Abstract
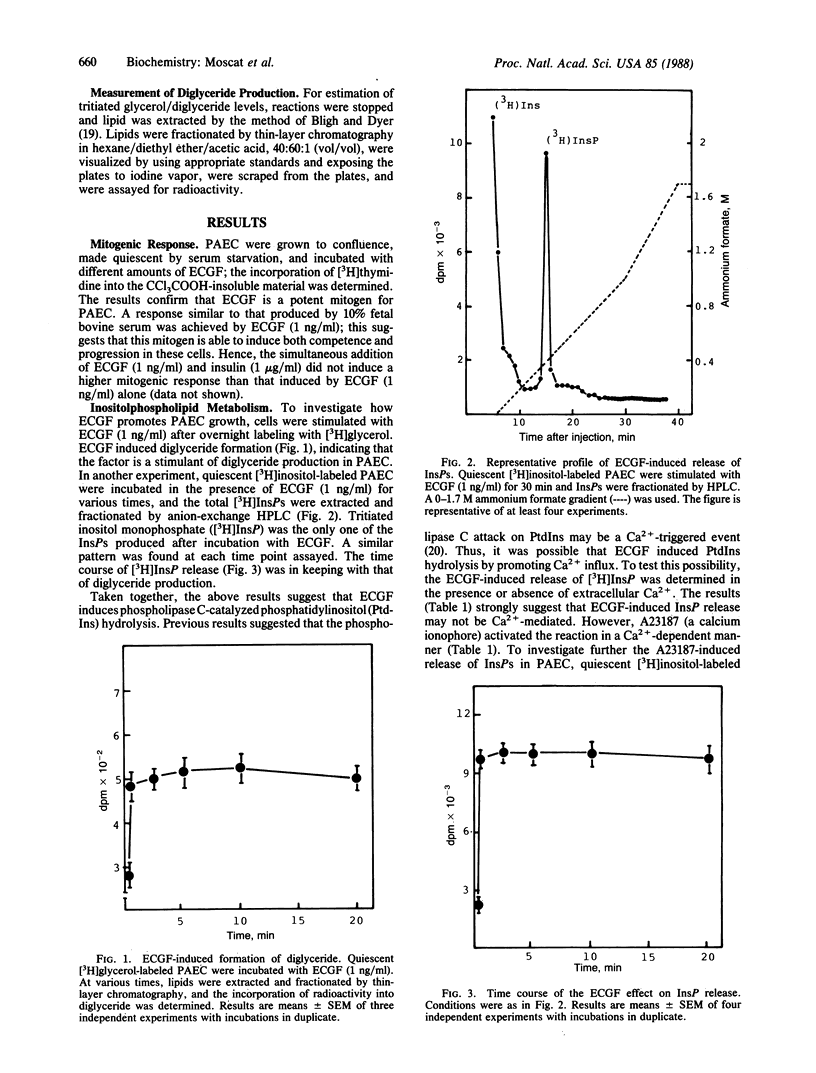
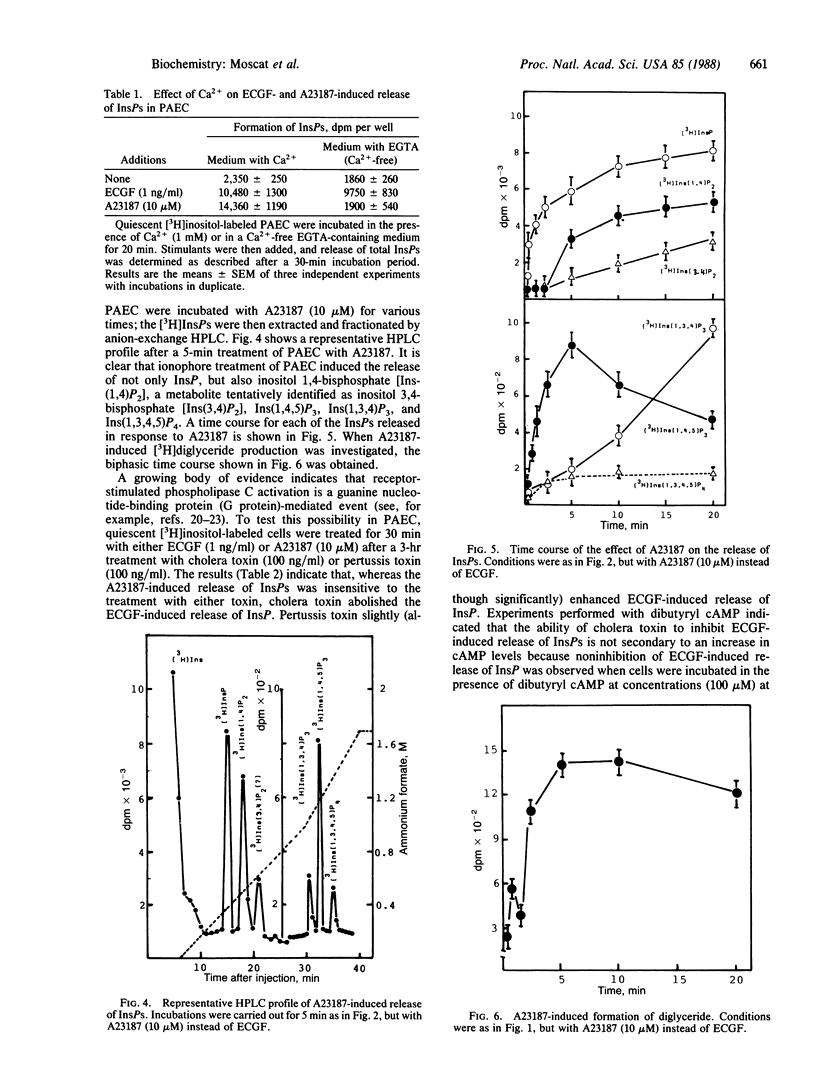
The existence of a bovine brain-derived endothelial cell growth factor has recently been reported, but its mode of action is unknown. We show that the endothelial cell growth factor is a potent stimulant of inositol monophosphate release in porcine aorta endothelial cells. Although the activation of phospholipase C by this factor does not appear to be dependent on Ca2+, the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 stimulates release of inositol phosphates. It is suggested that the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase/5-phosphomonoesterase pathway could account for the ionophore-induced changes in inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol lipids and cell proliferation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Feb;13(1):67–71. doi: 10.1042/bst0130067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Guanine nucleotide regulation of phospholipase C activity in permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. Inhibition by pertussis toxin and sensitization to submicromolar calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2390097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Scott D. L., Gordon E. A., LaBelle E. F. Phosphoinositides in mitogenesis: neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover and initiation of cell proliferation. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derian C. K., Moskowitz M. A. Polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in endothelial cells and carotid artery segments. Bradykinin-2 receptor stimulation is calcium-independent. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3831–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Blakeley D. M., Brown K. D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J. Effects of bombesin and insulin on inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate and inositol (1,3,4)trisphosphate formation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Shoback D. M., Pattison G., Stobo J. D. Cholera toxin inhibits the T-cell antigen receptor-mediated increases in inositol trisphosphate and cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Tsuda T., Kikuchi A., Tanimoto T., Yamashita T., Takai Y. Possible involvement of protein kinase C and calcium ion in growth factor-induced expression of c-myc oncogene in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1187–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Smith J. A. Human tumor cells synthesize an endothelial cell growth factor that is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert T. L., Kent R. S., Whorton A. R. Bradykinin stimulation of inositol polyphosphate production in porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15288–15293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T. Angiogenesis. