Abstract
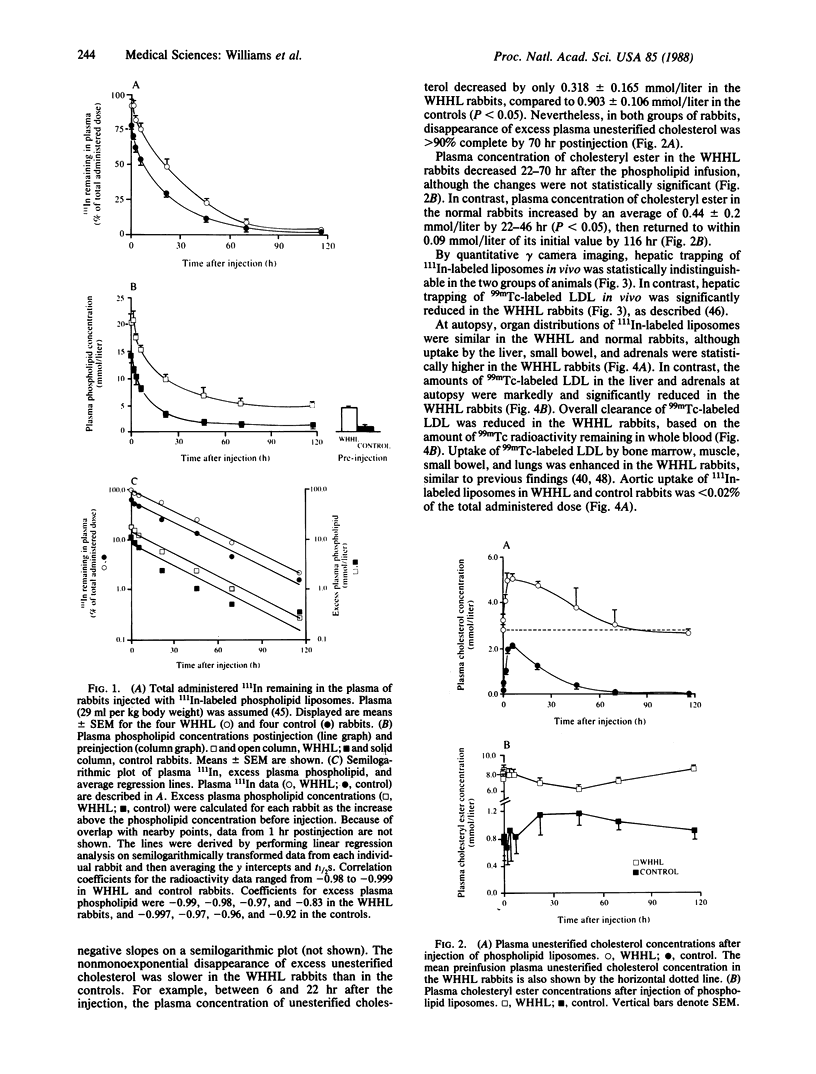
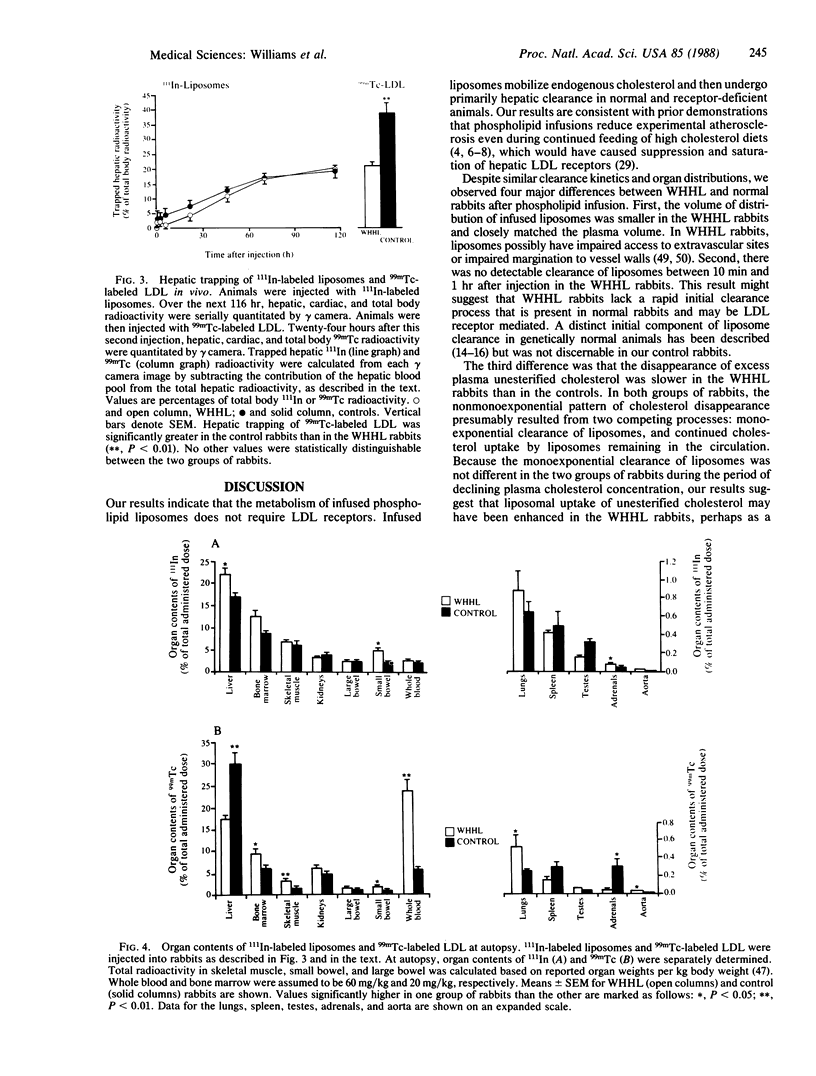
The metabolism of infused 111In-labeled phospholipid liposomes was examined in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic (WHHL) rabbits, which lack low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors, and in normal control rabbits. The half-times (t1/2) for clearance of 111In and excess phospholipid from plasma were 20.8 +/- 0.9 hr and 20.3 +/- 4.6 hr in WHHL and 20.0 +/- 0.8 hr and 19.6 +/- 2.2 hr in the normal rabbits (means +/- SEM; n = 4). By 6 hr postinfusion, the plasma concentration of unesterified cholesterol increased by 2.2 +/- 0.23 mmol/liter in WHHL and 2.1 +/- 0.04 mmol/liter in normal rabbits, presumably reflecting mobilization of tissue stores. Disappearance of excess plasma cholesterol was greater than 90% complete in both groups of rabbits by 70 hr postinfusion. By quantitative gamma camera imaging, hepatic trapping of 111In-labeled liposomes over time was indistinguishable between the two groups. At autopsy, the liver was the major organ of clearance, acquiring 22.0% +/- 1.7% (WHHL) and 16.8% +/- 1.0% (normal of total 111In. Aortic uptake of 111In was less than 0.02%. Thus, mobilization of cholesterol and hepatic uptake of phospholipid liposomes do not require LDL receptors. Because phospholipid infusions produce rapid substantial regression of atherosclerosis in genetically normal animals, our results suggest that phospholipid liposomes or triglyceride phospholipid emulsions (e.g., Intralipid) might reduce atherosclerosis in WHHL rabbits and in humans with familial hypercholesterolemia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Abdulla Y. H., Bayliss O. B., Morgan R. S. Modification of aortic atheroma and fatty liver in cholesterol-fed rabbits by intravenous injection of saturated and polyunsaturated lecithins. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):77–87. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R. F., de Mendonça J. M., Schaeffer G. M., de Souza J. R., Bandoli J. G., da Silva D. J., Lopes C. R. Phospholipids in experimental atherosclerosis. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 Jan;24(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Effect of infusions of phosphatides upon the atherosclerotic aorta in situ and as an ocular aortic implant. J Lipid Res. 1960 Jul;1:343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Role of hyperphospholipidemia and neutral fat increase in plasma in the pathogenesis of hypercholesteremia. Am J Physiol. 1956 Jul;186(1):13–18. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.186.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M., SUGIYAMA T. Mechanism underlying phosphatide-induced hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3375–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckdorfer K. R., Edwards P. A., Green C. Properties of aqueous dispersions of phospholipid and cholesterol. