus predicting interactions between these MODY genes in the generation of type 2 diabetes.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Random Oligonucleotide Binding (ROB) Assay
The ROB assay was performed essentially as described by Blackwell and Weintraub (24). In brief, a random library of DNA sequences was generated by synthesizing an oligonucleotide containing a 35-bp random core sequence flanked on each side by 20 bp. The double-stranded oligonucleotides used in the first round of DNA binding were generated by one cycle of PCR (3 min at 94 °C, 2 min at 55 °C, and 10 min at 72 °C) using Pwo polymerase (Roche Applied Science), with a 10-fold molar excess of reverse primer to random oligonucleotide. The PCR product was purified on a 3% low melting point agarose gel and end-labeled with [γ-32P]ATP and T4 polynucleotide kinase. Gel shift assays were performed using 200 ng of purified glutathione S-transferase or GST-KLF11. The bound DNA sequences were purified by excising the protein-probe complexes from the gel and by incubating the slice in a mixture of 0.5 m ammonium acetate, 10 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EDTA, and 0.1% SDS. The PCR-amplified bound sample was then purified on a 3% agarose gel, end-labeled, and used in the next round of gel shift analysis. Control PCRs with no oligonucleotide template were always used and did not yield a product. After the seventh round of purification, the PCR product was digested with EcoRI and BamHI, cloned, and sequenced. The sequences were analyzed with MacVector (Eastman Kodak Co.) and Genetics Computer Group DNA software (Madison, WI).
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
Nuclear extracts were prepared from the MIN6 β cell line as described previously (25). In vitro translated and His-tagged KLF11 was prepared from pcDNAHisA-KLF11 (27) using the TnT coupled reticulocyte lysate system (Promega). Supershift reactions were carried out by preincubating in vitro-translated KLF11 (10 μg) with α-histidine (4 μl) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or α-KLF11 (2 μl) antibodies (26). The polyclonal α-KLF11 antiserum was generated to a unique peptide region within the N-terminal region of human KLF11, and it recognized a single protein species in MIN6 extracts that comigrated with in vitro-translated KLF11 by Western analysis (data not shown). Approximately 5 μg of MIN6 extract protein or 5 μl of in vitro-translated KLF11 was used per reaction, with binding (30 μl) carried out in 100 mm Hepes, pH 7.5, 50 mm KCl, 25 mm MgCl2, 50 μm ZnCl2, 30% glycerol, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, and 250 mg/ml poly(dI-dC). The conditions for the competition analysis were the same, except that 50–250-fold molar excess of unlabeled competitor DNA was included in the binding mixture. The double-stranded oligonucleotide probes were end- labeled with polynucleotide kinase and [γ-32P]ATP. The probe sequences were as follows: human (h) GC1WT (−2026AGTAAACACTCCGGGGGTGGCAGGCGAGGCAGG−2020); hGC1Mut (−2026ACACTCCGttttgtGCAGGCGAGGCAGG−2020); hGC2WT (−1999GGCAGGGAGCAGGGGAGGGAGAGTGAGG−1993); hGC2Mut (−1999GGCAGGGAGCAGtttctttAGAGTGAGG−1993); hGC1WT+ GC2WT (−2033ACACTCCGGGGGTGGCAGGCGAGGCAGGGAGCAGGGGAGGGAGAG−1989); hGC1Mut+GC2WT (2033ACACTCCGttttgtGCAGGCGAGGCAGGGAGCAGGGGAGGGAGAG−1989); hGC1WT+GC2Mut (−2033ACACTCCGGGGGTGGCAGGCGAGGCAGGGAGCAGtttctttAGAG−1989); hGC1Mut+GC2Mut (−2033ACACTCCGttttgtGCAGGCGAGGCAGGGAGCAGtttctttAGAG−1989); KLF consensus (5′-AGCTTGAGAAGGAGGCGTGGCCAACGCATG-3′) (19, 27); hSMAD7WT (5′-ATTCGATCGGGGCGGGGCGAGC-3′) (28); and hSMAD7 Mut (5′-ATTCGATCGGttCGGGGCGAGC-3′) (27, 28). KLF consensus site sequences are underlined, and the mutated nucleotides within the binding domain are in lowercase. The samples were electrophoresed on 4% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels in 0.5× TBE (6 mm Tris base, pH 8.3, and 0.5 mm EDTA) before drying and autoradiography.
