Abstract
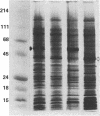
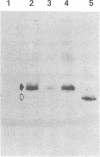
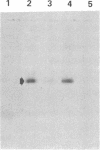
A cDNA clone for human interleukin 2 (IL-2) has been fused to the 5' end of a modified Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE) gene that lacks the sequences encoding the cell recognition domain. The chimeric protein IL-2-PE40 was produced in Escherichia coli. It was extremely toxic to IL-2 receptor-positive cells but had no measurable effect on cells lacking the IL-2 receptor. IL-2-PE40 might be a useful cytotoxic agent in the treatment of diseases involving IL-2 receptor-positive cells and in the treatment of allograft rejection.
Full text
PDF
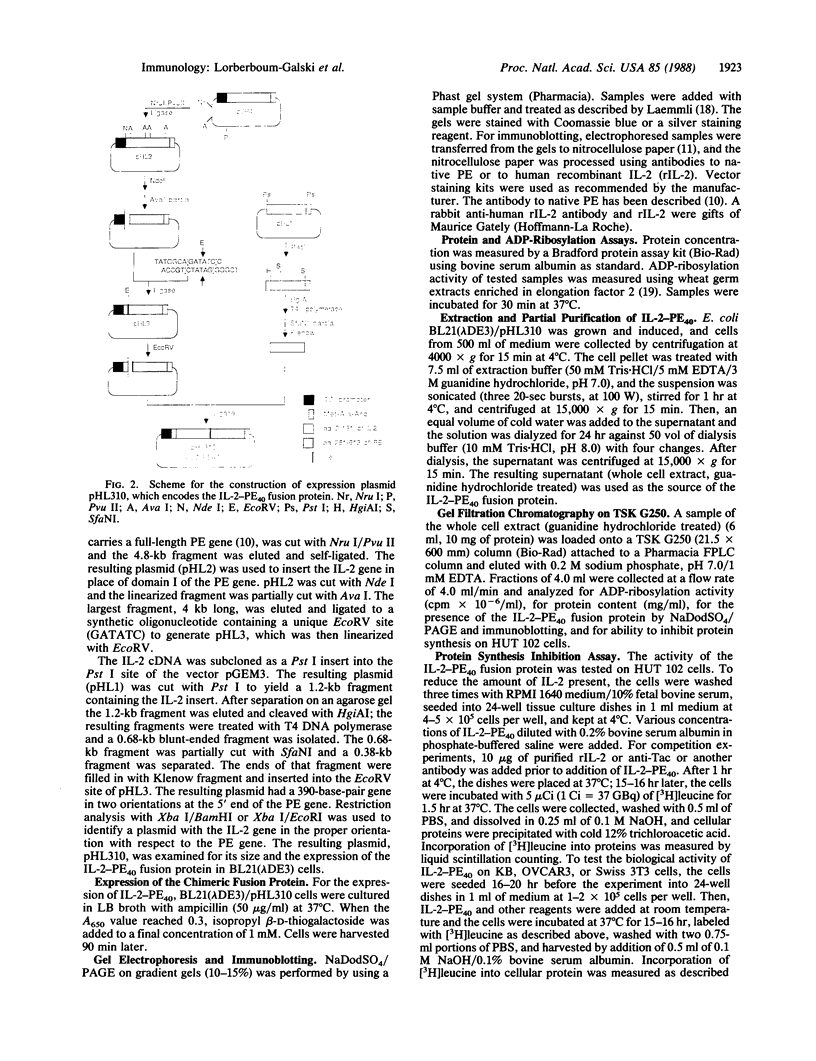
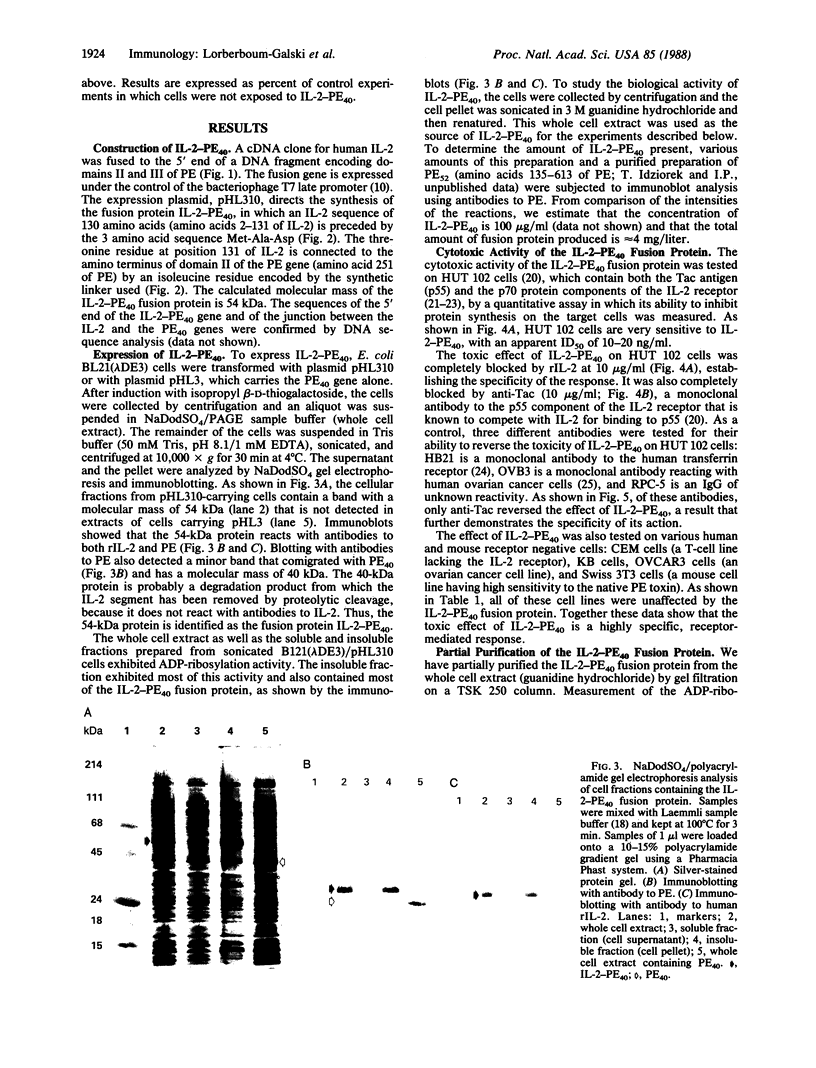
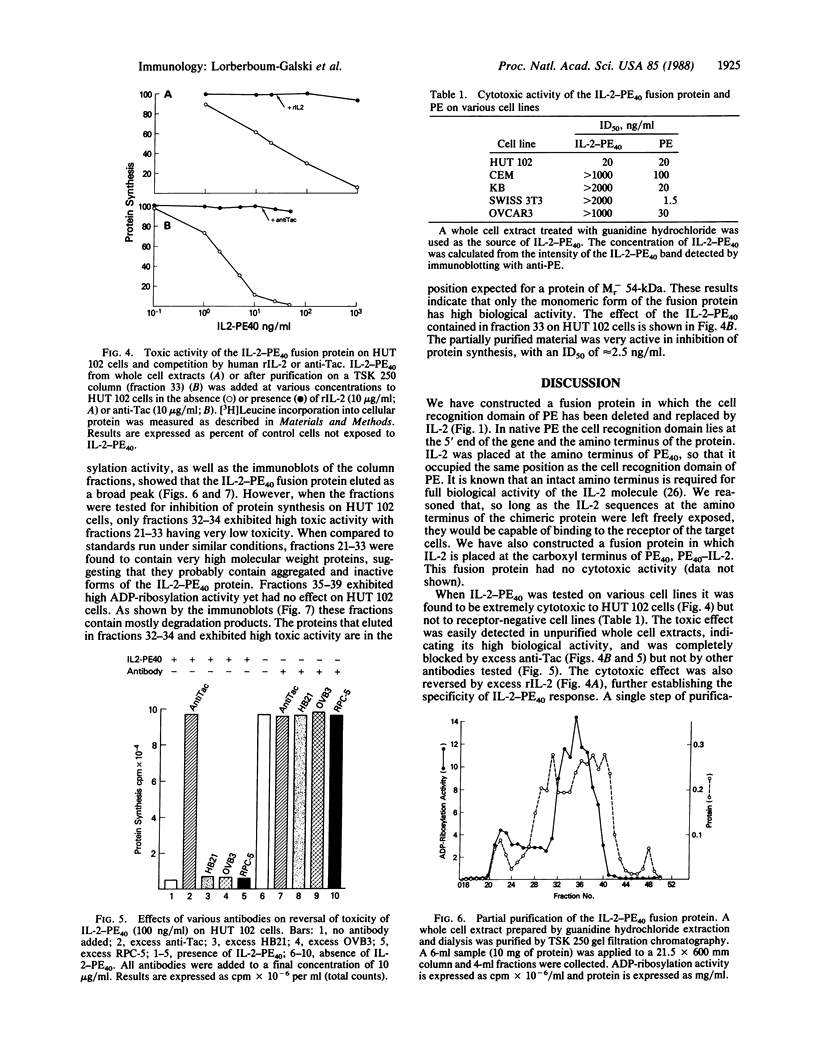

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allured V. S., Collier R. J., Carroll S. F., McKay D. B. Structure of exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.0-Angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacha P., Murphy J. R., Reichlin S. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-diphtheria toxin-related polypeptide conjugates. Potential role of the hydrophobic domain in toxin entry. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1565–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. M., Dazord A., Neville D. M., Jr Artificial hybrid protein containing a toxic protein fragment and a cell membrane receptor-binding moiety in a disulfide conjugate. II. Biochemical and biologic properties of diphtheria toxin fragment A-S-S-human placental lactogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1515–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Adhya S., Pastan I. Activity of a recombinant fusion protein between transforming growth factor type alpha and Pseudomonas toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukovich M., Wano Y., Le thi Bich Thuy, Katz P., Cullen B. R., Kehrl J. H., Greene W. C. A second human interleukin-2 binding protein that may be a component of high-affinity interleukin-2 receptors. