Abstract
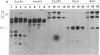
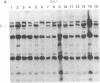
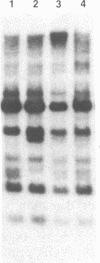
A correlative study was done to determine possible relationships between nonrandom aberrations in chromosomes 1, 6, and 7 occurring in human cutaneous malignant melanoma and the structure of oncogenes as well as specific genes encoding growth factors and growth factor receptors. Thirty cell lines derived from primary or metastatic melanomas of 28 patients were analyzed by Southern blotting with nick-translated probes for 28 different genes, some of which map near frequent chromosomal breakpoints observed in melanoma. An alteration in the MYB protooncogene was observed in a cell line derived from a primary melanoma in the vertical growth phase, which correlated with a 6q22 chromosomal abnormality. Another primary melanoma cell line had a cytogenetically undetected tumor-specific deletion within the gene for alpha-type protein kinase C. Polymorphic alleles for the genes encoding the epidermal growth factor receptor and alpha-type protein kinase C were also observed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albino A. P., Le Strange R., Oliff A. I., Furth M. E., Old L. J. Transforming ras genes from human melanoma: a manifestation of tumour heterogeneity? Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):69–72. doi: 10.1038/308069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Winqvist R., Lin C. C., de la Chapelle A., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Aberrant expression of an amplified c-myb oncogene in two cell lines from a colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban G. B., Herlyn M., Clark W. H., Jr, Nowell P. C. Karyotypic evolution in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Jan 1;19(1-2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban G., Herlyn M., Guerry D., 4th, Bartolo R., Koprowski H., Clark W. H., Nowell P. C. Cytogenetics of human malignant melanoma and premalignant lesions. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Apr;11(4):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale S. J., Chakravarti A., Greene M. H. Cutaneous malignant melanoma and familial dysplastic nevi: evidence for autosomal dominance and pleiotropy. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):188–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barletta C., Pelicci P. G., Kenyon L. C., Smith S. D., Dalla-Favera R. Relationship between the c-myb locus and the 6q-chromosomal aberration in leukemias and lymphomas. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1064–1067. doi: 10.1126/science.3469751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher R., Gibas Z., Karakousis C., Sandberg A. A. Nonrandom chromosome changes in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):5010–5016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher R., Gibas Z., Sandberg A. A. Chromosome 6 in malignant melanoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1983 Jun;9(2):173–175. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(83)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Lind P., Urdea M. S., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Philpott K., Mellor A. L. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):695–699. doi: 10.1038/320695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Bothwell M. A., Ross A. H., Koprowski H., Lanahan A. A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the human NGF receptor. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.3008331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. H., Jr, Elder D. E., Guerry D., 4th, Epstein M. N., Greene M. H., Van Horn M. A study of tumor progression: the precursor lesions of superficial spreading and nodular melanoma. Hum Pathol. 1984 Dec;15(12):1147–1165. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. S., Park M., Blair D. G., Tainsky M. A., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Vande Woude G. F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):29–33. doi: 10.1038/311029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Role of chromosome translocations in human neoplasia. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90552-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Pigott D. A., Lazarus J. A. Ectopic peptides released by a human melanoma cell line that modulate the transformed phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5015–5019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. H., Clark W. H., Jr, Tucker M. A., Elder D. E., Kraemer K. H., Guerry D., 4th, Witmer W. K., Thompson J., Matozzo I., Fraser M. C. Acquired precursors of cutaneous malignant melanoma. The familial dysplastic nevus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):91–97. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. H., Goldin L. R., Clark W. H., Jr, Lovrien E., Kraemer K. H., Tucker M. A., Elder D. E., Fraser M. C., Rowe S. Familial cutaneous malignant melanoma: autosomal dominant trait possibly linked to the Rh locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6071–6075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Marsden J. J., Whittle N., Ward B., Bobrow L., Waterfield M. D. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors on human cervical, ovarian, and vulval carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Koprowski H. Melanoma antigens: immunological and biological characterization and clinical significance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:283–308. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., ar-Rushdi A., Griffin C. A., Isobe M., Kozak C., Emanuel B. S., Nagarajan L., Cleveland J. L., Bonner T. I., Goldsborough M. D. Actively transcribed genes in the raf oncogene group, located on the X chromosome in mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3934–3938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Herlyn M., Balaban G., Parmiter A., Ross A., Nowell P. Expression of the receptor for epidermal growth factor correlates with increased dosage of chromosome 7 in malignant melanoma. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 May;11(3):297–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01534687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Nusbaum H. R., Razon N., Kris R., Lax I., Soreq H., Whittle N., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):144–147. doi: 10.1038/313144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Swan D. C., Tronick S. R., Gol R., Klimanis D., Moore D. E., Aaronson S. A. Regional chromosomal localization of N-ras, K-ras-1, K-ras-2 and myb oncogenes in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8221–8236. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölders H., Defesche J., Müller D., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R., Müller R. Integration of transfected LTR sequences into the c-raf proto-oncogene: activation by promoter insertion. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):693–698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan L., Louie E., Tsujimoto Y., Balduzzi P. C., Huebner K., Croce C. M. The human c-ros gene (ROS) is located at chromosome region 6q16----6q22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6568–6572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan L., Louie E., Tsujimoto Y., ar-Rushdi A., Huebner K., Croce C. M. Localization of the human pim oncogene (PIM) to a region of chromosome 6 involved in translocations in acute leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2556–2560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyashiki J. H., Ohyashiki K., Gibas Z., Karakousis C., Sandberg A. A. Cytogenetic findings in a malignant melanoma and its derived cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Sep;23(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padua R. A., Barrass N. C., Currie G. A. Activation of N-ras in a human melanoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):582–585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padua R. A., Barrass N., Currie G. A. A novel transforming gene in a human malignant melanoma cell line. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):671–673. doi: 10.1038/311671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmiter A. H., Balaban G., Herlyn M., Clark W. H., Jr, Nowell P. C. A t(1;19) chromosome translocation in three cases of human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1526–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M. I., Bennett J. W., Wang N. Nonrandom chromosome structural aberrations and oncogene loci in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Feb 1;20(1-2):11–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci P. G., Lanfrancone L., Brathwaite M. D., Wolman S. R., Dalla-Favera R. Amplification of the c-myb oncogene in a case of human acute myelogenous leukemia. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1117–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.6585957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Jarrett R., Reitz M. S., Jr, Wong-Staal F. Nucleotide sequence of transforming human c-sis cDNA clones with homology to platelet-derived growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5007–5018. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Thomas H. G. Purification of melanoma growth stimulatory activity. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Dec;129(3):375–384. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Fushimi M., Hori H., Hirohashi S., Nishimura S., Sugimura T. Molecular cloning and the total nucleotide sequence of the human c-Ha-ras-1 gene activated in a melanoma from a Japanese patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4771–4775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr N. K., Hughes D., Goodfellow P. N., Brook J. D., Padua R. A. Chromosomal assignment of c-MEL, a human transforming oncogene, to chromosome 19 (p13.2-q13.2). Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Nov;12(6):637–640. doi: 10.1007/BF01671949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure and activation of the human N-ras gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Rosenfeld S. B., Meyskens F. L. Chromosome 6q involvement in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1983 Jun;9(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(83)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1440–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3874430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Berman C. H., Dull T. J., Gray A., Lee J. M. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene using a single synthetic DNA probe. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):361–364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Berman C., Dull T. J. Human beta-nerve growth factor gene sequence highly homologous to that of mouse. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):821–825. doi: 10.1038/303821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R., Nishikura K., Sorrentino J., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Rovera G. The structure and nucleotide sequence of the 5' end of the human c-myc oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6307–6311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. H., Ishii S., Clark A. J., Sullivan M., Wilson R. K., Ma D. P., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA is homologous to a variety of RNAs overproduced in A431 carcinoma cells. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):806–810. doi: 10.1038/309806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut-Houri R., Bienz-Tadmor B., Givol D., Oren M. Human p53 cellular tumor antigen: cDNA sequence and expression in COS cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Veer L. J., van Kessel A. G., van Heerikhuizen H., van Ooyen A., Nusse R. Molecular cloning and chromosomal assignment of the human homolog of int-1, a mouse gene implicated in mammary tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2532–2534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]