Abstract
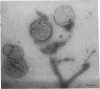
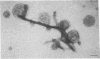
The cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells is a major determinant of cellular architecture and of many cellular functions. In addition to or in place of the transcellular cytoskeleton, many eukaryotic cells also contain membrane-associated cytoskeletal structures (membrane skeletons), which are important for cellular structure and function. The membrane skeleton of the parasitic hemoflagellate Trypanosoma brucei consists of a dense array of singlet microtubules (subpellicular microtubules), which are tightly associated to the overlying cell membrane. This study reports the identification of a microtubule-associated protein from Trypanosoma brucei that constitutes a component of the link between this microtubular array and the cell membrane. The protein can bind in vitro both to microtubules and to membrane vesicles or liposomes. Furthermore, it can crosslink microtubules and membrane vesicles, suggesting that it exerts a similar function in the membrane skeleton.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aamodt E. J., Culotti J. G. Microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: periodic cross-links connect microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):23–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos E. Pellicular microtubules in the family Trypanosomatidae. J Protozool. 1970 Feb;17(1):39–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb05157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apgar J. R., Herrmann S. H., Robinson J. M., Mescher M. F. Triton X-100 extraction of P815 tumor cells: evidence for a plasma membrane skeleton structure. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1369–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. J., Bennett V. Synapsin I is a microtubule-bundling protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):145–147. doi: 10.1038/319145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramblett G. T., Chang S. L., Flavin M. Periodic crosslinking of microtubules by cytoplasmic microtubule-associated and microtubule-corset proteins from a trypanosomatid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. J., Branton D. Visualization of the protein associations in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6153–6157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. T., Reid C. G., Voorheis H. P. Calcium ions initiate the selective depolymerization of the pellicular microtubules in bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Sci. 1986 Feb;80:123–140. doi: 10.1242/jcs.80.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Stokke B. T., Mikkelsen A., Branton D. The molecular basis of erythrocyte shape. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1217–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.3775380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves A. J., Wandosell F., Avila J. Phosphorylation of tubulin enhances its interaction with membranes. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):827–828. doi: 10.1038/323827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J., Chapman K. A novel microtubule-associated protein from mammalian nerve shows ATP-sensitive binding to microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1539–1545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden M., Blum B., DeLange T., Braun R., Seebeck T. Tubulin mRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C. G., Smaill B. H. A technique for analyzing the spatial organization of microtubular arms and bridges (MAPs). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:417–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney D. M., Linck R. W. The cystoskeleton of unstimulated blood platelets: structure and composition of the isolated marginal microtubular band. J Cell Sci. 1985 Oct;78:1–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.78.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Fowler V. M., Swanson J., Branton D., Taylor D. L. A membrane cytoskeleton from Dictyostelium discoideum. I. Identification and partial characterization of an actin-binding activity. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):396–409. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. Stabilizing infrastructure of cell membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:531–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M. Three-dimensional structure of a membrane-microtubule complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):283–295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Microtubule-associated proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:421–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather S., Agabian N. A 5' spliced leader is added in trans to both alpha- and beta-tubulin transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5695–5699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Sherwin T., Sasse R., Russell D. G., Gull K., Seebeck T. Subpellicular and flagellar microtubules of Trypanosoma brucei brucei contain the same alpha-tubulin isoforms. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):431–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Porter M. E., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Identification of kinesin in sea urchin eggs, and evidence for its localization in the mitotic spindle. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):483–486. doi: 10.1038/318483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Gehr P. Trypanocidal action of neuroleptic phenothiazines in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Nov;9(3):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Whittaker P. A., Imboden M. A., Hardman N., Braun R. Tubulin genes of Trypanosoma brucei: a tightly clustered family of alternating genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4634–4638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin T., Schneider A., Sasse R., Seebeck T., Gull K. Distinct localization and cell cycle dependence of COOH terminally tyrosinolated alpha-tubulin in the microtubules of Trypanosoma brucei brucei. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):439–446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Membrane tubulin. Biol Cell. 1986;57(2):95–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1986.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger J., Seebeck T. Monoclonal antibodies against a 60 kDa phenothiazine-binding protein from Trypanosoma brucei can discriminate between different trypanosome species. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Oct;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Milhausen M., Rutter W. J., Agabian N. Tubulin genes are tandemly linked and clustered in the genome of trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):435–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorheis H. P., Gale J. S., Owen M. J., Edwards W. The isolation and partial characterization of the plasma membrane from Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):11–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1800011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]