Immunoprecipitation Assays
Human L3.6 cells were transfected with 15 μg of FLAG-tagged KLF11, His-tagged p300, and/or control vector. Whole cells extracts were prepared 24 h later using lysis buffer (150 mm NaCl, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 20 mm MgCl2) supplemented with Complete Protease Inhibitor tablets. Immunoprecipitations were performed using α-FLAG M2 antibody (Sigma) and complexes detected with α-p300 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or α-FLAG antibodies by Western blot analysis. The α-KLF11/TIEG2 and p300 antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were used for endogenous protein immunoprecipitations.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
Confluent cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde for 10 min at 37 °C. DNA was fragmented to ∼500 bp by sonication and then immunoprecipitated using α-KLF11/TIEG2 or p300 antibodies with salmon sperm DNA/protein A-agarose beads (Upstate Cell Signaling Solutions, Lake Placid, NY) in ChIP dilution buffer (16.7 mm Tris, pH 8.1, 0.01% SDS, 1.1% Triton X-100, 1.2 mm EDTA, and 167 mm NaCl). The eluted, immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by PCR using the following primers: mouse Area II, 5′-GGTGGGAAATCCTTCCCTCAAG and 5′-CCTTAGGGATAGACCCCCTGC; mouse Area I, 5′-GGGACAGACTCTCAGCAGAAGTGG and 5′-TCTGGCTCCCAGCACCATCAGGTG; human Area II, 5′-CCTTCTGCAGGGCCGAGCAAAAATA and 5′-GTTGACTTGGCGACGCGGTTATGA; and human Area I, 5′-TAAACCGCGTCTCTGTGAAGGGA and 5′-TCTAGCTCCTGGTATCGTAAAATC. The amplified products were visualized on an ethidium bromide-stained 2% agarose gel. Amplification of the appropriate gene fragments was ensured by comparison with molecular weight markers run on the same gel and DNA sequencing.
Transfection Constructs
The Pdx-1 reporter constructs were made using human sequences cloned directly upstream of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase minimal promoter in the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase expression vector, pTk(An). The construction of the Pdx-1-pTk construct representing human Area II (bp −2139/−1958) was described previously (18). Block mutations in the GC-rich motifs were generated using the QuikChange mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). The following oligonucleotides were used for mutagenesis: hGC1, −2026AGTAAACACTCCGttttgtGCAGGCGAGGCAGG−2020, and hGC2, −1999GGCAGGGAGCAGtttctttAGAGTGAGG−1993. The GC2 mutation was introduced into the Area II GC1Mut-pTk construct to generate Area II GC1+GC2Muts-pTk. All of the mutated sequences are in lowercase, with the accuracy of each construct confirmed by sequencing at least 500 bp spanning the mutation(s). The p300 wild type and mutants were obtained from Upstate Cell Signaling Solutions (Lake Placid, NY). The expression constructs of the wild type and diabetes-associated variants of KLF11 have been described previously (19). The siRNA to KLF11 was obtained from Dharmacon RNAi Technology (Lafayette, CO).
Semiquantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). A total of 1–2 μg of RNA was reverse-transcribed using SuperScript III reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen). A portion of the total cDNA was amplified by PCR using 94 °C denaturation, 57 °C annealing, and 72 °C extension temperatures. Positive and negative strand primers and the number of cycles used for amplification of each mRNA species were as follows: Pdx-1, 35 cycles, 5′-AGGAGGAGGACAAGAAGCGCG and 5′-CCAGGAGCAGCTCCTGCCTC; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 26 cycles, 5′-GACCTGACCTGCCGTCTAGAAAAA and 5′-ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAAT; and KLF11, 35 cycles, 5′-CAGTGTTCATCACCTCTAGC and 5′-AACGAGCAAACTTTTTATCA. Amplified products were visualized under UV illumination following electrophoresis on an ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel.
Transfections and Tissue Culture Conditions
The monolayer MIN6, βTC-3, and L3.6 cell lines were maintained as described previously (19, 29). Transfection of βTC-3 cells was carried out using the Lipofectamine reagent (Invitrogen) and L3.6 cells by electroporation (31) using 1 μg of Pdx-1-pTk and 1 μg of RSV-LUC (2 μg total). Rous sarcoma virus enhancer-driven luciferase (pRSV-LUC) activity was used to normalize the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity from cotransfected Pdx-1-pTk. Extracts were prepared 40–48 h after transfection and luciferase and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase enzymatic assays were performed as described previously (10, 19, 25). Each experiment was performed on at least three independent occasions.
Histological Assessment of Pancreas and Isolated Islets
Human islets were obtained from the Diabetes Research Institute Islet Cell Resource at the University of Miami through the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Human Islet Distribution Program. The islets were shipped in CMRL media by overnight courier to Vanderbilt University and cultured for an additional 24 h in CMRL media, 95% CO2, 5% O2 at 37 °C. Human and mouse islets were embedded by first immobilizing in Collagen I (BD Biosciences) that was allowed to solidify for 40 min at 37 °C. These islets were then fixed at 4 °C in freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde in 1× phosphate-buffered saline for 20 min, followed by three 20-min washes with 1× phosphate-buffered saline and 3 h in 30% sucrose, 1× phosphate-buffered saline. The islets were cryopreserved in Optimum Cutting Temperature Compound (VWR Scientific Products, Willard, OH). Adult mouse pancreatic tissues were preserved as described previously (30). Immunocytochemistry on 8-μm cryosections was performed as described previously (33). The primary antibodies used for immunocytochemical analysis were monoclonal mouse α-KLF11 (1:1000 (25)), guinea pig α-insulin (1:2000; Linco Research Immunoassay, St. Charles, MO), guinea pig α-glucagon (1:2000; Linco), guinea pig α-pancreatic polypeptide (1:2000; Linco), sheep α-somatostatin (1:2000; American Research Products, Belmont, MA), and goat α-Pdx-1 (1:100,000; gift of Dr. C. Wright, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN). The primary antibody-antigen complexes were visualized using secondary antibodies conjugated with Cy2, Cy3, or Cy5 fluorophores from Jackson ImmunoResearch (West Grove, PA). Nuclear counterstaining was performed using YoPro1, 1:1000 (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR). Digital sample images were acquired with a Zeiss LSM510 META confocal laser-scanning microscope at 1-μm optical depth.