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):518–522. doi: 10.1038/327518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland D. G., Collier R. J., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Chimeric toxins: toxic, disulfide-linked conjugate of concanavalin A with fragment A from diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5319–5323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. J., Kuttler B., Dunger A., Klöting I., Lucke S., Volk H. D., von Baehr R., Diamantstein T. Prolongation of rat pancreatic islet allograft survival by treatment of recipient rats with monoclonal anti-interleukin-2 receptor antibody and cyclosporin. Diabetologia. 1987 Jan;30(1):44–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01788907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hemler M., Cotner T., Mann D. L., Eisenbarth G. S., Strominger J. L., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (5E9) that defines a human cell surface antigen of cell activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Fitzgerald D. J., Adhya S., Pastan I. Functional domains of Pseudomonas exotoxin identified by deletion analysis of the gene expressed in E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Collins L., Kaffka K. L., Tsien W. H., Chizzonite R., Crowl R., Bhatt R., Kilian P. L. Structure-function analysis of human interleukin-2. Identification of amino acid residues required for biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5723–5731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkman R. L., Barrett L. V., Gaulton G. N., Kelley V. E., Ythier A., Strom T. B. Administration of an anti-interleukin 2 receptor monoclonal antibody prolongs cardiac allograft survival in mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):358–362. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec-Weglinski J. W., Diamantstein T., Tilney N. L., Strom T. B. Therapy with monoclonal antibody to interleukin 2 receptor spares suppressor T cells and prevents or reverses acute allograft rejection in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2624–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemm G., Warnatz H. Evidence for enhanced