Abstract
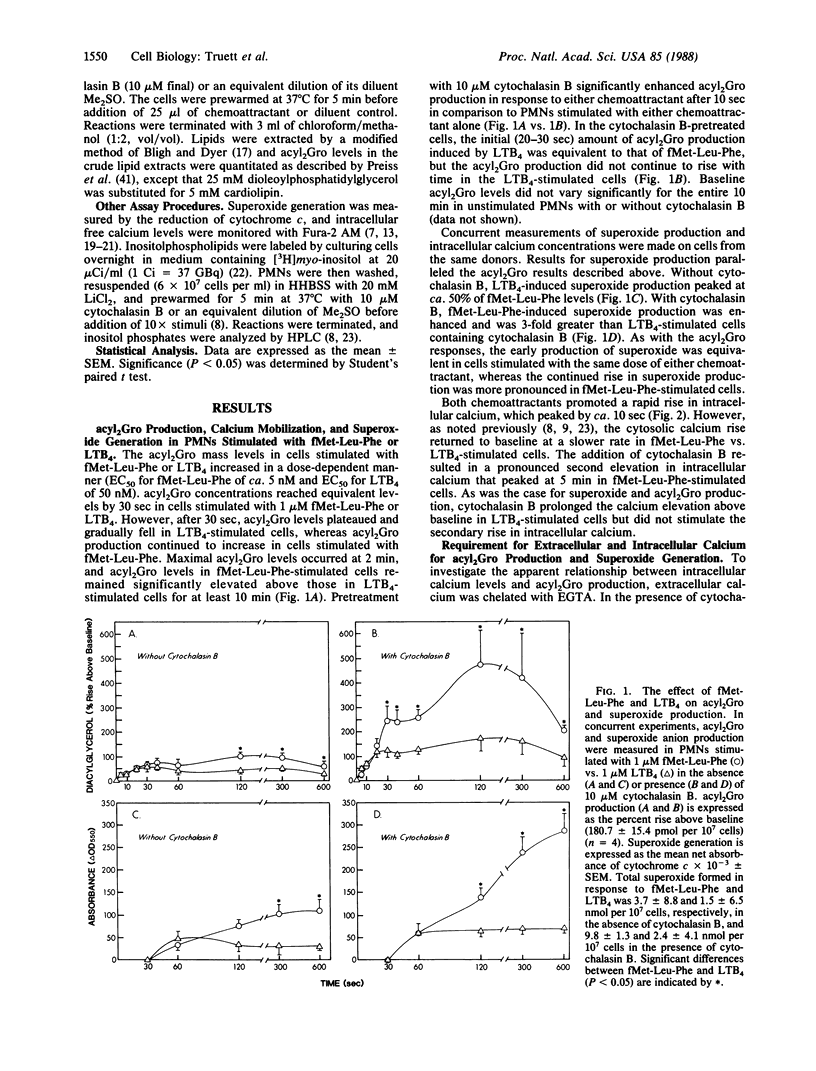
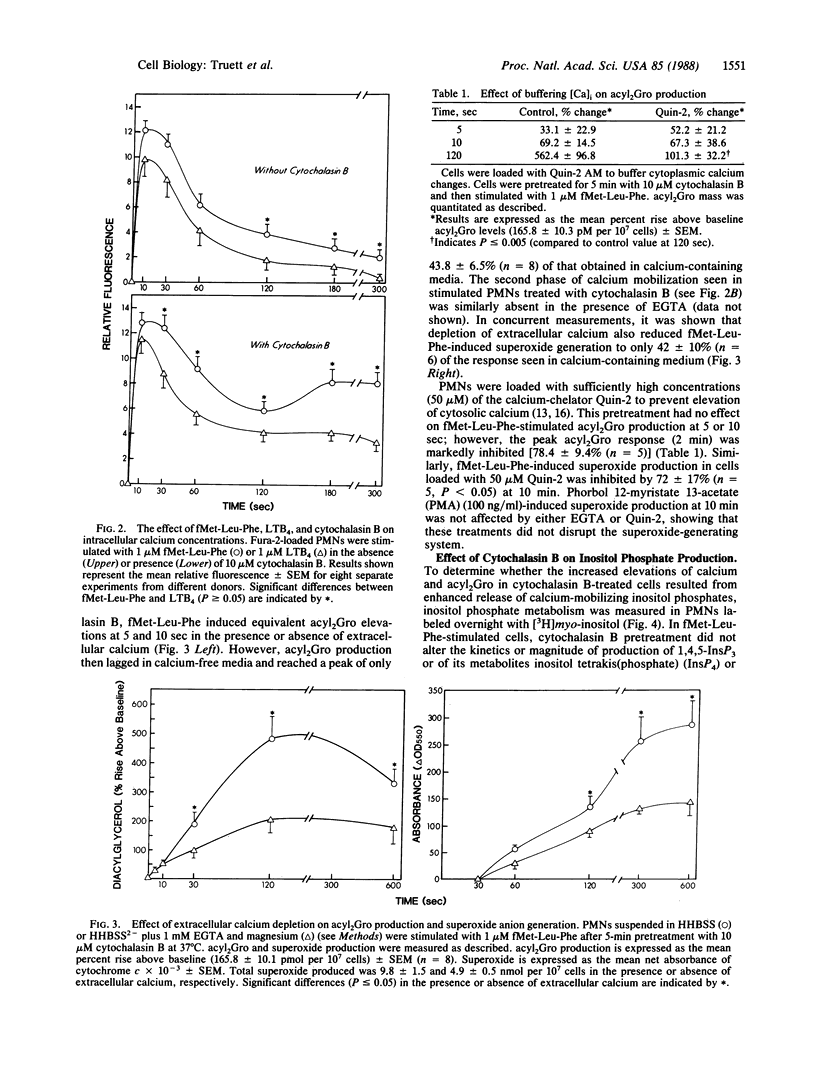
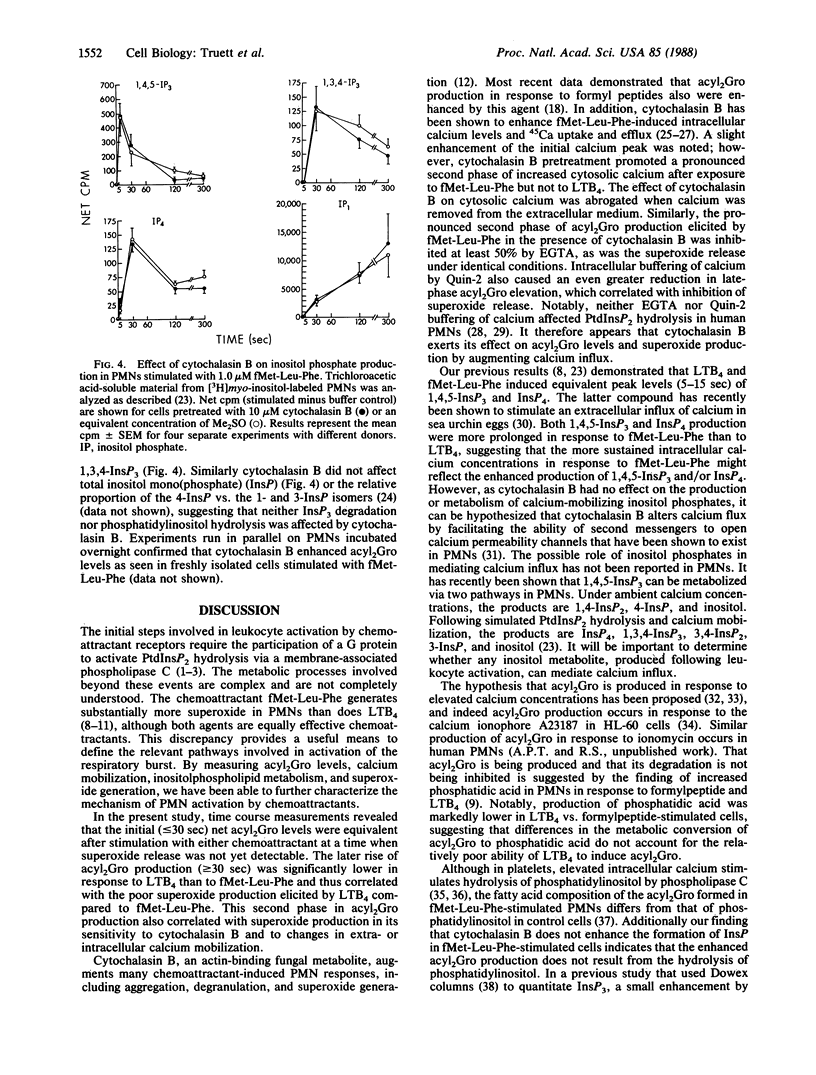
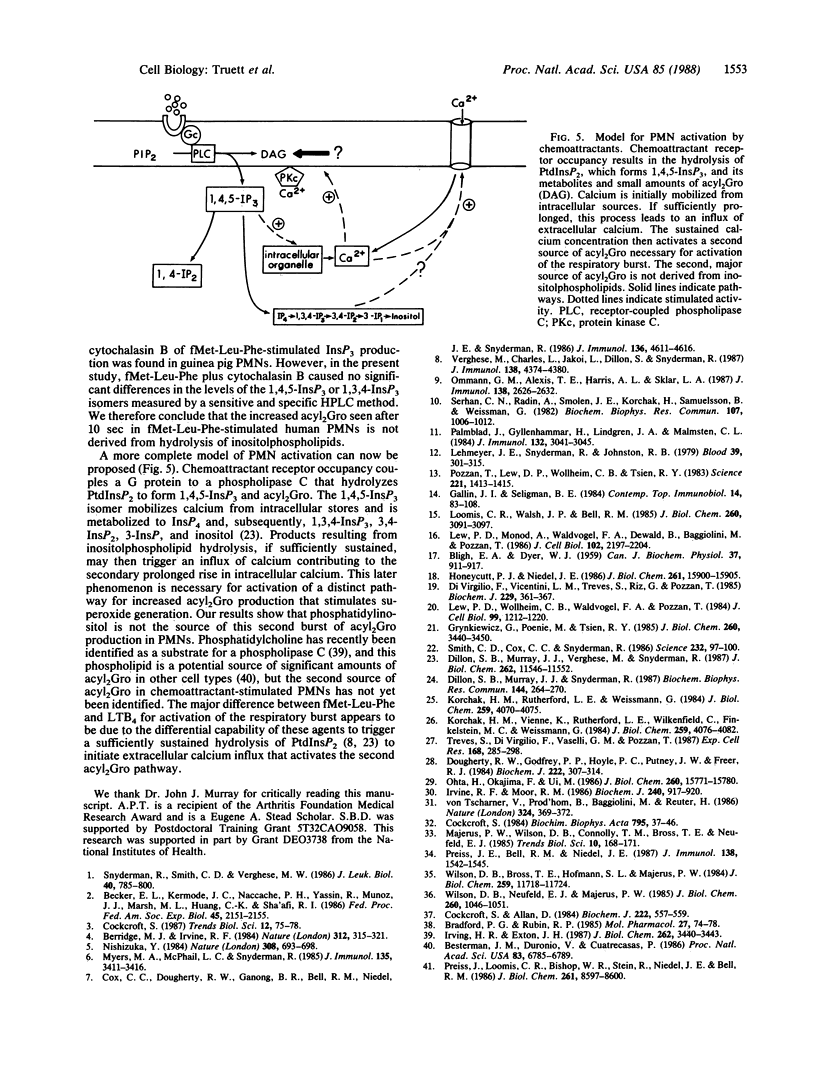
Metabolic pathways involved in the activation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) were characterized by using chemoattractants with equivalent chemotactic activity but widely disparate ability to stimulate superoxide production [N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (fMet-Leu-Phe) much greater than leukotriene B4]. Leukotriene B4 stimulated a low level of superoxide production that plateaued at 60 sec, whereas with fMet-Leu-Phe the response continued to increase for 5 min. Both agents produced equivalent initial rises in diacylglycerol (acyl2Gro) (less than or equal to 30 sec); however, only fMet-Leu-Phe induced a second increase of acyl2Gro peaking at ca. 120 sec. Both chemoattractants also caused an equivalent initial (less than or equal to 10 sec) rise in intracellular calcium; however, the elevation induced by fMet-Leu-Phe was more sustained. We sought to determine the biochemical mechanisms underlying these discrepancies. Superoxide production and the second phase of acyl2Gro generation were both inhibited ca. 56% by depleting extracellular calcium or ca. 79% by buffering intracellular calcium. Cytochalasin B greatly enhanced the respiratory burst, acyl2Gro production, and calcium influx, but not inositolphospholipid turnover in PMNs stimulated with chemoattractants. These data indicate that sequential metabolic pathways activate the respiratory burst in PMNs stimulated by chemoattractants. The response is initiated by inositolpolyphospholipid hydrolysis, which results in rapid (less than or equal to 5 sec) calcium mobilization from intracellular stores and acyl2Gro release (peak at ca. 30 sec). To fully activate the respiratory burst, the chemoattractant must also trigger calcium influx, which leads to a sustained cytosolic calcium elevation. This supports a prolonged new phase of acyl2Gro production that is independent of inositolphospholipid hydrolysis and is correlated with superoxide production.