Statistical Analysis
Comparisons between groups were based on the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. Analysis was performed on Statview software (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
RESULTS
In Vitro Studies Reveal a Potential for KLF11 to Transregulate Pdx-1
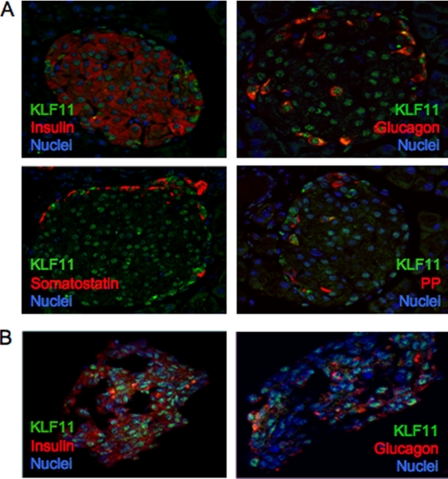
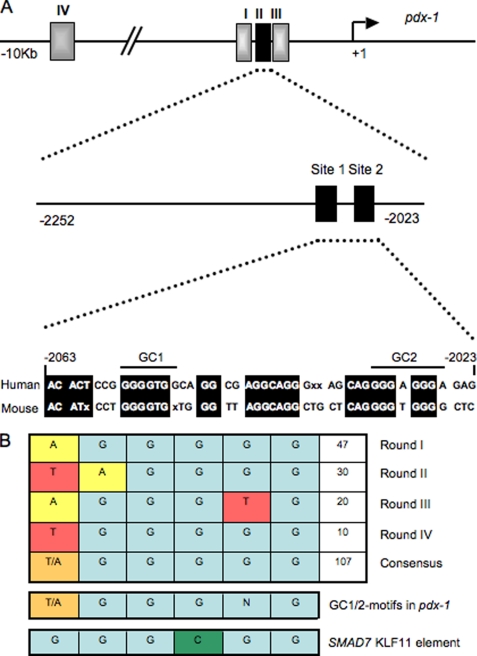
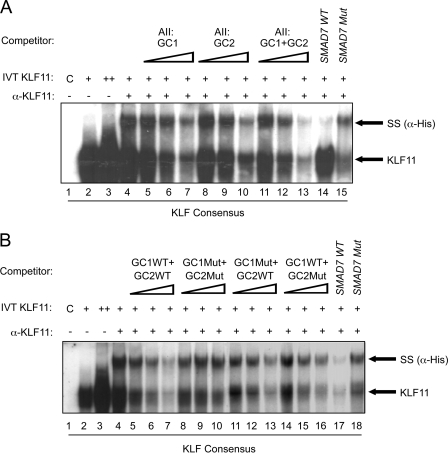
Dysregulation of key islet-enriched transcription factors has been implicated in the pathogenesis of MODY type 2 diabetes, although the detailed mechanisms underlying these events remain elusive. Our experiments led us to investigate the potential transregulation of Pdx-1 (MODY4) by KLF11 (MODY7). These transcription factors colocalize in the pancreas, with KLF11 enriched in Pdx-1+ islet β cells relative to the surrounding pancreatic acinar and duct cells in mice (Fig. 1A) and humans (Fig. 1B). Bioinformatics analyses of human Pdx-1 Areas I, II, and III revealed two potential GC-rich KLF11-binding sites at bp −2061/−2055 and bp −2033/−2026 in the Area II control region (Fig. 2A). Interestingly, these sequences were very similar to those defined for KLF11 in the ROB assay (Fig. 2B). Moreover, they were also remarkably similar to the high affinity binding element in the SMAD7 gene, a verified target of KLF11 in vivo (Fig. 2B) (28). Gel shift analysis was performed using in vitro-translated KLF11 to directly examine the binding potential of GC1 and GC2. These individual elements both competed effectively for binding to the ROB-defined consensus probe, which can be observed on formation of either the normal or α-histidine-tagged supershifted KLF11 complex (Fig. 3A). A GC1 and GC2 spanning competitor functioned as efficiently as the SMAD7 KLF11-binding element, whereas GC1 or GC2 consensus core mutants reduced effectiveness (Fig. 3B). KLF11 binding was eliminated in the GC1 and GC2 double mutant. Our gel shift data indicated that KLF11 binds in vitro to the Pdx-1 GC1 and GC2 sites. These in vitro results suggested a potential role for KLF11 in Pdx1 transcription.
