Abstract
Vaccinia virus recombinants encoding the hemagglutinin or fusion protein of measles virus have been constructed. Infection of cell cultures with the recombinants led to the synthesis of authentic measles proteins as judged by their electrophoretic mobility, recognition by antibodies, glycosylation, proteolytic cleavage, and presentation on the cell surface. Mice vaccinated with a single dose of the recombinant encoding the hemagglutinin protein developed antibodies capable of both inhibiting hemagglutination activity and neutralizing measles virus, whereas animals vaccinated with the recombinant encoding the fusion protein developed measles neutralizing antibodies. Mice vaccinated with either of the recombinants resisted a normally lethal intracerebral inoculation of a cell-associated measles virus subacute sclerosing panencephalitis strain.
Full text
PDF

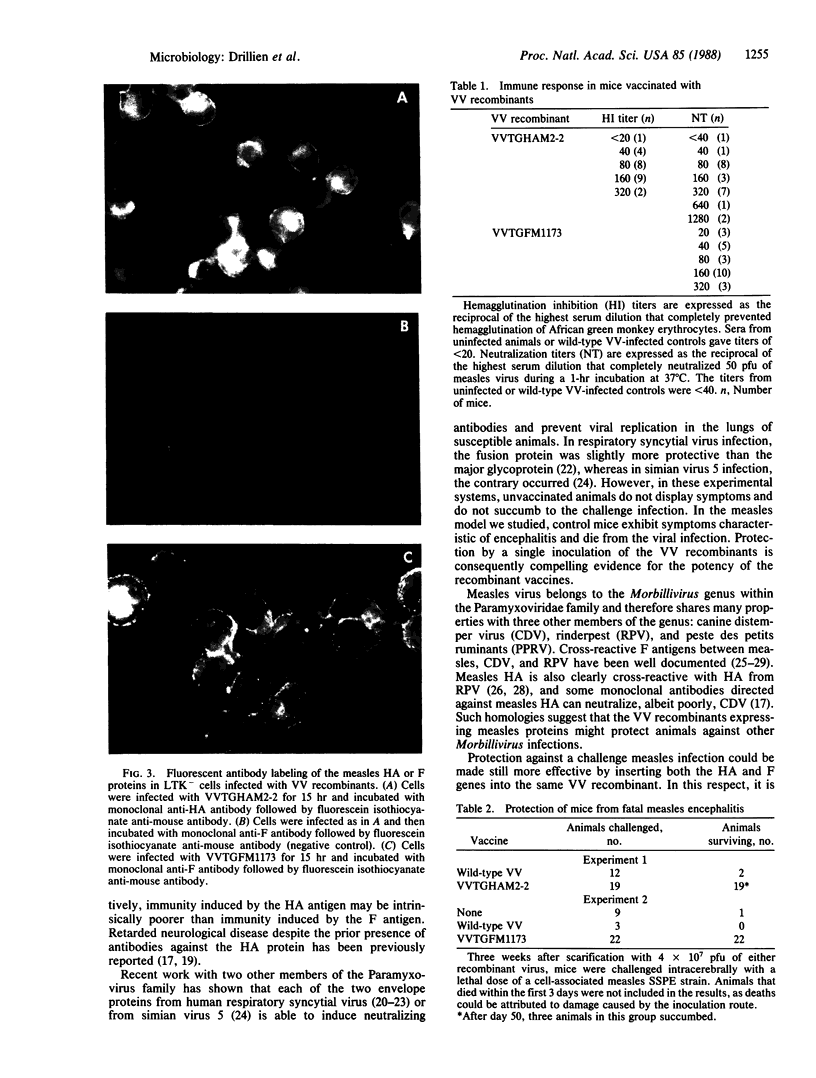

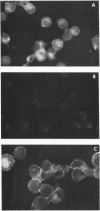
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht P., Burnstein T., Klutch M. J., Hicks H. T., Ennis F. A. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: experimental infection in primates. Science. 1977 Jan 7;195(4273):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.831255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. The predicted primary structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel M. J., Shek W. R., Shesberadaran H., Norrby E. Measles virus and inactivated canine distemper virus induce incomplete immunity to canine distemper. Arch Virol. 1984;82(1-2):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF01309369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., Young K. K., Anderson K., Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. Expression of the major glycoprotein G of human respiratory syncytial virus from recombinant vaccinia virus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R., Gerald C., Barker R., Wild T. F. Fusion glycoprotein of measles virus: nucleotide sequence of the gene and comparison with other paramyxoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1695–1703. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Spehner D. Physical mapping of vaccinia virus temperature-sensitive mutations. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Venkatesan S., Chanock R. M., Moss B. Resistance to human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection induced by immunization of cotton rats with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the RSV G glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald C., Buckland R., Barker R., Freeman G., Wild T. F. Measles virus haemagglutinin gene: cloning, complete nucleotide sequence analysis and expression in COS cells. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2695–2703. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudon P., Wild T. F. Correlation between epitopes on hemagglutinin of measles virus and biological activities: passive protection by monoclonal antibodies is related to their hemagglutination inhibiting activity. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):46–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The polypeptides of canine distemper virus: synthesis in infected cells and relatedness to the polypeptides of other morbilliviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa D. T. Relationships among measles, canine distemper and rinderpest viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:160–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Drillien R., Spehner D., Skory S., Schmitt D., Wiktor T., Koprowski H., Lecocq J. P. Expression of rabies virus glycoprotein from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):163–166. doi: 10.1038/312163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Hirth P., DeWilde M., Harford N., Lecocq J. P. Cell-free synthesis of enterotoxin of E. coli from a cloned gene. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):473–474. doi: 10.1038/284473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a selectable eukaryotic cloning and expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2067–2082. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Flexner C. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:305–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRBY E. Hemagglutination by measles virus. 4. A simple procedure for production of high potency antigen for hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) tests. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:814–818. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Gollmar Y. Identification of measles virus-specific hemolysis-inihibiting antibodies separate from hemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):231–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.231-239.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Sheshberadaran H., McCullough K. C., Carpenter W. C., Orvell C. Is rinderpest virus the archevirus of the Morbillivirus genus? Intervirology. 1985;23(4):228–232. doi: 10.1159/000149609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Utter G., Orvell C., Appel M. J. Protection against canine distemper virus in dogs after immunization with isolated fusion protein. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):536–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.536-541.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Elango N., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Johnson P. R., Moss B., Chanock R. M., Collins P. L. Expression of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus by a recombinant vaccinia virus: comparison of the individual contributions of the F and G glycoproteins to host immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Norrby E. Immunological relationships between homologous structural polypeptides of measles and canine distemper virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):231–245. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Paoletti E. Construction of poxviruses as cloning vectors: insertion of the thymidine kinase gene from herpes simplex virus into the DNA of infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A., Moss B., Murphy B. R. Comparison of the relative roles of the F and HN surface glycoproteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 in inducing protective immunity. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1972–1977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1972-1977.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkus M. E., Piccini A., Lipinskas B. R., Paoletti E. Recombinant vaccinia virus: immunization against multiple pathogens. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):981–984. doi: 10.1126/science.2992092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Mackett M., Moss B. Infectious vaccinia virus recombinants that express hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):490–495. doi: 10.1038/302490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Moss B. Infectious poxvirus vectors have capacity for at least 25 000 base pairs of foreign DNA. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Ball L. A., Young K. K., Furze J., Wertz G. W. Human respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G expressed from a recombinant vaccinia virus vector protects mice against live-virus challenge. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.607-613.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild T. F., Giraudon P., Bernard A., Huppert J. Isolation and characterisation of a defective measles virus from a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis patient. J Med Virol. 1979;4(2):103–114. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]