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Isomers of inositol trisphosphate in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):825–829. doi: 10.1042/bj2380825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Moore J. P., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R. Calcium and cell proliferation. Br Med Bull. 1986 Oct;42(4):405–412. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Todd J. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. c-fos and c-myc gene activation, ionic signals, and DNA synthesis in thymocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8158–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Herrero C., Garcia-Barreno P., Municio A. M. Zymosan-induced release of inositol phosphates at resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations in macrophages. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2420441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Moreno F., García-Barreno P. Mitogenic activity and inositide metabolism in thrombin-stimulated pig aorta endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 30;145(3):1302–1309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Moreno F., Herrero C., Iglesias S., Garcia-Barreno P. Arachidonic acid releasing systems in pig aorta endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1098–1103. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandra A., Bar R. S., Dolash S., Marshall S. J., Kaduce T. L., Spector A. A. Morphological alterations in cultured endothelial cells induced by arachidonic acid. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jun;158(2):484–492. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Kenney J., Kowalski W. J., Friesel R., Mehlman T., Maciag T. Interaction of endothelial cell growth factor with heparin: characterization by receptor and antibody recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6138–6142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Florine D. L., Wille J. J., Jr, Yun K. Coupling of growth arrest and differentiation at a distinct state in the G1 phase of the cell cycle: GD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):845–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