FIGURE 1.
KLF11 is localized in the nuclei of islet cells. Double immunofluorescence was used to analyze coexpression in mouse adult pancreatic tissue (A) and isolated human islets of KLF11 (green) with hormones (red) (B). A and B, insulin and glucagon, somatostatin (A), and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) (A). The nuclei are counterstained in blue.
FIGURE 2.
Pdx-1 Area II control region contains two KLF11-like binding motifs, termed GC1 and GC2. A, diagram of the human Pdx-1 promoter region, illustrating the relative position of the conserved Area I (bp −2839/−2521), Area II (bp −2252/−2023), Area III (bp −1879 to −1600), and Area IV (bp −8656 to −8155) control regions. The KLF11-like sites of Area II are shown, with conserved sequences of identity between human and mouse species highlighted. B, KLF11 binding consensus sequences recognized after four cycles of random oligonucleotide binding. Also illustrated is the similarity to GC1, GC2, and the SMAD7 binding element.
FIGURE 3.
KLF11 binds to the GC1 and GC2 elements. A, binding with an ROB consensus probe was performed with in vitro-translated (IVT) His-tagged KLF11. The two bands containing KLF11 were identified by addition of α-His antibody. Importantly, the levels of supershifted (SS) and parent complex were effectively reduced upon addition of 50-, 100-, and 250-fold excess of unlabeled wild type (WT) GC1, GC2, or GC1+GC2 competitor, although the GC1 and/or GC2 mutant did so inefficiently in B, if at all. A and B, results with 250-fold excess of the wild type and mutant (Mut) SMAD7 competitor parallel that found for GC1+GC2 binding.
KLF11 Transregulates Pdx1 in Vivo
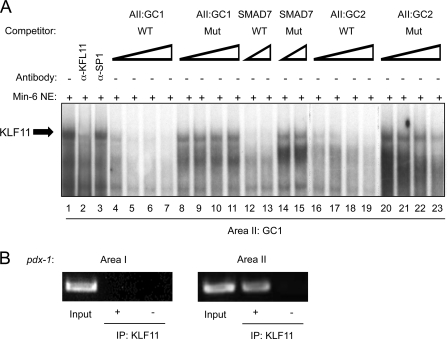
Based upon our in vitro predictions, binding to GC1 and GC2 was analyzed in MIN6 nuclear extracts, a KLF11-producing β cell line (19). The protein-GC1 probe complex was disrupted by addition of α-KLF11, and not the α-Sp1 antibody (Fig. 4A). The binding specificity of the α-KLF11-sensitive β cell complex was also identical to that observed with in vitro-translated KLF11 with the wild type GC1, GC2, and SMAD7 elements reducing complex formation, whereas the KLF11 binding mutant site competitors had no impact. We used ChIP to define whether endogenous KLF11 indeed binds within the GC1 and GC2 region of the Pdx-1 gene in β cells in vivo. KLF11 binding enrichment to Area II was compared with the Area I region, with the latter serving as a negative control due to the lack of KLF11-like element sequences. The Area II signal was highly enriched relative to the no antibody (−) control or the α-KLF11 precipitation of Area I (Fig. 4B). Collectively, these results strongly suggest that KLF11 binds to GC1 and/or GC2 of Area II in β cells in vivo.
FIGURE 4.
KLF11 binds within Area II in vivo. A, gel mobility shift assays were performed with the Pdx1 GC1 probe and MIN6 β nuclear extracts (NE). The competitions were conducted with 10-, 25-, 50-, and 100-fold molar excess of wild type (WT) and mutant (Mut) GC1 and GC2, or 50- and 100-fold excess of SMAD7. B, formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin from βTC-3 cells was incubated with antibodies raised to KLF11 (demarcated by +). Immunoprecipitated (IP) DNA was analyzed by PCR with primers specific to transcriptional regulatory sequences of mouse Pdx-1 Area I and Area II. The signal obtained from input DNA and the no antibody (−) control is shown.
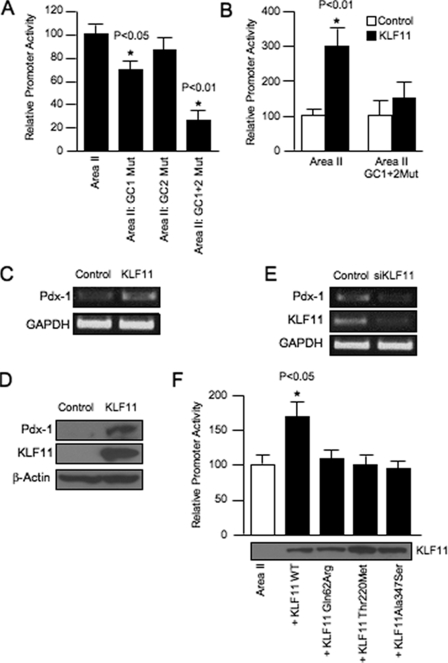
Subsequently, we used reporter assays to investigate how GC1 and GC2 influenced human Area II activation. KLF11-binding defective mutants were constructed into a reporter driven by Area II alone. The GC1 mutant resulted in an ∼25% reduction from wild type Area II reporter activity in transfected L3.6 (human pancreatic cell line that produces low endogenous levels of KLF11 and Pdx-1 (see Ref. 31 and data not shown)), βTC-3 and MIN6 cells (data not shown), although there was no statistically significant change in the GC2 mutant (Fig. 5A). Notably, many of the block mutants constructed within conserved sequences of Area II had little or no effect on β cell activity (11, 15), perhaps suggesting functional redundancy within this control region. Consistent with this proposal, the GC1+GC2 double mutant significantly reduced Area II enhancer activity (Fig. 5A), implying that both elements are important to KLF11-mediated activation of Pdx-1.