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Kermode J. C., Naccache P. H., Yassin R., Munoz J. J., Marsh M. L., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin as a probe of neutrophil activation. Fed Proc. 1986 Jun;45(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Characterization of formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine stimulation of inositol trisphosphate accumulation in rabbit neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):74–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Allan D. The fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidate and 1,2-diacylglycerol in stimulated human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):557–559. doi: 10.1042/bj2220557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Ca2+-dependent conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidate in neutrophils stimulated with fMet-Leu-Phe or ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 15;795(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. C., Dougherty R. W., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E., Snyderman R. Differential stimulation of the respiratory burst and lysosomal enzyme secretion in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by synthetic diacylglycerols. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4611–4616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Vicentini L. M., Treves S., Riz G., Pozzan T. Inositol phosphate formation in fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated human neutrophils does not require an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2290361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon S. B., Murray J. J., Snyderman R. Identification of a novel inositol bisphosphate isomer formed in chemoattractant stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon S. B., Murray J. J., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Regulation of inositol phosphate metabolism in chemoattractant-stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Definition of distinct dephosphorylation pathways for IP3 isomers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11546–11552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Seligmann B. E. Neutrophil chemoattractant fMet-Leu-Phe receptor expression and ionic events following activation. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;14:83–108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4862-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeycutt P. J., Niedel J. E. Cytochalasin B enhancement of the diacylglycerol response in formyl peptide-stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15900–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving H. R., Exton J. H. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and P2-purinergic agonists. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3440–3443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Rutherford L. E., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. I. Kinetic analysis of changes in calcium permeability. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4070–4075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vienne K., Rutherford L. E., Wilkenfeld C., Finkelstein M. C., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. II. Temporal analysis of changes in cytosolic calcium and calcium efflux. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4076–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Monod A., Waldvogel F. A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M., Pozzan T. Quantitative analysis of the cytosolic free calcium dependency of exocytosis from three subcellular compartments in intact human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2197–2204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Wollheim C. B., Waldvogel F. A., Pozzan T. Modulation of cytosolic-free calcium transients by changes in intracellular calcium-buffering capacity: correlation with exocytosis and O2-production in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1212–1220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. A., McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Redistribution of protein kinase C activity in human monocytes: correlation with activation of the respiratory burst. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Traynor A. E., Harris A. L., Sklar L. A. LTB4 induced activation signals and responses in neutrophils are short-lived compared to formylpeptide. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2626–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmblad J., Gyllenhammar H., Lindgren J. A., Malmsten C. L. Effects of leukotrienes and f-Met-Leu-Phe on oxidative metabolism of neutrophils and eosinophils. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3041–3045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Lew D. P., Wollheim C. B., Tsien R. Y. Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.6310757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. E., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerol mass measurements in stimulated HL-60 phagocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1542–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Radin A., Smolen J. E., Korchak H., Samuelsson B., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 is a complete secretagogue in human neutrophils: a kinetic analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90622-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Smith C. D., Verghese M. W. Model for leukocyte regulation by chemoattractant receptors: roles of a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein and polyphosphoinositide metabolism. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Dec;40(6):785–800. doi: 10.1002/jlb.40.6.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treves S., Di Virgilio F., Vaselli G. M., Pozzan T. Effect of cytochalasins on cytosolic-free calcium concentration and phosphoinositide metabolism in leukocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Feb;168(2):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Charles L., Jakoi L., Dillon S. B., Snyderman R. Role of a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in the activation of phospholipase C by different chemoattractants. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4374–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Bross T. E., Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides by purified sheep seminal vesicle phospholipase C enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11718–11724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Prod'hom B., Baggiolini M., Reuter H. Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):369–372. doi: 10.1038/324369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


