Abstract
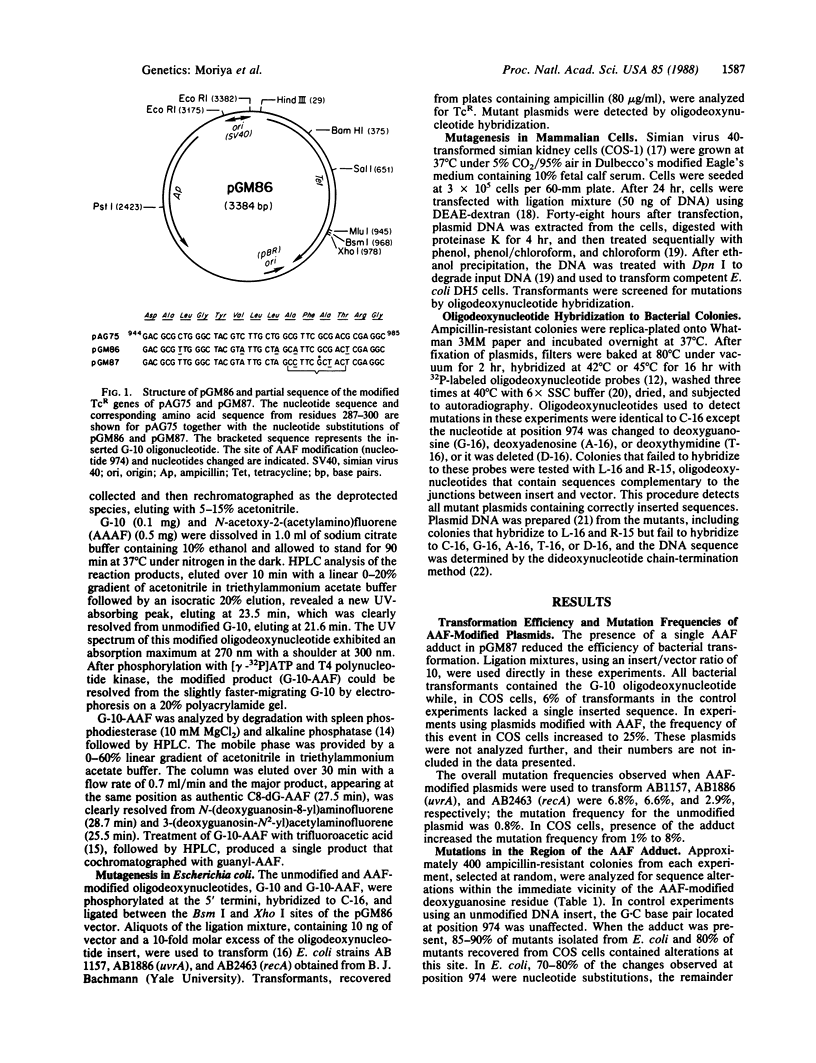
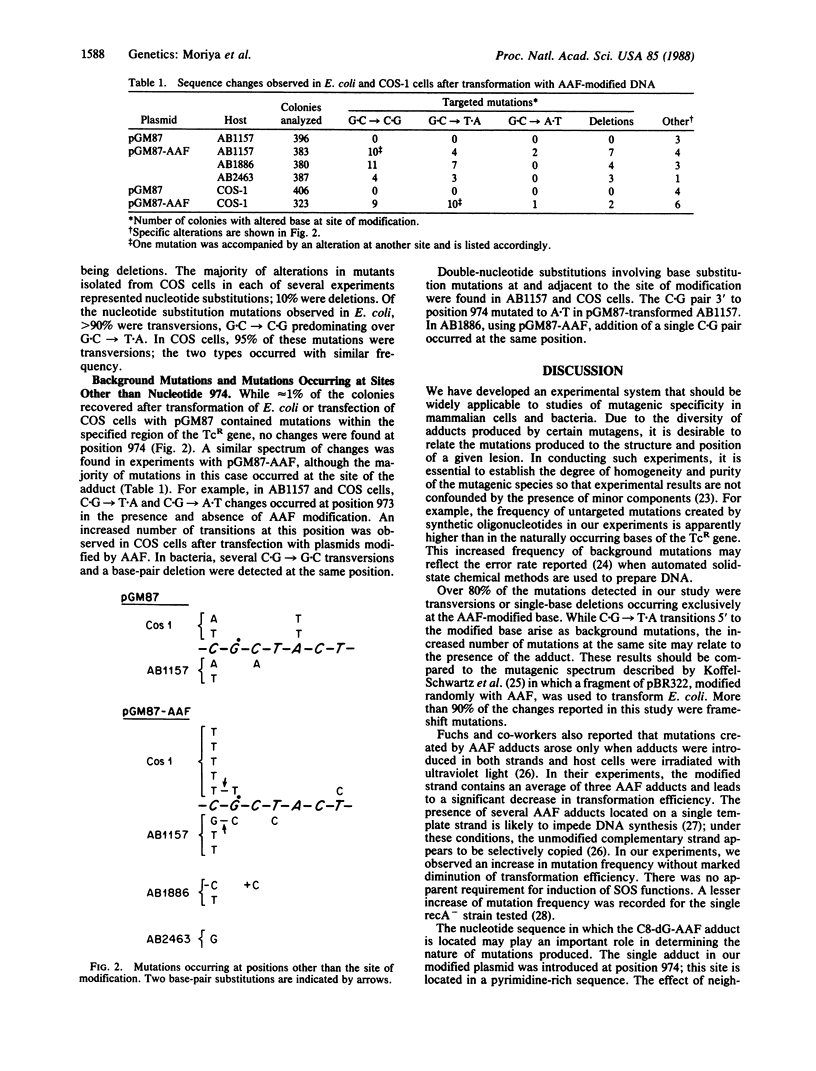
Mutagenic specificity of 2-acetylaminofluorene (AAF) has been established in mammalian cells and several strains of bacteria by using a shuttle plasmid vector containing a single N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)acetylaminofluorene (C8-dG-AAF) adduct. The nucleotide sequence of the gene conferring tetracycline resistance was modified by conservative codon replacement so as to accommodate the sequence d(CCTTCGCTAC) flanked by two restriction sites, Bsm I and Xho I. The corresponding synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide underwent reaction with 2-(N-acetoxy-N-acetylamino)-fluorene (AAAF), forming a single dG-AAF adduct. This modified oligodeoxynucleotide was hybridized to its complementary strand and ligated between the Bsm I and Xho I sites of the vector. Plasmids containing the C8-dG-AAF adduct were used to transfect simian virus 40-transformed simian kidney (COS-1) cells and to transform several AB strains of Escherichia coli. Colonies containing mutant plasmids were detected by hybridization to 32P-labeled oligodeoxynucleotides. Presence of the single DNA adduct increased the mutation frequency by 8-fold in both COS cells and E. coli. Over 80% of mutations detected in both systems were targeted and represented G.C----C.G or G.C----T.A transversions or single nucleotide deletions. We conclude that modification of a deoxyguanosine residue with AAF preferentially induces mutations targeted at this site when a plasmid containing a single C8-dG-AAF adduct is introduced into mammalian cells or bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhanot O. S., Ray A. The in vivo mutagenic frequency and specificity of O6-methylguanine in phi X174 replicative form DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7348–7352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowy-Borowski H., Chambers R. W. A study of side reactions occurring during synthesis of oligodeoxynucleotides containing O6-alkyldeoxyguanosine residues at preselected sites. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2465–2471. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drinkwater N. R., Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Estimation of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites and phosphotriesters in deoxyribonucleic acid treated with electrophilic carcinogens and mutagens. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):5087–5092. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P., Lefevre J. F., Pouyet J., Daune M. P. Comparative orientation of the fluorene residue in native DNA modified by N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene and two 7-halogeno derivatives. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3347–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. L., Loechler E. L., Fowler K. W., Essigmann J. M. Construction and characterization of extrachromosomal probes for mutagenesis by carcinogens: site-specific incorporation of O6-methylguanine into viral and plasmid genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):13–17. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K. Nucleic acid adducts of chemical carcinogens and mutagens. Arch Toxicol. 1983 Apr;52(4):249–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00316495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingerty B., Broyde S. Conformation of the deoxydinucleoside monophosphate dCpdG modified at carbon 8 of guanine with 2-(acetylamino)fluorene. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3243–3252. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. L., Reid T. M., Lee M. S., King C. M., Romano L. J. Preparation and characterization of a viral DNA molecule containing a site-specific 2-aminofluorene adduct: a new probe for mutagenesis by carcinogens. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):449–456. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffel-Schwartz N., Maenhaut-Michel G., Fuchs R. P. Specific strand loss in N-2-acetylaminofluorene-modified DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):651–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffel-Schwartz N., Verdier J. M., Bichara M., Freund A. M., Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P. Carcinogen-induced mutation spectrum in wild-type, uvrA and umuC strains of Escherichia coli. Strain specificity and mutation-prone sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):33–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loechler E. L., Green C. L., Essigmann J. M. In vivo mutagenesis by O6-methylguanine built into a unique site in a viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Mittelstadt K. L., Schneider J. Variants in clones of gene-machine-synthesized oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6770–6770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H. Carcinogens induce targeted mutations in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell N., Stöhrer G. Mutagenesis originating in site-specific DNA damage. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Rabkin S. D., Osborn A. L., King C. M., Strauss B. S. Effect of acetylated and deacetylated 2-aminofluorene adducts on in vitro DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7166–7170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. E., Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P. Repair and mutagenesis of plasmid DNA modified by ultraviolet irradiation or N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöhrer G., Osband J. A., Alvarado-Urbina G. Site-specific modification of the lactose operator with acetylaminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5093–5102. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Chang C. N., Johnson F., Will S., Grollman A. P. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites. Model substrates for DNA polymerases and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10171–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M., Lieberman M. W. Quantification of adducts formed in DNA treated with N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene or N-hydroxy-2-aminofluorene: comparison of trifluoroacetic acid and enzymatic degradation. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Aug;4(8):1001–1006. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.8.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Bos J. L., Marshall C. J., Phillips D. H. Mutations activating human c-Ha-ras1 protooncogene (HRAS1) induced by chemical carcinogens and depurination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1222–1226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Pulkrabek P., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B. Differential excision from DNA of the C-8 and N2 guanosine adducts of N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene by single strand-specific endonucleases. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3756–3760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