FIGURE 5.
KLF11 stimulates Area II-driven activation through GC1 and GC2. A, wild type (WT) and mutant (Mut) Area II-pTk constructs were transfected into βTC-3 cells. The normalized activity ± S.D. of each mutant construct is presented as the percentage of wild type Area II-pTk. B, L3.6 cells were transfected with wild type Area II-pTk, mutant GC1+GC2 Area II-pTk, the pcDNA3.1HisA parental vector, and/or the KLF11 expression construct. The activity ± S.D. is presented as the KLF11-normalized activity relative to that of the reporter construct alone. C, representative results of reverse transcription-PCR analysis performed on isolated L3.6 pancreatic RNA cells from KLF1l or empty vector-transfected cells. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an internal control. D, Western blot analysis for Pdx-1 levels in His-tagged KLF11 or control vector-transfected L3.6 whole cell lysates. β-Actin was used as a loading control. E, KLF11, Pdx-1, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA levels from a typical transfection experiment with siRNA targeting KLF11 or control scrambled siRNA in L3.6 cells. The siRNAs were present in transfected cells for 72 h prior to RNA extraction. F, wild type KLF11 and the Q62R, T220M, and A347S mutants were cotransfected with Area II-pTk into L3.6 cells. KLF11+Area II-pTk activity ± S.D. is shown relative to Area II-pTk alone. KLF11 protein level from a representative transfection is shown. p values in A, B, and F were determined relative to the Area II-pTk point.
To further define whether the KLF11 directly activates Pdx-1 expression, we analyzed the effect of this zinc finger transcription factor upon cotransfected wild type and GC1+GC2 double mutant Area II reporter activity in L3.6 cells. Interestingly, KLF11 expression increased Area II activity by roughly 3-fold compared with the empty vector or the Area II GC1+GC2 mutant reporter (Fig. 5B). Congruent with these results, KLF11 also increased by ∼2.5-fold endogenous Pdx-1 mRNA levels (Fig. 5C) and protein even more appreciably (Fig. 5D). Conversely, KLF11 siRNA knockdown decreased Pdx-1 mRNA expression ∼60% in L3.6 cells (Fig. 5E). Similar results were obtained in other cell lines (data not shown). When considering the data collectively, we believe that KLF11 specifically interacts with GC1 and GC2 and transregulates Pdx-1 expression in pancreatic cells in vivo.
MODY7-associated Variants of KLF11 Have Impaired Activity on the Pdx-1 (MODY4) Area II Enhancer
Previous genetic studies identified KLF11 variants that segregate in families with early onset type 2 diabetes, specifically Q62R, T220M, and A347S. All of these variants were less effective than wild type KLF11 at stimulating transfected catalase 1 promoter-driven activity, and only Q62R impaired insulin-driven activation (19). Consequently, based upon the fact that KLF11 transregulates Pdx-1 expression in β cells in vivo, we examined whether Q62R, T220M, and A347S influenced KLF11 activation of the Area II reporter in βTC3 cells. Each of these variants had a similar low activity, with the residual comparable with Area II alone. Significantly, their relative inactivity was not because of differences in protein production (Fig. 5F). These results suggest that the MODY7 mutants would compromise Pdx-1 activation, and in so doing broadly impact islet β cell activity in affected individuals.
KLF11 Interacts with p300 to Activate Pdx-1
Transcription factors impact gene expression not only through their inherent activation/repression properties but also through protein-protein interactions with coactivators/corepressors. For example, the relative inactivity of the MODY7 Q62R variant is likely due to increased association with the mSin3A corepressor (19). Here, we tested if activation by KLF11 involved p300, a histone acetyltransferase transcriptional coactivator that functions, at least in part by bridging, through direct interactions, the activator to both chromatin and the basal transcriptional machinery.