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):506–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Thorpe S. R., Lange L. G., Sobel B. E., Schonfeld G. Loci of catabolism of beta-very low density lipoprotein in vivo delineated with a residualizing label, 125I-dilactitol tyramine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14564–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewanjee M. K., Rao S. A., Didisheim P. Indium-111 tropolone, a new high-affinity platelet label: preparation and evaluation of labeling parameters. J Nucl Med. 1981 Nov;22(11):981–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Gorder N. L., Benson D. M., Gotto A. M., Jr Apolipoprotein A-IV. A determinant for binding and uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15714–15718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O. Enhancement of phosphatide-induced hypercholesteremia by prior ingestion of cholesterol and triglyceride. Am J Physiol. 1958 Mar;192(3):546–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.3.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O., ROSENMAN R. H. Resolution of aortic atherosclerotic infiltration in the rabbit by phosphatide infusion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jul;95(3):586–588. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O. Source of excess plasma cholesterol in phosphatide-induced hypercholesteremia. Am J Physiol. 1958 Oct;195(1):185–188. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.195.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Raz A., Fogler W. E., Poste G. Pulmonary localization of intravenously injected liposomes. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1980;75:246–251. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81491-4_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Weissmann G. The introduction of enzymes into cells by means of liposomes. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):289–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freise J., Müller W. H., Brölsch C., Schmidt F. W. "In vivo" distribution of liposomes between parenchymal and non parenchymal cells in rat liver. Biomedicine. 1980 Oct;32(3):118–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Kita T., Brown M. S. Defective lipoprotein receptors and atherosclerosis. Lessons from an animal counterpart of familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 4;309(5):288–296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308043090507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Neerunjun D. E. Control of the rate of hepatic uptake and catabolism of liposome-entrapped proteins injected into rats. Possible therapeutic applications. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Ryman B. E. Fate of protein-containing liposomes injected into rats. An approach to the treatment of storage diseases. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 21;24(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb19710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin E., Breckenridge W. C., Kuksis A., Bryan M. H., Angel A. Appearance and characterization of lipoprotein X during continuous intralipid infusions in the neonate. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1703–1712. doi: 10.1172/JCI109633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. N., Patelski J., Bowyer D. E., Gresham G. A. Atherosclerosis induced in hypercholesterolaemic baboons by immunological injury; and the effects of intravenous polyunsaturated phosphatidyl choline. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Thompson T. E. Preparation of homogeneous, single-walled phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:485–489. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Brecht W. J., Hall E. A., Friedman G., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of the apolipoprotein E receptor from canine and human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4256–4267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. J., Merriam J. E., Beaumier P. L., Luk K. F. Encapsulation, with high efficiency, of radioactive metal ions in liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 5;716(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T. T., MacGee J., Morrison J. A., Glueck C. J. Quantitative analysis of cholesterol in 5 to 20 microliter of plasma. J Lipid Res. 1974 May;15(3):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenko C., 3rd, Anderson A. P., Scott T. H., Jr, Wheeler M. L. Organ weights and water composition of the New Zealand albino rabbit (Oryctalagus cuniculus). Am J Vet Res. 1971 Oct;32(10):1637–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Maine G. T. Kinetics and mechanism of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol exchange between single bilayer vesicles and bovine serum high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1722–1728. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao Y. J., Juliano R. L. Interactions of liposomes with the reticuloendothelial system. Effects of reticuloendothelial blockade on the clearance of large unilamellar vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. S., Garabedian H. D., Lees A. M., Schumacher D. J., Miller A., Isaacsohn J. L., Derksen A., Strauss H. W. Technetium-99m low density lipoproteins: preparation and biodistribution. J Nucl Med. 1985 Sep;26(9):1056–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauk M. R., Gamble R. C. Preparation of lipid vesicles containing high levels of entrapped radioactive cations. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muckle T. J., Bradford J. A., Aukland P. Occurrence of lipoprotein-X associated with intravenous administration of lipid emulsion in adults. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Oct;78(4):523–526. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patelski J., Bowyer D. E., Howard A. N., Jennings I. W., Thorne C. J. Modification of enzyme activities in experimental atherosclerosis in the rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 1970 Jul-Aug;12(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(70)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Attie A. D., Witztum J. L., Watanabe Y., Steinberg D. Receptor-dependent and receptor-independent degradation of low density lipoprotein in normal rabbits and in receptor-deficient mutant rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7994–8000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proffitt R. T., Williams L. E., Presant C. A., Tin G. W., Uliana J. A., Gamble R. C., Baldeschwieler J. D. Tumor-imaging potential of liposomes loaded with In-111-NTA: biodistribution in mice. J Nucl Med. 1983 Jan;24(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Y. E., Cerny E. A., Patel K. R., Lau E. H., Wright B. J. Differential uptake of liposomes varying in size and lipid composition by parenchymal and kupffer cells of mouse liver. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 8;31(19):2061–2071. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifici V. A., Eder H. A. A hepatocyte receptor for high-density lipoproteins specific for apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13814–13818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerdink F., Dijkstra J., Hartman G., Bolscher B., Scherphof G. The involvement of parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial liver cells in the hepatic uptake of intravenously injected liposomes. Effects of lanthanum and gadolinium salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 18;677(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai K., Matsuoka N., Jackson R. L. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with phospholipid vesicles. Role of apolipoprotein C-II and heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Patel H. M., Ryman B. E. The effect of reticuloendothelial blockade on the blood clearance and tissue distribution of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 18;674(3):354–371. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Bilheimer D. W., Dietschy J. M. Rates of receptor-dependent and -independent low density lipoprotein uptake in the hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalenhoef A. F., Malloy M. J., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in patients with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):722–728. doi: 10.1172/JCI112632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone B. G., Schreiber D., Alleman L. D., Ho C. Y. Hepatic metabolism and secretion of a cholesterol-enriched lipoprotein fraction. J Lipid Res. 1987 Feb;28(2):162–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama M., Itoh S., Nagasaki T., Tanimizu I. A new enzymatic method for determination of serum choline-containing phospholipids. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Aug 15;79(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90465-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Segura R., Hoff H., Gotto A. M., Jr Contrasting effects on plasma lipoproteins of intravenous versus oral administration of a triglyceride-phospholipid emulsion. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep 12;5(5):373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Untracht S. H. Intravascular metabolism of an artificial transporter of triacylglycerols. Alterations of serum lipoproteins resulting from total parenteral nutrition with Intralipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 15;711(1):176–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Scanu A. M. Uptake of endogenous cholesterol by a synthetic lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Tall A. R., Bisgaier C., Brocia R. Phospholipid liposomes acquire apolipoprotein E in atherogenic plasma and block cholesterol loading of cultured macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1466–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI112975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Tall A. R., Tabas I., Blum C. Recognition of vesicular lipoproteins by the apolipoprotein B,E receptor of cultured fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):892–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Werth V. P., Wolff J. A. Intravenously administered lecithin liposomes: a synthetic antiatherogenic lipid particle. Perspect Biol Med. 1984 Spring;27(3):417–431. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1984.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Bishop R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1230–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