interleukin 2 (IL-2) secretion and IL-2 receptor presentation by synovial fluid lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):71–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeltmann T. N., Heath E. C. A hybrid protein containing the toxic subunit of ricin and the cell-specific subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. I. Synthesis and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1022–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J. Immunotoxins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations in inflammatory bowel disease: an analysis by immunohistological and cell isolation techniques. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):32–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. E., Kirkman R. L., Reed M. H., Puskas J. D., Mazoujian G., Letvin N. L., Carpenter C. B., Milford E. L., Waldmann T. A., Strom T. B. Monoclonal anti-IL-2 receptor antibody in primate renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Krolick K. A., Miyama-Inaba M., Cushley W., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: a new approach to cancer therapy. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):644–650. doi: 10.1126/science.6218613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. R., Baur R., Schleusener H., Bandy-Dafoe P. Peripheral blood and intrathyroidal mononuclear cell populations in patients with autoimmune thyroid disorders enumerated using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jan;56(1):164–169. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-1-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Pseudomonas exotoxin coupled to a monoclonal antibody against ovarian cancer inhibits the growth of human ovarian cancer cells in a mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2474–2478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Kato R., Beppu M., Terao T., Inoue Y., Ikawa Y., Osawa T. Preparation of concanavalin A-ricin A-chain conjugate and its biologic activity against various cultured cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1387–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]