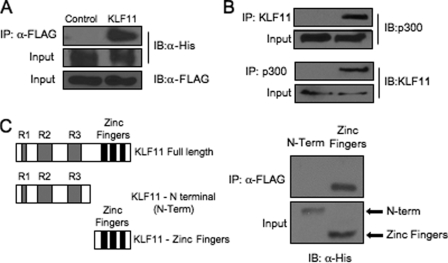
A possible interaction between KLF11 and p300 was first examined in immunoprecipitation assays performed on L3.6 cell lysates cotransfected with KLF11 and p300 expression vectors. The presence of p300 in a α-FLAG immunocomplex was detected in FLAG-tagged KLF11-transfected cells, and not those with only the parental vector (Fig. 6A). Significantly, an endogenous p300-KLF11 complex was also detected using α-KLF11 and α-p300 antibodies (Fig. 6B). Mapping of this interaction revealed that the sequences in KLF11 necessary spanned the zinc finger motifs in the C terminus (Fig. 6C).
FIGURE 6.
KLF11 interacts with the p300 coactivator in pancreatic L3.6 cells. A, FLAG-tagged KLF11 and His-tagged p300 expression vectors were transfected into L3.6 cells. Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis was performed with α-FLAG antibody, and the precipitates were immunoblotted (IB) with α-His antibody. B, L3.6 total lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-KLF11 and α-p300 and then probed with α-KLF11 or α-p300. C, FLAG-p300 was cotransfected with His-tagged KLF11 expression constructs spanning the N-terminal repressor domains R1, R2, R3 (N-Term), or C-terminal zinc finger domains (32). Only the C-terminal domain interacted with p300, although comparable levels of both KLF11 constructs were produced.
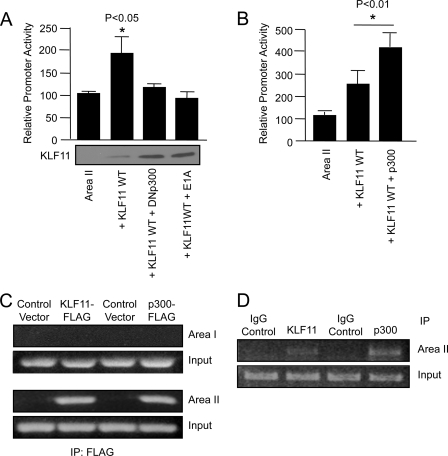
The p300-binding adenovirus E1A protein and a dominant-negative acting p300 were also able to inhibit KLF11 activation of the Area II reporter in transfected L3.6 cells (Fig. 7A). Notably, these effectors of p300 action did not compromise KLF11 activator levels. Furthermore, ChIP analysis showed that only endogenous Area II sequences and not Area I were α-KLF11- or α-p300-immunoprecipitable in KLF11- or p300-transfected L3.6 cells (Fig. 7C) or upon analyzing endogenous protein binding (Fig. 7D). These results indicate that physical and functional interactions between p300 and KLF11 play an important role in Pdx-1 transcription. More importantly, however, because several MODY genes function via p300 in β cells, these data support a central role for this coactivator with diabetes-associated transcription factors (35, 37–39).
FIGURE 7.
p300 coactivator increases KLF11-mediated activation. A and B, L3.6 cells were transfected with Area II-pTk and either KLF11, p300, dominant-negative acting p300 (DNp300), or adenovirus E1A. Promoter activity ± S.D. is presented relative to Area II-pTk alone. KLF11 protein level from a representative transfection is shown. The p values were determined relative to the Area II-pTk point. C and D, KLF11 and p300 bind to endogenous Pdx-1 Area II sequences. C, L3.6 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged KLF11 or p300. Cross-linked DNA immunoprecipitated with α-FLAG antibody was analyzed by PCR with Pdx-1 Area I and Area II control region-specific primers. The input chromatin (1:100 dilution) signal in the ChIP is shown. D, endogenous p300 and Pdx-1 binding to Area II was determined in L3.6 cells by ChIP. Note, no signal is detected in IgG-treated samples.
DISCUSSION
KLF11 is a member of the SP/KLF factors of zinc finger DNA-binding regulatory proteins, whose functions include tissue-specific regulation of pancreatic acinar SMAD7, SOD2, and catalase 1 (19, 28) and islet β cell insulin gene expression (19). KLF11 coding region variants are also associated with type 2 diabetes-afflicted French Moroccan families. However, our understanding of how islet β cell physiology is impacted in these patients has remained incomplete, as earlier functional tests merely showed that human insulin-driven reporter activity was affected in the Q62R variant (19). Here, we have linked KLF11 to Pdx-1 transcriptional regulation, which encodes a transcription factor essential to pancreas development and adult islet β cell activity, including glucose metabolism, insulin transcription, insulin processing, and insulin secretion. Our data provide a broader perspective on how compromising expression of this master regulator in the KLF11 Q62R, T220M, or A347S variants diminishes β cell function in affected type 2 patients.
KLF11 activates Pdx-1 through the conserved GC1 and GC2 elements of Area II, which represents the principal control domain for islet β cell expression. In contrast, KLF11 binding was not detected to other control regions in gel shift or ChIP experiments. Notably, Area II is the only one of the four Pdx-1 control domains to possess enhancer-like properties in vitro and independently direct transgenic reporter expression in vivo (10, 11). Importantly, the Q62R, T220M, and A347S type 2 diabetes variants are all ineffective activators of Area II, suggesting that Pdx-1 expression levels would be compromised in each. Islet β cell function could be impacted at multiple levels as a result, because Pdx-1 evolves from a critical growth and differentiation factor impacting islet cell mass and function during embryogenesis to a master regulator of glucose responsiveness and insulin secretion in adult cells (6, 7).
KLF11 (MODY7) can function as a transcriptional repressor and activator, with Sin3a-histone deacetylase complex-mediating repression (32). Here, we now show that p300 facilitates KLF11 transcriptional activity. In light of these results, we searched for evidence as whether this coactivator is necessary for other proteins either critically involved in the regulation of β cell biology or, more importantly, in MODY syndromes. Interestingly, this coactivator is not only important for other islet-enriched activators, including Pax6 and NeuroD1 (33, 34), but more strikingly its coregulator activity is shared among 90% of MODY genes, including MODY1 (HNF4α), MODY2 (GCK), MODY3 (HNF1α), MODY4 (PDX-1), MODY5 (TCF2), MODY6 (NEUROD1/BETA2), and MODY7 (KLF11). Therefore, an emerging theme in this field is that most MODY factors act in a coordinated manner to regulate islet-enriched gene expression, with p300-catalyzed acetylation of histones key to their activation (8). In fact, in some of these syndromes, like in the MODY1-associated HNF4α gene, p300 recruitment was effected in the R154X and E276Q variants (37). A similar effect has been defined in some MODY3 families, where the R263L HNF1α mutant had a defect in p300 coupling (37). Other complications of diabetes, such as extracellular matrix production with cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, have been associated with deficiencies in p300 activation (35, 37–39). Collectively, these data support a key role for this coactivator as a transcriptional node that integrates many diabetes-associated pathways.
The proper expression of Pdx-1 is essential for pancreatic exocrine and endocrine cell development and the maintenance of adult islet β cell function. Consistent with a role in pancreatic expression, KLF11 was enriched in the nuclei of human and mouse islet cell expression as well as at a lower level in acinar cells. Misexpression of Pdx-1 in the endocrine pancreas results in β cell inactivity. For example, inactivating mutations cause symptoms of glucose intolerance and are genetically linked with an early onset form of type 2 diabetes, termed MODY4 (35, 36). The increased binding properties of the KLF11 Q62R type 2 diabetes variant to the corepressor mSin3A (19) would also compromise Pdx-1 expression in β cells. Although it is unclear how the KLF11 T220M and A347S mutants impact the β cell, it is tempting to speculate that dysfunction results from reduced association with p300 and/or other coactivator factors. These data also indicate that aberrant association of MODY7 mutants with the corepressor Sin3a-histone deacetylase complex could contribute to diabetes progression. Together, these results indicate that chromatin dynamics, in particular the histone deacetylase-acetyltransferase system, is at the center of MODY7 and other related forms of diabetes. Notably, these results may fuel future experiments focused on more carefully investigating the direct role of corepressors and coactivators in MODY.
In summary, we revealed for the first time a hierarchical transregulatory pathway involving two MODY-related transcription factors, with KLF11 activating Pdx-1. The association of KLF11 with p300, a coactivator shared among most MODY proteins, supports a critical role for this histone acetyltransferase protein in pancreatic β cell development and function. In light of these interactions, we predict that the pathophysiological forms of type 2 diabetes result from reduced activity/expression of key transcriptional regulators, like the MODY-affected factors.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant P60 DK20593 from USPHS and Grant RO1 DK-50203 (to R. S.), Training Grant 5T32 CA09385-18 (to J. C. V. V.), Grants CA125127 and CA136526 (to M. E. F.-Z.), and Grant DK 52913 (to R. U.). This work was also supported by French National Research Agency Grant ANR-06-BLAN-0236, European Regional Development Fund, and Region Nord-Pas de Calais grants (to P. F. and B. N.).
- E
- embryonic day
- siRNA
- small interfering RNA
- ChIP
- chromatin immunoprecipitation
- ROB
- random oligonucleotide binding
- MODY
- maturity onset diabetes of the young patients.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jonsson J., Carlsson L., Edlund T., Edlund H. (1994) Nature 371, 606–609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Offield M. F., Jetton T. L., Labosky P. A., Ray M., Stein R. W., Magnuson M. A., Hogan B. L., Wright C. V. (1996) Development 122, 983–995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stoffers D. A., Heller R. S., Miller C. P., Habener J. F. (1999) Endocrinology 140, 5374–5381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stoffers D. A., Ferrer J., Clarke W. L., Habener J. F. (1997) Nat. Genet. 17, 138–139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Clocquet A. R., Egan J. M., Stoffers D. A., Muller D. C., Wideman L., Chin G. A., Clarke W. L., Hanks J. B., Habener J. F., Elahi D. (2000) Diabetes 49, 1856–1864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oliver-Krasinski J. M., Stoffers D. A. (2008) Genes Dev. 22, 1998–2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Babu D. A., Deering T. G., Mirmira R. G. (2007) Mol. Genet. Metab. 92, 43–55 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keller D. M., McWeeney S., Arsenlis A., Drouin J., Wright C. V., Wang H., Wollheim C. B., White P., Kaestner K. H., Goodman R. H. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 32084–32092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ahlgren U., Jonsson J., Edlund H. (1996) Development 122, 1409–1416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Van Velkinburgh J. C., Samaras S. E., Gerrish K., Artner I., Stein R. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 38438–38444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Samaras S. E., Cissell M. A., Gerrish K., Wright C. V., Gannon M., Stein R. (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 4702–4713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wiebe P. O., Kormish J. D., Roper V. T., Fujitani Y., Alston N. I., Zaret K. S., Wright C. V., Stein R. W., Gannon M. (2007) Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 4093–4104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fujitani Y., Fujitani S., Boyer D. F., Gannon M., Kawaguchi Y., Ray M., Shiota M., Stein R. W., Magnuson M. A., Wright C. V. (2006) Genes Dev. 20, 253–266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gerrish K., Cissell M. A., Stein R. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 47775–47784 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gerrish K., Gannon M., Shih D., Henderson E., Stoffel M., Wright C. V., Stein R. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3485–3492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Samaras S. E., Zhao L., Means A., Henderson E., Matsuoka T. A., Stein R. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 12263–12270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Artner I., Blanchi B., Raum J. C., Guo M., Kaneko T., Cordes S., Sieweke M., Stein R. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 3853–3858 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gerrish K., Van Velkinburgh J. C., Stein R. (2004) Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 533–548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Neve B., Fernandez-Zapico M. E., Ashkenazi-Katalan V., Dina C., Hamid Y. H., Joly E., Vaillant E., Benmezroua Y., Durand E., Bakaher N., Delannoy V., Vaxillaire M., Cook T., Dallinga-Thie G. M., Jansen H., Charles M. A., Clément K., Galan P., Hercberg S., Helbecque N., Charpentier G., Prentki M., Hansen T., Pedersen O., Urrutia R., Melloul D., Froguel P. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 102, 4807–4812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Black A. R., Black J. D., Azizkhan-Clifford J. (2001) J. Cell. Physiol. 188, 143–160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katz J. P., Perreault N., Goldstein B. G., Lee C. S., Labosky P. A., Yang V. W., Kaestner K. H. (2002) Development 129, 2619–2628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.De Graeve F., Smaldone S., Laub F., Mlodzik M., Bhat M., Ramirez F. (2003) Gene 314, 55–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shindo T., Manabe I., Fukushima Y., Tobe K., Aizawa K., Miyamoto S., Kawai-Kowase K., Moriyama N., Imai Y., Kawakami H., Nishimatsu H., Ishikawa T., Suzuki T., Morita H., Maemura K., Sata M., Hirata Y., Komukai M., Kagechika H., Kadowaki T., Kurabayashi M., Nagai R. (2002) Nat. Med. 8, 856–863 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. (1990) Science 250, 1104–1110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cissell M. A., Zhao L., Sussel L., Henderson E., Stein R. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 751–756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fernandez-Zapico M. E., Mladek A., Ellenrieder V., Folch-Puy E., Miller L., Urrutia R. (2003) EMBO J. 22, 4748–4758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaczynski J. A., Conley A. A., Fernandez Zapico M., Delgado S. M., Zhang J. S., Urrutia R. (2002) Biochem. J. 366, 873–882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ellenrieder V., Buck A., Harth A., Jungert K., Buchholz M., Adler G., Urrutia R., Gress T. M. (2004) Gastroenterology 127, 607–620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bruns C. J., Harbison M. T., Kuniyasu H., Eue I., Fidler I. J. (1999) Neoplasia 1, 50–62 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stoffers D. A., Kieffer T. J., Hussain M. A., Drucker D. J., Bonner-Weir S., Habener J. F., Egan J. M. (2000) Diabetes 49, 741–748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Truty M. J., Lomberk G., Fernandez-Zapico M. E., Urrutia R. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 6291–6300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang J. S., Moncrieffe M. C., Kaczynski J., Ellenrieder V., Prendergast F. G., Urrutia R. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 5041–5049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brissova M., Fowler M., Wiebe P., Shostak A., Shiota M., Radhika A., Lin P. C., Gannon M., Powers A. C. (2004) Diabetes 53, 1318–1325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hussain M. A., Habener J. F. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28950–28957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Qiu Y., Guo M., Huang S., Stein R. (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 412–420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sharma A., Zangen D. H., Reitz P., Taneja M., Lissauer M. E., Miller C. P., Weir G. C., Habener J. F., Bonner-Weir S. (1999) Diabetes 48, 507–513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Eeckhoute J., Formstecher P., Laine B. (2001) Mol. Endocrinol. 15, 1200–1210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stanojevic V., Habener J. F., Thomas M. K. (2004) Endocrinology 145, 2918–2928 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ban N., Yamada Y., Someya Y., Miyawaki K., Ihara Y., Hosokawa M., Toyokuni S., Tsuda K., Seino Y. (2002) Diabetes 51, 1409–1418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]